Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Health-related quality of life (HRQOL) is decreased in individuals with chronic rheumatic diseases (CRD) yet remains undefined in adults with SAPHO syndrome and chronic nonbacterial osteomyelitis (SAPHO-CNO). We measured HRQOL with the EuroQol-5 Dimension instrument (EQ-5D-5L) and determined factors associated with HRQOL in adult SAPHO-CNO.
Methods: Adults with SAPHO-CNO (≥18 years of age) enrolled in the SAPHO-CNO study (SCS), a prospective longitudinal observational study, completed the EQ-5D-5L, a validated instrument for measuring HRQOL across five health dimensions, along with baseline questionnaires on demographics, clinical symptoms, disease activity, patient reported outcomes (PROs) and comorbidities. The EQ-5D value index reflects the subject’s health state profile, which can range from negative values (0=health state equivalent to dead) to 1 (full health). To model predictors of EQ-5D, variables were selected from literature review of HRQOL in CRDs, and SCS cohort characteristics (disease features, PROs, comorbidities, demographics). SAPHO-CNO disease features were inflammatory arthritis, spine involvement, skin rash, and total MSK symptom score (sum of painful and swollen skeletal areas in 42 regions; range 0-166). PROs were measured by the 21-point numeric rating scale (NRS, range 0-10) for patient-reported pain, function, and overall disease activity.
Patient characteristics were summarized as medians (interquartile range) or proportions. We performed bivariable analyses between each predictor and EQ-5D index with simple linear regression. We checked model assumptions and linearity by plotting. Next, multivariable linear regression (MLR) models were fit by multiple selection criteria (stepwise, forward, adjusted R2, Mallow’s Cp) to identify best predictors of EQ-5D. We tested for inclusion of interaction terms, checked for collinearity, and evaluated overall model fit (i.e., plot residuals, inspect outliers). All analyses were performed using SAS (9.4).
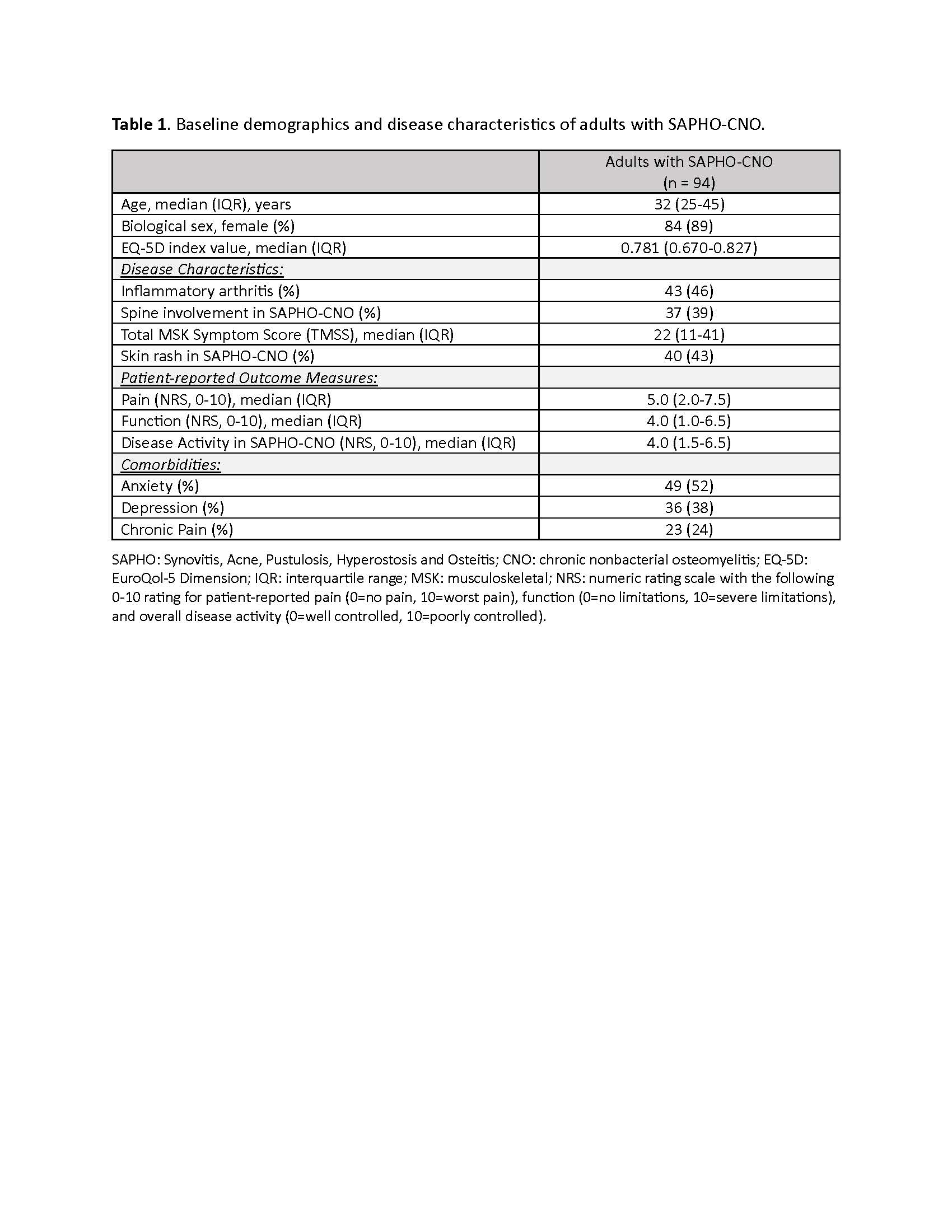
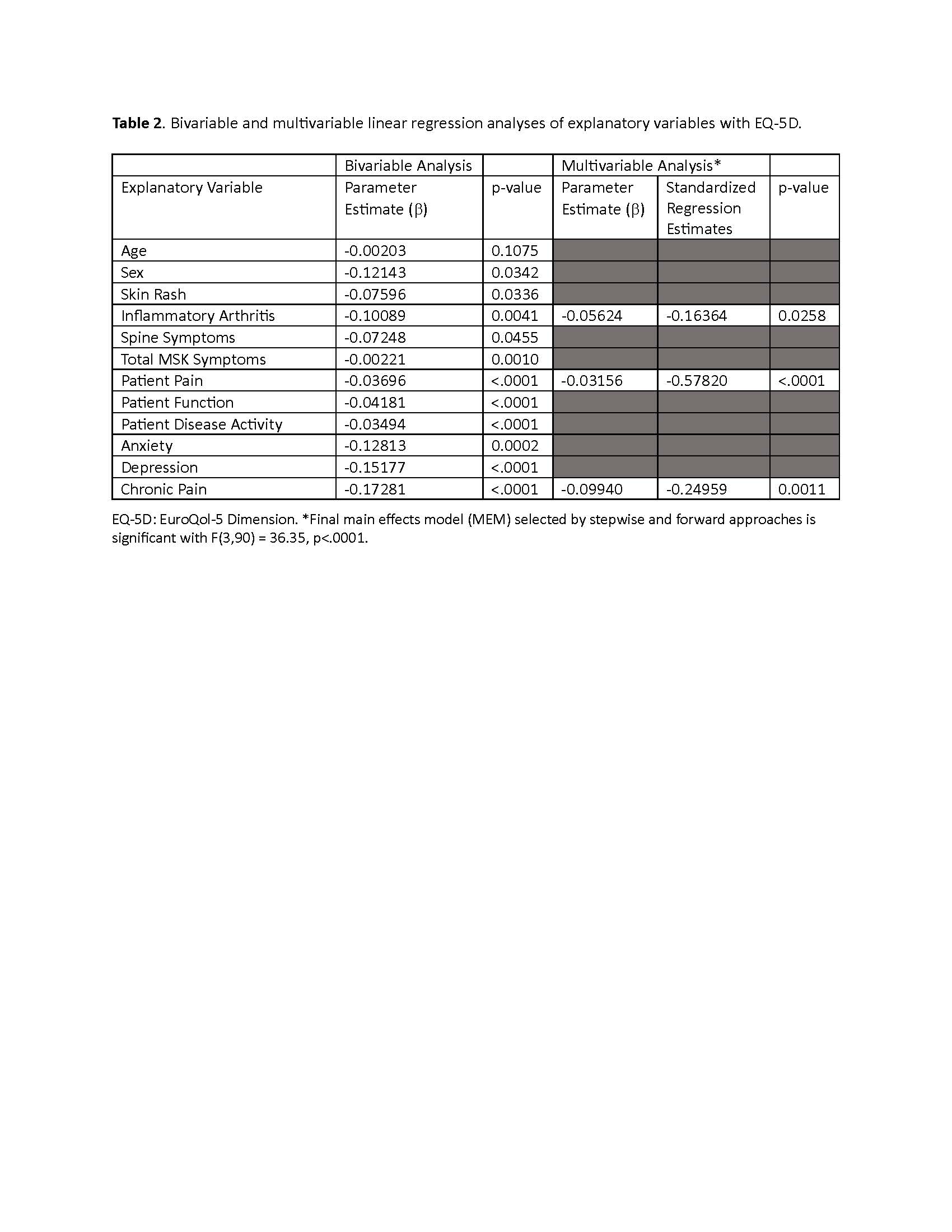
Results: Baseline characteristics of 94 adults with SAPHO-CNO who were included in this cross-sectional analysis are summarized in Table 1. All explanatory variables were significantly associated with EQ-5D in bivariable analyses (p< 0.05). In MLR analyses, repeated modeling using alternative selection criteria determined that a three-variable model (Pain Score, Inflammatory Arthritis, Chronic Pain) provided the best fit (adjusted-R2 = 0.53; p< .001). Due to collinearity of Pain and Function (rho=0.80), models were fit with Pain only. Thus, higher pain score, presence of inflammatory arthritis and chronic pain were significantly associated with a decrease in mean EQ-5D. Comparing standardized regression coefficients suggests that increases in pain score are associated with the largest decrease in EQ-5D (Table 2).
Conclusion: We identified novel factors associated with decreased HRQOL in adults with SAPHO-CNO. Patient-reported pain or function, presence of inflammatory arthritis, and comorbid chronic pain should be addressed in the treatment of adults with SAPHO-CNO towards improving QOL.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Lenert A, Abodeely H, Chan K, Hong S, Jayatilleke A, Kremer C, Leisinger E, Lenert P, Oliver M, Sato T, Smith M, Jenna T, Zhao Y, Templin J, Domsic R, Vaughan-Sarrazin M, Solomon D, Ferguson P. Factors Associated with Health-related Quality of Life in Adults with SAPHO and Chronic Nonbacterial Osteomyelitis – a Cross Sectional Analysis from the SAPHO-CNO Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/factors-associated-with-health-related-quality-of-life-in-adults-with-sapho-and-chronic-nonbacterial-osteomyelitis-a-cross-sectional-analysis-from-the-sapho-cno-study/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/factors-associated-with-health-related-quality-of-life-in-adults-with-sapho-and-chronic-nonbacterial-osteomyelitis-a-cross-sectional-analysis-from-the-sapho-cno-study/