Session Information
Date: Monday, November 11, 2019
Title: 4M114: Osteoporosis & Metabolic Bone Disease – Basic & Clinical Science (1872–1877)
Session Type: ACR Abstract Session
Session Time: 4:30PM-6:00PM
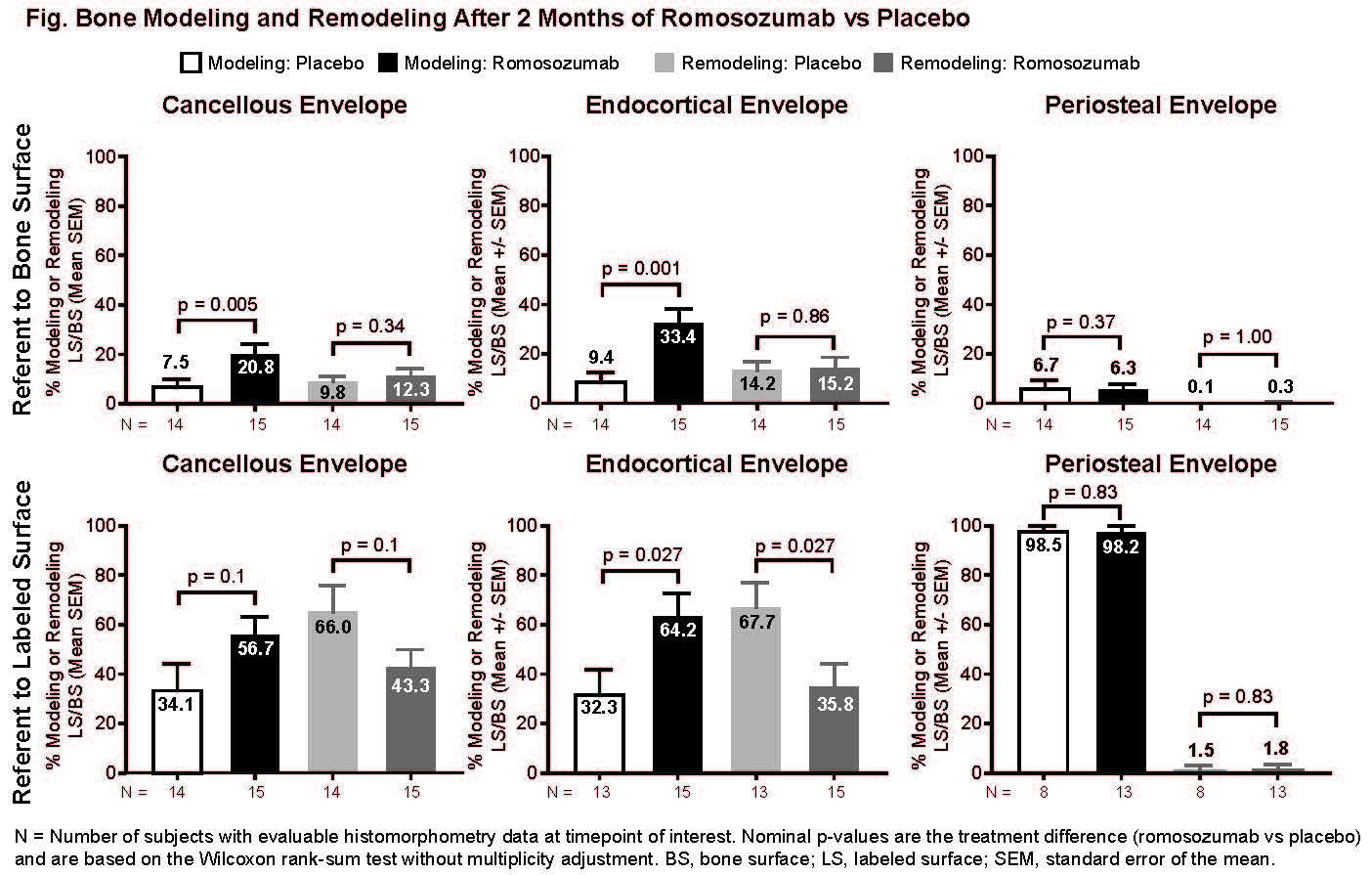
Background/Purpose: The bone-forming agent romosozumab (Romo) is a monoclonal antibody that binds to/inhibits sclerostin, leading to increased bone formation and decreased bone resorption. The highest levels of bone formation markers in human subjects are observed in the first 2 months of treatment (McClung, NEJM 2014). Studies in cynomolgus monkeys demonstrated that most new bone formation following Romo treatment was modeling-based (MBBF; Ominsky, JBMR 2014). Histomorphometric analysis of bone biopsies in a substudy of the FRAME trial (NCT01575834) showed an early significant increase in bone formation with concomitant decreased resorption (Chavassieux, ASBMR 2017). Here we analyzed bone biopsies from FRAME to assess the effect of 2 months of Romo vs placebo (Pbo) on the surface extent of MBBF and remodeling-based bone formation (RBBF) on cancellous (Cn), endocortical (Ec), and periosteal (Ps) envelopes.
Methods: In FRAME, postmenopausal women aged ≥55 years with osteoporosis (BMD T-score ≤–2.5 and >–3.5 at the total hip or femoral neck) were randomized 1:1 to 210 mg Romo or Pbo SC QM for 12 months, followed by 60 mg denosumab SC Q6M for 12 months. Subjects in the bone biopsy substudy who had a transiliac biopsy at month 2 received quadruple labeling (double labeling at baseline and prior to biopsy). Unstained, 7 µm bone sections were analyzed by fluorescence microscopy. Histomorphometric parameters were measured separately at the Cn, Ec, and Ps envelopes using an ocular linear test system, randomly rotated between fields of view for unbiased sampling of bone surfaces. At each line intersection of the ocular sampling grid with either single or double tetracycline labels administered at month 2, the underlying cement line was classified as smooth (signifying bone modeling) or scalloped (signifying bone remodeling). The effect of 2 months of Romo vs Pbo on MBBF/RBBF at each envelope referent to bone surface and labeled surface was compared using the Wilcoxon rank-sum test, without multiplicity adjustment.
Results: After 2 months of Romo, MBBF referent to bone surface was significantly increased on Ec and Cn, but not Ps, surfaces with no significant difference in the surface extent of RBBF vs Pbo (Fig.). Romo at month 2 reversed proportions of MBBF/RBBF from approximately 33%/66% in Pbo to 66%/33% in Ec and Cn envelopes.
Conclusion: These data show that stimulation of bone formation in the first 2 months of Romo treatment is predominately due to increased MBBF on the Ec and Cn surfaces.
-3.28.19 all p values- FRAME Modeling ASBMR 2019 Fig
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Eriksen E, Chapurlat R, Boyce R, Brown J, Horlait S, Libanati C, Shi Y, Wagman R, Chavassieux P. Extensive Modeling-Based Bone Formation After 2 Months of Romosozumab Treatment: Results from the FRAME Clinical Trial [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/extensive-modeling-based-bone-formation-after-2-months-of-romosozumab-treatment-results-from-the-frame-clinical-trial/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/extensive-modeling-based-bone-formation-after-2-months-of-romosozumab-treatment-results-from-the-frame-clinical-trial/
