Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 5:00PM-6:00PM
Background/Purpose: To investigate the frequency and factors associated with disease flare following vaccination against SARS-CoV-2 in people with inflammatory/autoimmune rheumatic and musculoskeletal diseases (I-RMD).
Methods: The European Alliance of Associations for Rheumatology (EULAR) Coronavirus Vaccine (COVAX) physician-reported registry is an observational registry of patients with a pre-existing inflammatory or non-inflammatory RMD who have received one or more doses of any vaccine against SARS-CoV-2. Four diagnostic groups were defined: (1) inflammatory joint diseases (IJD), (2) connective tissue diseases (CTD), (3) vasculitis, and (4) other I-RMD (OIRD). As disease activity was only collected at baseline, patients that received more than 2 vaccine doses were excluded from the analyses. Missing values for vaccine type and disease activity were derived by multiple imputation using full conditional specification. Predictors of flare were investigated using multivariable logistic regression adjusted for demographic and clinical factors. Two separate multivariable models were built, one using “disease flare” as dependent variable, and one using “new medication or dosage increase due to flare” as dependent variable.
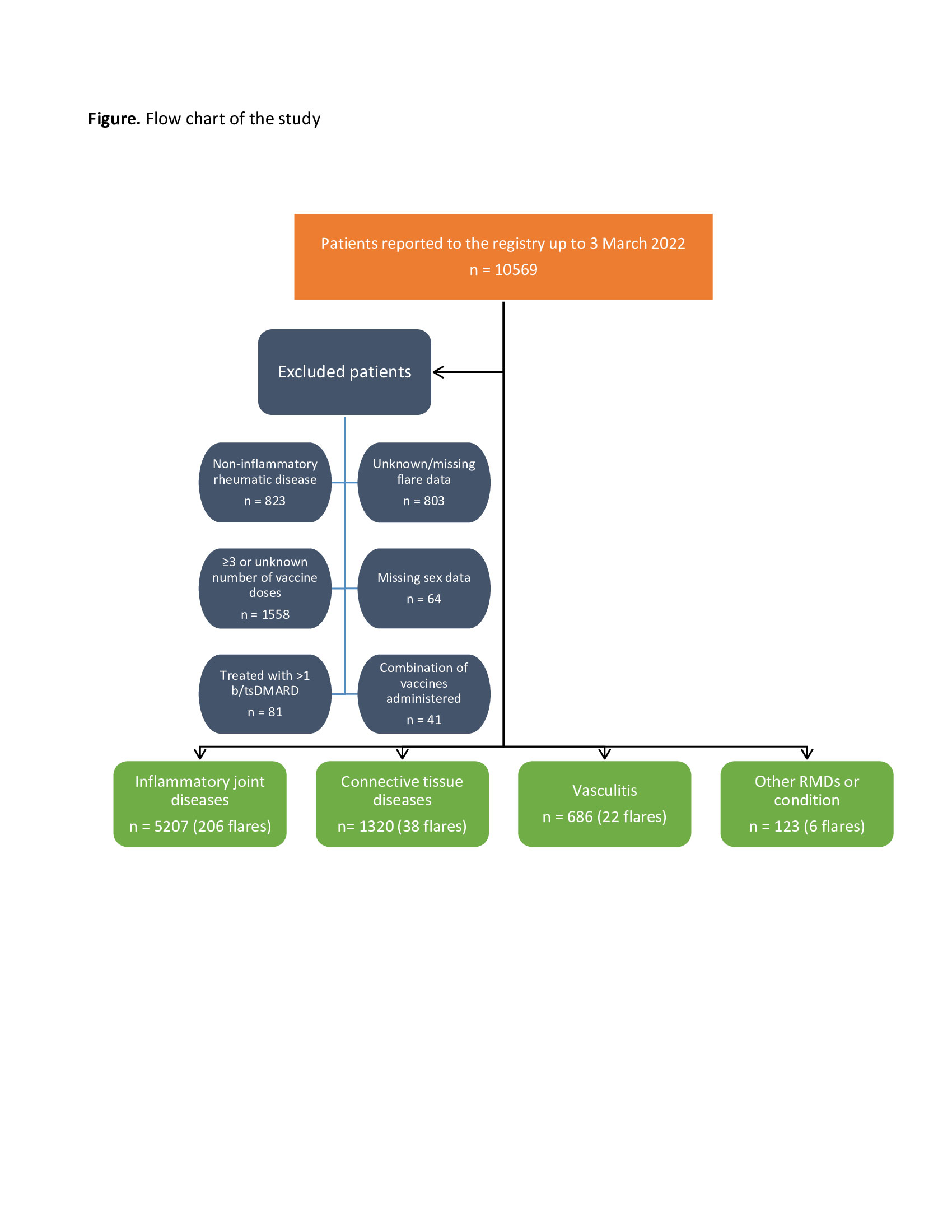
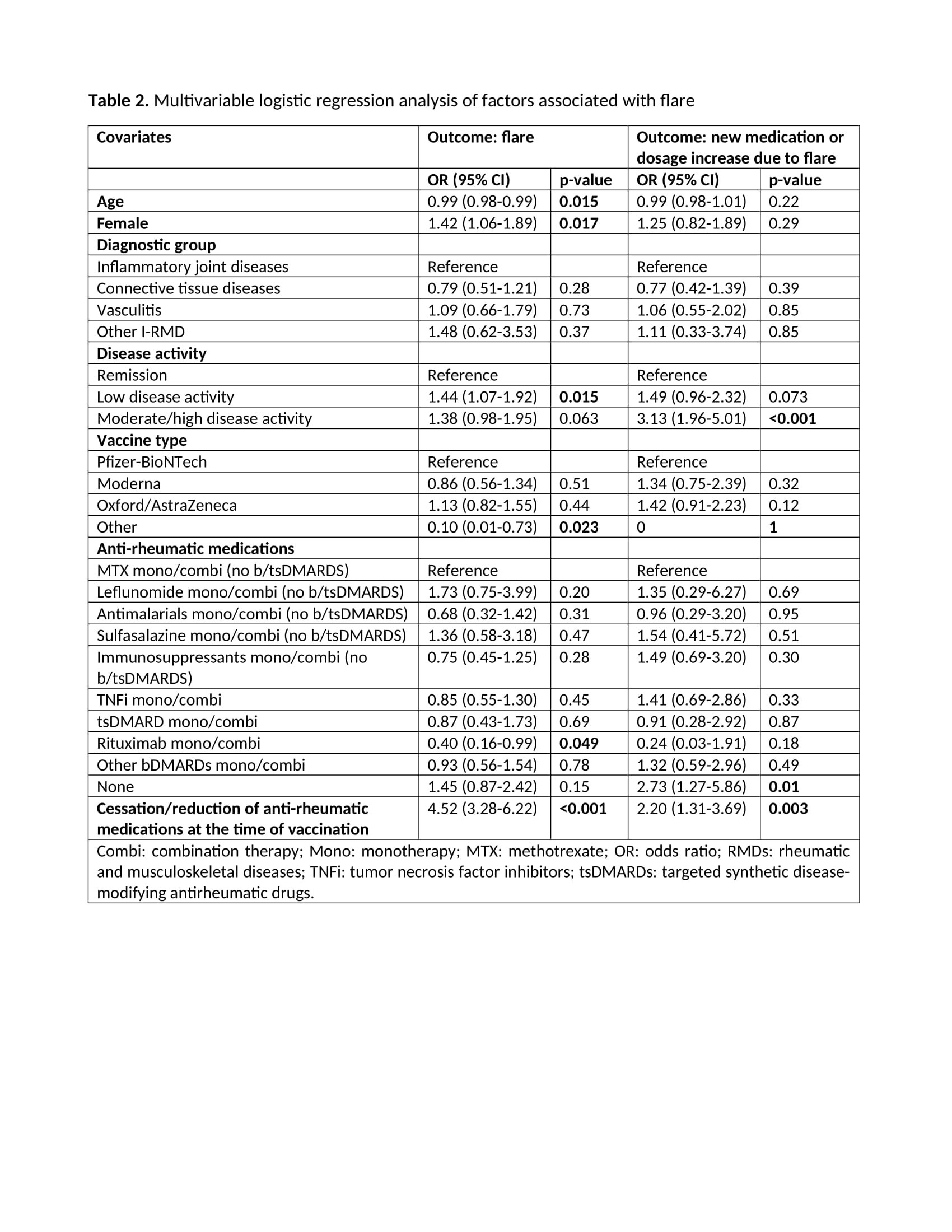
Results: Of 10569 patients reported to the registry by 3 March 2022, 7336 were included in this study (Figure). Most patients had IJD (71%), followed by CTD (18%), vasculitis (9.4%), and OIRD (1.7%). Disease flares were reported in 272/7336 (3.7%) patients (Table 1). Flares requiring starting a new medication or increasing the dosage of an existing medication were reported in 121/7336 (1.6%) patients. Mean time between flare and the most recent vaccine dose was 7.2 days (SD 8.2) (Table 1). Age (OR 0.99, 95%CI 0.98-0.99), female sex (OR 1.42, 95%CI 1.06-1.89), active disease (low disease activity (LDA), OR 1.44, 95%CI 1.07-1.92; moderate/high disease activity (M/HDA), OR 1.38, 95%CI 0.98-1.95; vs remission), other vaccine types different from Pfizer/BioNTech, Oxford/AstraZeneca and Moderna (OR 0.10, 95%CI 0.01-0.73; vs Pfizer/BioNTech), rituximab exposure (OR 0.40, 95%CI 0.16-0.99), and cessation/reduction of anti-rheumatic medication before or after vaccination (OR 4.52, 95%CI 3.28-6.22) were factors independently associated with disease flare (Table 2). In the model using new medication or dosage increase due to flare as dependent variable (Table 2), active disease (LDA, OR 1.49, 95%CI 0.96-2.32; M/HDA, OR 3.13, 95%CI 1.96-5.01; vs remission), not using anti-rheumatic medication (OR 2.73, 95%CI 1.27-5.86), and cessation/reduction of anti-rheumatic medication before or after vaccination (OR 2.20, 95%CI 1.31-3.69) were the only factors independently associated with this more strict flare definition.
Conclusion: Flares of underlying I-RMD following SARS-CoV-2 vaccination were uncommon. Factors associated with potential flares were identified, namely higher disease activity and cessation/reduction of anti-rheumatic medications before or after vaccination. These data will inform SARS-CoV-2 vaccination strategies in patients with I-RMDs.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Farisoğulları B, Lawson-Tovey S, Hyrich K, Gossec L, Carmona L, Strangfeld A, Mateus E, Schaefer M, Rodrigues A, Hachulla E, Gomez-Puerta J, Mosca M, Durez P, Trefond L, Goulenok T, Cornalba M, Šteňová E, Bulina I, Strakova E, Zepa J, Roux N, Brocq O, Eric V, Raffeiner B, Burmester G, Mariette X, Machado P. Factors Associated with Disease Flare Following SARS-CoV-2 Vaccination in People with Inflammatory Rheumatic and Musculoskeletal Diseases – Results from the Physician-Reported EULAR Coronavirus Vaccine (COVAX) Registry [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022; 74 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/factors-associated-with-disease-flare-following-sars-cov-2-vaccination-in-people-with-inflammatory-rheumatic-and-musculoskeletal-diseases-results-from-the-physician-reported-eular-coronaviru/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2022
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/factors-associated-with-disease-flare-following-sars-cov-2-vaccination-in-people-with-inflammatory-rheumatic-and-musculoskeletal-diseases-results-from-the-physician-reported-eular-coronaviru/