Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 7, 2021
Title: Spondyloarthritis Including PsA – Treatment Poster I: Axial Spondyloarthritis (0908–0939)
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: Axial spondyloarthritis (axSpA) is a chronic inflammatory rheumatic disease affecting sacroiliac joints and spine as well as peripheral joints and entheses. Tumour necrosis factor inhibitors (TNFi) are widely used in patients with persistently high disease activity despite non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Some patients fail to respond or loose responsiveness during therapy with TNFi. The development of anti-drug antibodies (ADA) might play a role in non-response or some adverse events. However it has never been evaluated for 2-years period.
Objectives: Therefore, the aim of the present study was to evaluate the development of ADA against TNFi longitudinally during 2-years period in axSpA patients and factors associated with it.
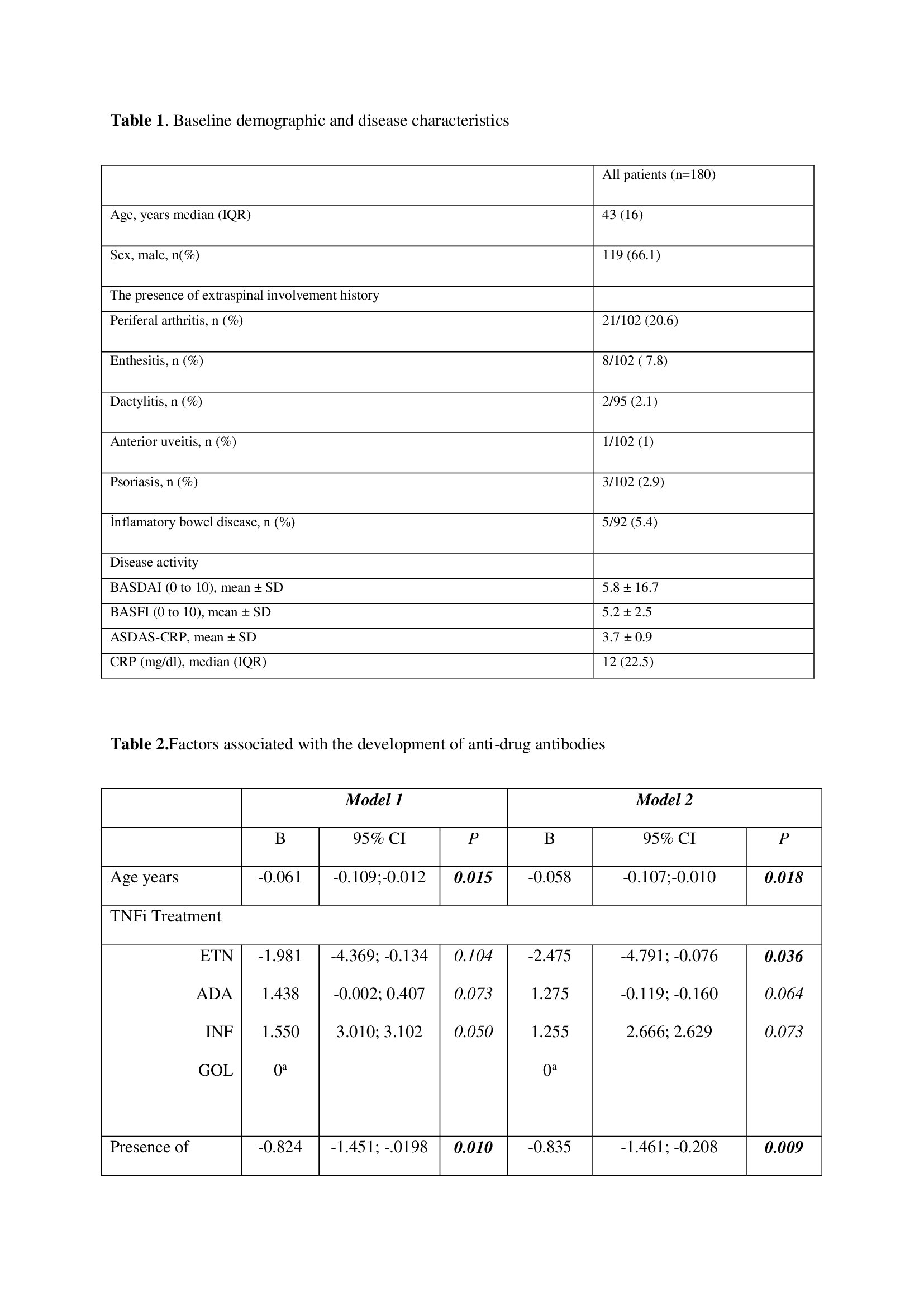
Methods: In total 180 axSpA patients according to ASAS classification criteria with a new TNFi prescription in the last two weeks period were included in this observational study. Clinical data and serum samples were collected at baseline and at every 12 weeks. Serum drug levels and ADAs were measured on 12, 24, 52 and 104 weeks of treatment by ELISA in one center to avoid inter-assay variability. The development of ADA over time was investigated by using generalized estimating equations (GEE) which is a technique for longitudinal data analysis allowing the use of all available data even deviated from normality.
Results: 180 biologic naive axSpA patients (116 male, median [IQR] 44,5 [14,5] years) who started anti-TNF agents (infliximab [20%], adalimumab [27,2%], etanercept [32,2%] and golimumab [20,6%]) were included in the analysis (Table 1). In comparison to baseline values BASDAI, ASDAS-CRP and CRP values were significantly decreased in third months of follow-up (Figure 1). In total 172 patients had at 12 weeks, 154 at 24, 121 at 52, and 73 at 104 week serum samples available for ADA determination. In longitudinal analysis; baseline age and TNFi type, as well as longitudinal BASDAI, ASDAS, serum CRP levels and the development of adverse events and discontinuation of the drug were found to be associated with the development of ADA. In order to determine independent association/s with the development of ADA two longitudinal multivariable models were run; (a) with ASDAS as an activity measure, (b) with BASDAI and CRP levels and produced that all the variables were independently associated with longitudinally development of anti-drug antibodies (Table 2). Antibodies to adalimumab were related with lower serum drug levels.
Conclusion: The results of the present study with up to 2 years of follow-up, revealed that the development of ADA against TNFi therapy is associated with high disease activity, the development of adverse events and treatment discontinuation in patients with axSpA. And etanercept might be negatively associated with the development of ADA.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Ediboglu E, Solmaz D, Kabadayi G, Ozmen M, Kaya K, Çınar M, Sargın G, Hatemi G, Karadağ , Kınıklı G, Gercik O, Kalyoncu U, Yılmaz S, Şentürk T, Keser G, Yargucu F, Cefle A, Kozacı D, Kısacık B, Akar S. Factors Associated with the Development of Anti-drug Antibodies to Tumour Necrosis Factor Inhibitors in Patients with Axial Spondyloarthritis; A Two Year Follow-up Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/factors-associated-with-the-development-of-anti-drug-antibodies-to-tumour-necrosis-factor-inhibitors-in-patients-with-axial-spondyloarthritis-a-two-year-follow-up-study/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/factors-associated-with-the-development-of-anti-drug-antibodies-to-tumour-necrosis-factor-inhibitors-in-patients-with-axial-spondyloarthritis-a-two-year-follow-up-study/