Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Primary CNS vasculitis (PCNSV) is an uncommon and poorly understood disease that affects the brain and spinal cord. It includes heterogeneous histopathological patterns, clinical subsets, outcomes, and response to treatment. PCNSV has also been associated with lymphoma suggesting an immunological paraneoplastic mechanism. The molecular hallmarks of PCNSV are still unknown. We investigated the gene expression profile of granulomatous vasculitis (GV) including with Hodgkin lymphoma (HL), lymphocytic vasculitis (LV) and amyloid β-related angiitis (ABRA).
Methods: Formalin fixed paraffin embedded (FFPE) brain biopsy samples were cut for histology and RNA extraction (n=3 GV with HL, n=1 GV without HL, n=5 LV, n=4 ABRA, n=4 normal brain). RNA-sequencing was performed using Illumina® Hiseq-4000 platform and the Illumina® TruSeq® Total-RNA library. Student’s t-test and false discovery rate (FDR) tests were performed for each of the differentially expressed transcripts. Ingenuity Pathway Analysis® was used for the pathway expression analysis.
Results: Samples clustered in three groups by unsupervised analysis of gene expression profile. Cluster 1 (C1) included all samples of GV with HL plus one of the samples of LV. Cluster 2 (C2) included all ABRA samples plus 4/5 LV samples and the GV not associated with HL. Normal brain samples clustered together in cluster 3 (C3). Results indicated that PCNSV has specific transcriptomes compared to normal brain and GV with HL have a distinct profile from the other types of PCNSV. Pathway analysis revealed upregulation of dendritic cell maturation and antigen processing, T helper type 1 lymphocyte activation and neuroinflammation in PCNSV versus normal brain. The comparison of the different kinds of PCNSV showed that GV expressed CD28 at lower levels than LV (FDR < 0.01) suggesting a lower activation of lymphocytes. The top differentially expressed genes between GV and ABRA were TRAJ13 and CD27 suggesting an expansion of naïve and memory T cells in GV. Finally, only one gene, namely CD163, was expressed at lower levels in LV than in ABRA (FDR < 0.05) suggesting a lower presence of macrophages or the presence of anti-inflammatory mediators.
Conclusion: RNA sequencing revealed pathways deregulated in PCNSV and genes differentially expressed between the different kinds of PCNSV increasing the knowledge on PCNSV pathogenesis. It also sugested that GV with HL has an distinct gene expression profile compared to other types of PCNSV.
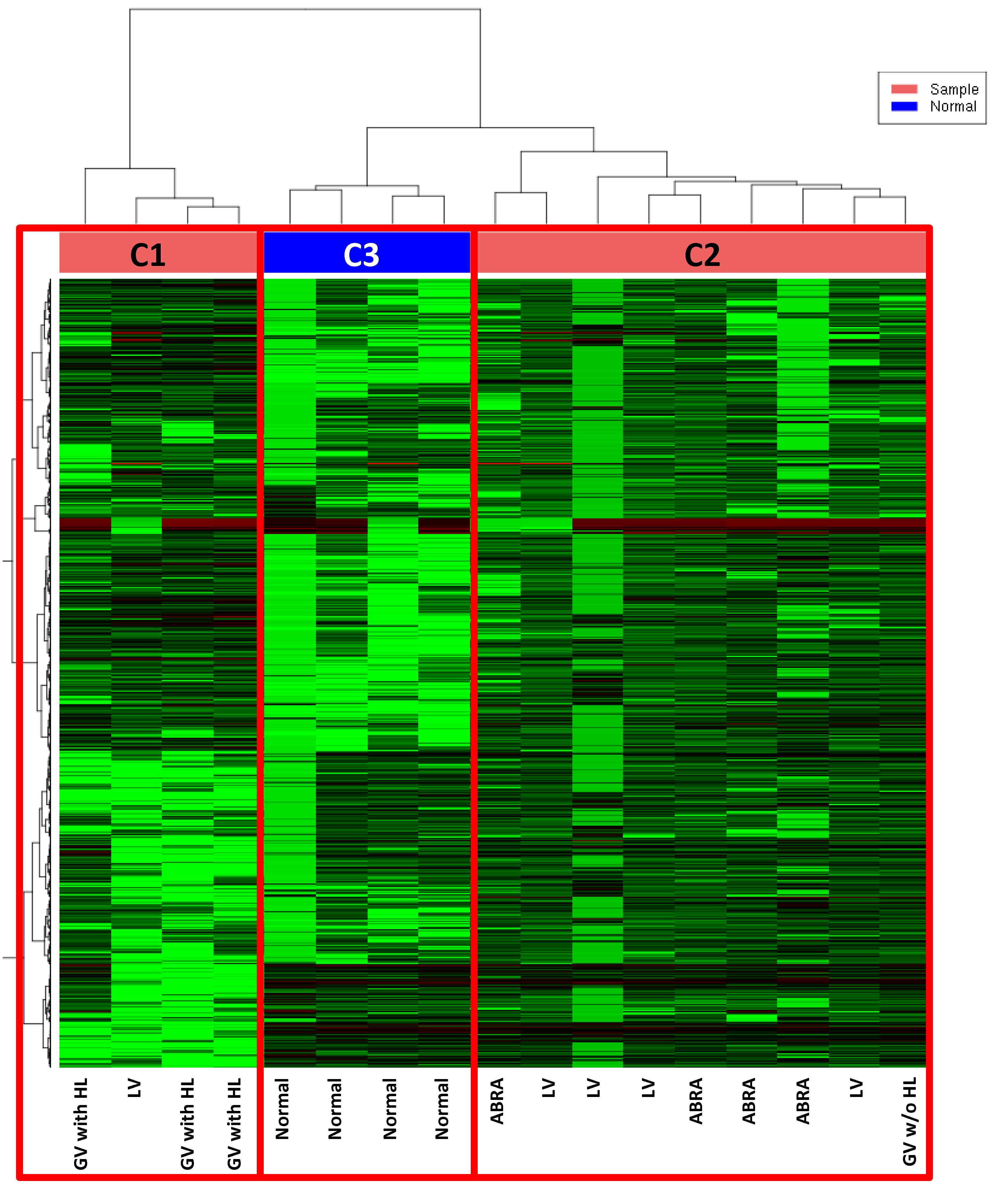 Unsupervised Clustering by RNAseq: 3 clusters are clearly defined. No cases clustered with normal samples
Unsupervised Clustering by RNAseq: 3 clusters are clearly defined. No cases clustered with normal samples
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Salvarani C, Brown R, Paludo J, Croci S, Ansell S, Giannini C, Parisi J, Warrington K, Hunder G. Exploring Gene Expression Profile of Primary Central Nervous System Vasculitis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/exploring-gene-expression-profile-of-primary-central-nervous-system-vasculitis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/exploring-gene-expression-profile-of-primary-central-nervous-system-vasculitis/
