Session Information
Date: Monday, November 9, 2020
Title: RA – Diagnosis, Manifestations, & Outcomes Poster IV: Lifespan of a Disease
Session Type: Poster Session D
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
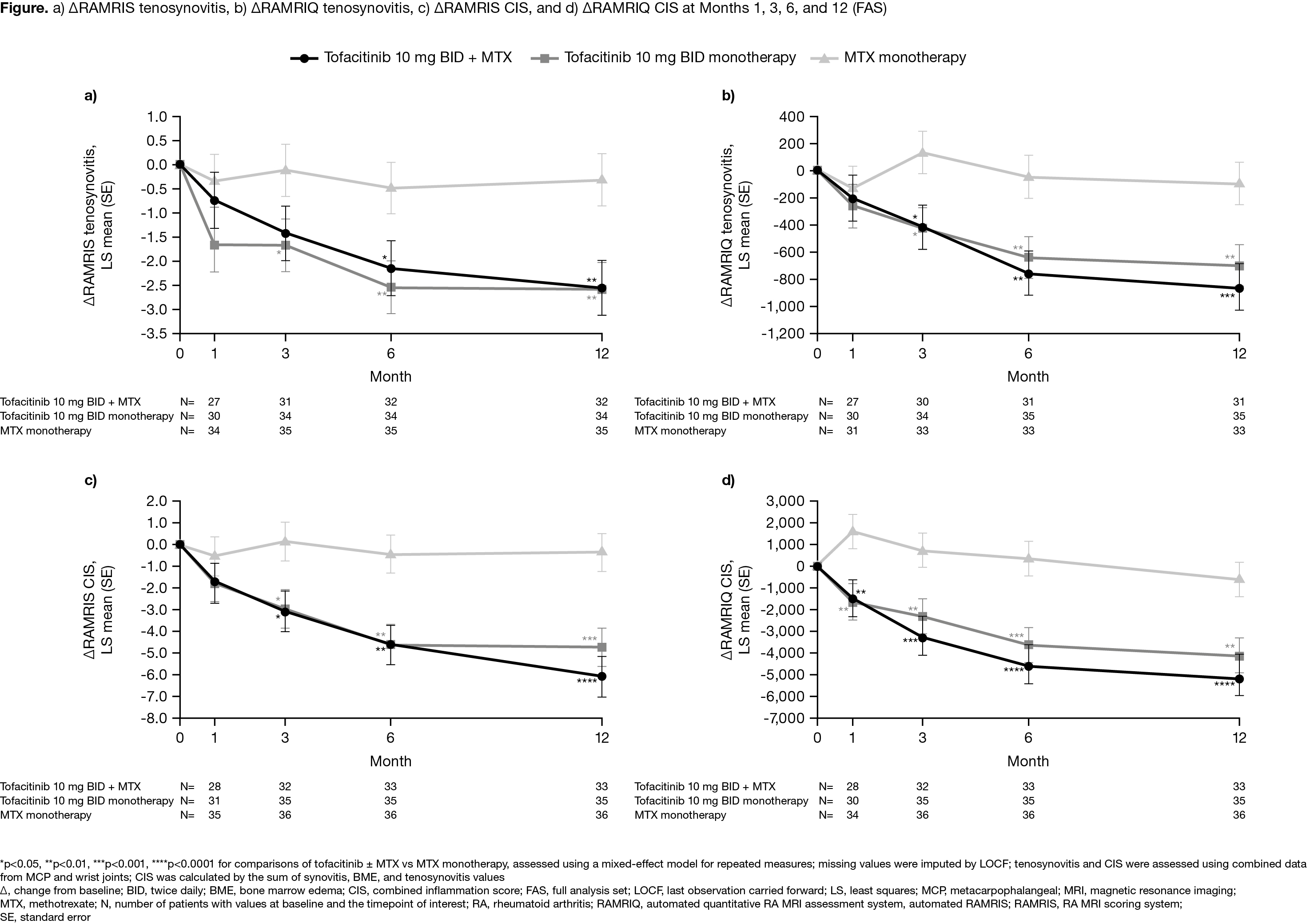
Background/Purpose: MRI trial outcomes have largely focused on synovitis, bone marrow edema (BME), and erosions. Tenosynovitis is a common manifestation of RA, but is relatively understudied; a combined inflammation score (CIS) that sums the 3 inflammatory markers (synovitis, BME, and tenosynovitis) may be a highly responsive outcome measure. We have previously demonstrated the responsiveness of the OMERACT RA MRI scoring system (RAMRIS) and a machine-learning derived automated tool (RAMRIQ) in a randomized trial of tofacitinib and MTX in MTX-naïve patients (pts) with early RA.1 This post hoc analysis evaluated the effects of tofacitinib ± MTX on MRI tenosynovitis and CIS in pts with early RA using semiquantitative and quantitative MRI outcomes.
Methods: Study A3921068 (NCT01164579) was a 1-year, exploratory, Phase 2, randomized controlled trial comparing tofacitinib 10 mg twice daily (BID) ± MTX, and MTX monotherapy, in MTX-naïve pts with early, active RA.1 MRI of unilateral wrist and MCP joints was performed at screening/baseline (BL) and Months (M)1, 3, 6, and 12. MRI tenosynovitis and CIS were assessed using RAMRIS and RAMRIQ. Changes from BL (Δ) in RAMRIS and RAMRIQ tenosynovitis and CIS were evaluated at M1, 3, 6, and 12. Data were assessed using a mixed-effect model for repeated measures, with treatment arms as factors and BL values as covariates. Using data pooled across all treatment arms, Spearman’s rank correlation coefficients were calculated for associations between BL RAMRIS and BL RAMRIQ tenosynovitis and CIS vs BL DAS28-4(C-reactive protein [CRP]) and between ΔRAMRIS and ΔRAMRIQ tenosynovitis and CIS at M12 vs ΔDAS28-4(CRP) at M12.
Results: In total, 109 pts were randomized and treated (mean RA duration 0.7 years). ΔRAMRIS and ΔRAMRIQ tenosynovitis (Figure a,b) and ΔRAMRIS and ΔRAMRIQ CIS (Figure c,d) were generally significantly greater at M3, 6, and 12 in pts receiving tofacitinib ± MTX vs MTX alone, with significant improvements also seen at M1 for ΔRAMRIQ CIS. Compared with RAMRIS, RAMRIQ outcomes were generally more responsive to treatment with tofacitinib ± MTX. Significant correlations were seen between BL RAMRIS and BL RAMRIQ tenosynovitis and BL RAMRIS CIS vs BL DAS28-4(CRP), while significant correlations were also observed between ΔRAMRIS and ΔRAMRIQ tenosynovitis and CIS at M12 vs ΔDAS28-4(CRP) at M12 (Table). In general, stronger correlations were seen between BL DAS28-4(CRP) and BL RAMRIS parameters vs BL RAMRIQ parameters, whereas correlations were similar between ΔDAS28-4(CRP) at M12 and ΔRAMRIS and ΔRAMRIQ parameters at M12.
Conclusion: Responsiveness of RAMRIS and RAMRIQ tenosynovitis and CIS was demonstrated with significant improvements through M12 in pts receiving tofacitinib 10 mg BID ± MTX vs MTX alone. Construct validity for RAMRIS and RAMRIQ tenosynovitis and CIS was evident from correlations with DAS28-4(CRP). Further work is required to validate these novel imaging biomarkers in terms of relative responsiveness and prediction for later structural progression.
- Conaghan PG et al. Ann Rheum Dis 2016; 75: 1024-1033.
Acknowledgments: Study sponsored by Pfizer Inc. Medical writing support was provided by Jennifer Arnold, CMC Connect, and funded by Pfizer Inc.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Conaghan P, Østergaard M, Troum O, Xie Z, Brett A, Snyder M, Ebrahim A, Chapman D, Sawyerr G, Andrews J. Exploring Novel Tenosynovitis and Combined Inflammation Imaging Outcomes: Results from a Randomized Controlled Trial in Early Rheumatoid Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/exploring-novel-tenosynovitis-and-combined-inflammation-imaging-outcomes-results-from-a-randomized-controlled-trial-in-early-rheumatoid-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/exploring-novel-tenosynovitis-and-combined-inflammation-imaging-outcomes-results-from-a-randomized-controlled-trial-in-early-rheumatoid-arthritis/