Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session (Sunday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Data-driven principal component (PC) and cluster analysis has the potential to identify previously unknown patient subgroups within a rheumatoid arthritis (RA) registry to establish prognosis, predict disease trajectory, and help inform treatment. The Brigham and Women’s Rheumatoid Arthritis Sequential Study (BRASS), established in 2003, is a single-center, prospective observational registry cohort providing a comprehensive set of clinical disease activity measures in >1400 patients with RA. Our objective was to use PC and cluster analysis of baseline demographic, socio-economic, health and disease characteristics in BRASS to identify and characterize distinct patient clusters in RA.
Methods: Patient variables recorded at entry into BRASS were refined and combined using PC analysis to reduce dimensionality and collinearity. The number of PCs was established by eigenvalue >1, cumulative variance, and interpretability. Patients were clustered using a k-means approach with non-hierarchical, exclusive, and complete clustering, with minimum cluster size 5% of population, and maximum 19 clusters. The final number of clusters was determined according to the cubic clustering criterion and pseudo F.
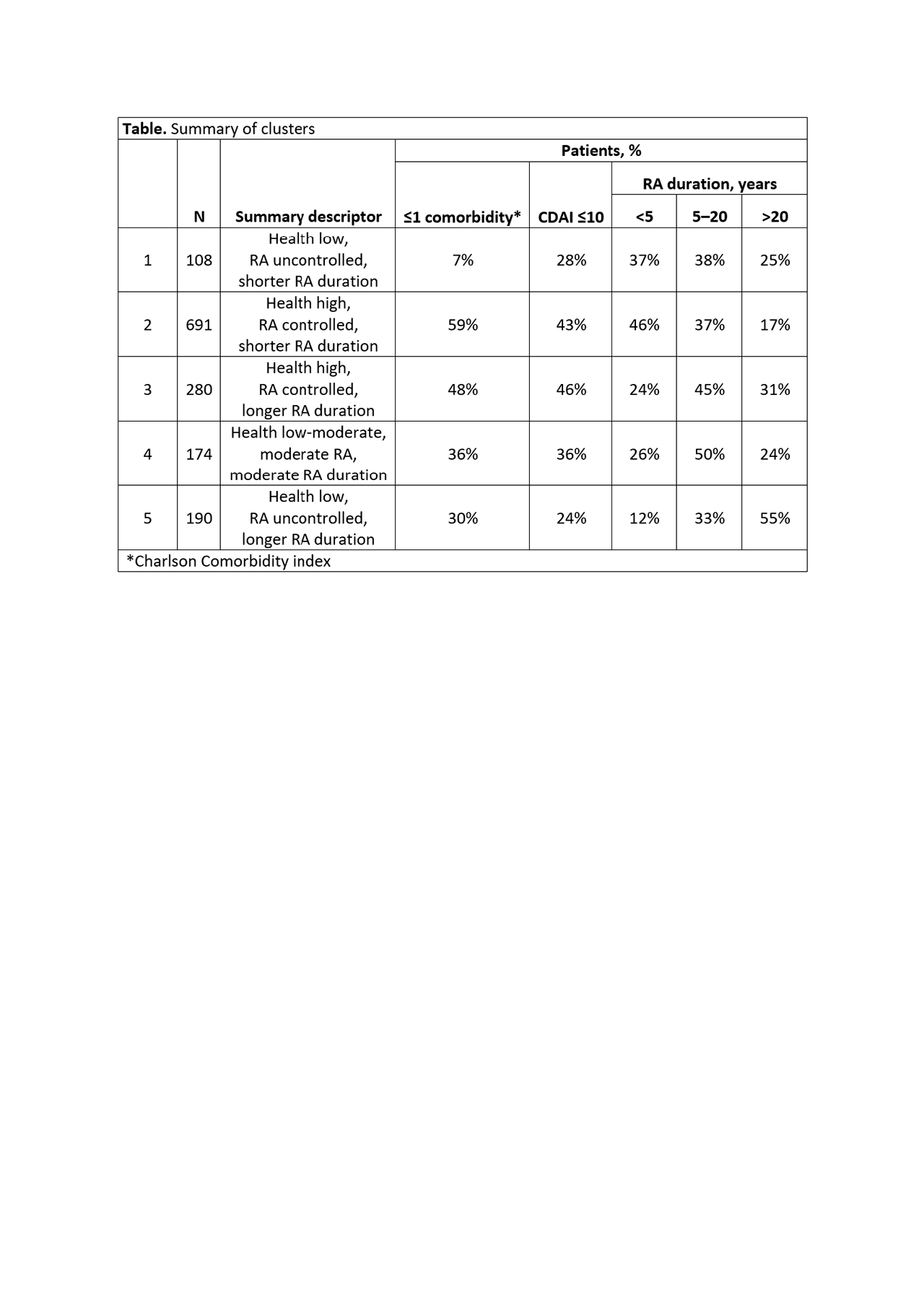
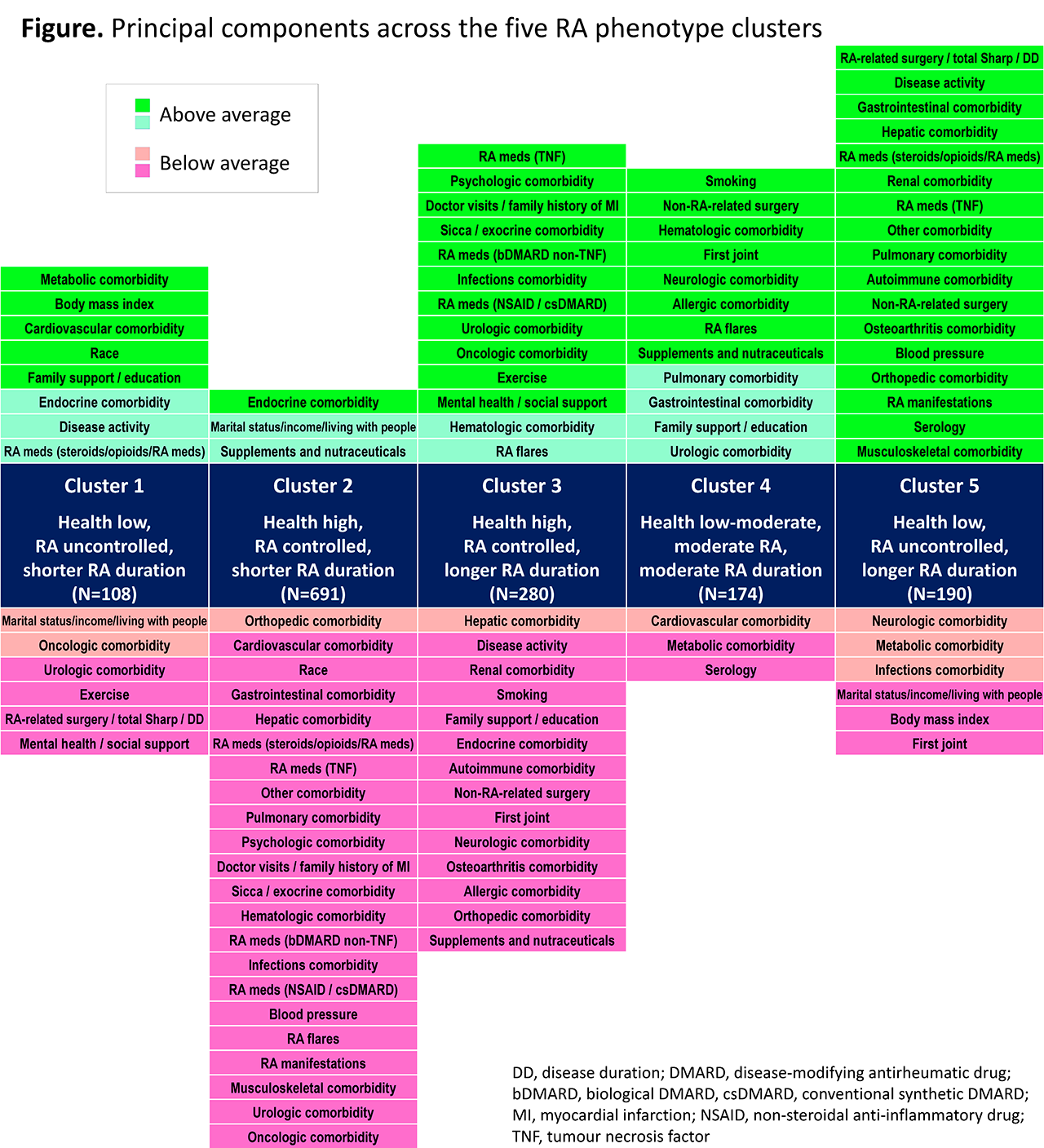
Results: Analysis of baseline data from 1443 patients identified 41 PCs that capture the fundamental characteristics involved in RA. Cluster analysis distinguished 5 patient clusters. Each cluster reflected a different profile of PCs, and can be described based on overall health, RA disease activity and duration (Table). Key differentiators between clusters include comorbidity PCs (metabolic comorbidities predominate in cluster 1, neurologic in cluster 4, and orthopedic in cluster 5) and patient characteristics/social PCs (greatest number of doctor visits and family history of MI in cluster 3, greatest BMI in cluster 1, highest income in cluster 2, lowest income in cluster 5, and least emotional support in cluster 1).
Conclusion: Data-driven cluster analysis of RA patient characteristics at entry into the BRASS registry identified five distinct patient phenotypes, providing a convenient method to potentially derive novel insights into the multifactorial drivers, commonly co-occurring health conditions, and manifestations of RA. Investigation of longitudinal outcomes in these different clusters in the BRASS registry and validation in an independent dataset is ongoing.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Curtis J, Weinblatt M, Saag K, Bykerk V, Charles-Schoeman C, Fiore S, St John G, Kimura T, Zheng S, Bingham C, Wright G, Bergman M, Nola K, Furst D, Shadick N. Exploring Heterogeneity in Rheumatoid Arthritis: Patient Profiling Through Principal Component and Cluster Analysis of the BRASS Registry [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/exploring-heterogeneity-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-patient-profiling-through-principal-component-and-cluster-analysis-of-the-brass-registry/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/exploring-heterogeneity-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-patient-profiling-through-principal-component-and-cluster-analysis-of-the-brass-registry/