Session Information
Date: Monday, October 22, 2018
Title: Muscle Biology, Myositis and Myopathies Poster II: Basic and Translational Science
Session Type: ACR Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Extracellular vesicles (EVs) are micron-scale bilayer membrane vesicles released from almost all cell types under activation or apoptosis. They have been detected in various bodily fluids, organs, and tissues in different pathologic states. EVs harbor molecules from their parental cells, which may mediate intercellular communications, and are thought to play an important role in autoimmune inflammation as they have been shown to induce the synthesis of various proinflammatory cytokines in several immune cell types. Previous studies have demonstrated that circulating EVs are increased in a variety of autoimmune diseases, including dermatomyositis (DM). In the current study, we aim to characterize the induction of pro-inflammatory cytokines by EVs isolated from patients with dermatomyositis.
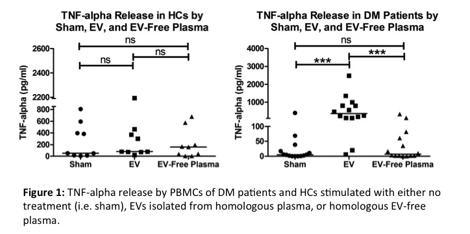
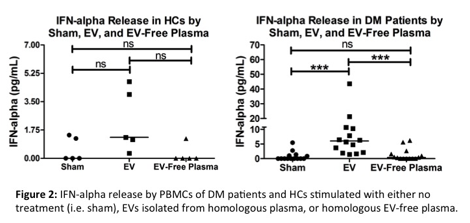
Methods: Fourteen DM patients and nine healthy controls were recruited in the dermatology clinic at the Hospital of the University of Pennsylvania. Peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) were isolated from the DM patients and healthy controls and subsequently stimulated with either no treatment, EVs isolated from the homologous plasma, or homologous EV-free plasma. The levels of TNF-α, IFN-α, IFN-β, IL-8, and IL-6 secreted by the PBMCs in the conditioned medium were then quantified with an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). A one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) was used to compare cytokine levels secreted by cells stimulated with either EVs, EV-free plasma, or no treatment.
Results: In the DM patients, EVs significantly increased the cellular secretion of TNF-α, IFN-α, IL-8, and IL-6 from homologous PBMCs compared to no treatment (p<0.001, p<0.001, p<0.001, p<0.001, respectively) and EV-free plasma (p<0.001, p<0.001, p<0.001, p<0.001, respectively). In the healthy controls, EVs either did not significantly or less significantly increased TNF-α, IFN-α, IL-8, and IL-6 secretion from the homologous PBMCs compared to no treatment (p>0.05, p>0.05, p<0.01, p<0.05, respectively) and EV-free plasma (p>0.05, p>0.05, p>0.05, p<0.05, respectively). In both the DM patients and the healthy controls, the EVs did not significantly increase IFN-β secretion.
Conclusion: Therefore, EVs from DM patients induce secretion of key immunostimulatory cytokines from their homologous immune cells, suggesting that EVs likely play a role in the pathogenesis of DM. Our preliminary studies indicate that circulating EVs are important proinflammatory mediators that amplify proinflammatory responses in patients with DM.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Desai K, Zeidi M, Liu ML, Werth VP. Extracellular Vesicles Induce Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines in Dermatomyositis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018; 70 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/extracellular-vesicles-induce-pro-inflammatory-cytokines-in-dermatomyositis/. Accessed .« Back to 2018 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/extracellular-vesicles-induce-pro-inflammatory-cytokines-in-dermatomyositis/