Session Information
Date: Monday, November 6, 2017
Title: Spondyloarthropathies and Psoriatic Arthritis – Pathogenesis, Etiology Poster II
Session Type: ACR Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: F759 mice with a single amino-acid substitution in signal transducer subunit of IL-6 receptor gp130 (Y759F) develops arthritisspontaneously due to IL-17A and IL-6 mediated synergistic activation of positive-feedback loop of NF-kB signaling (inflammation amplifier).We sought to see whether this mechanism is operational in Reactive arthritis.
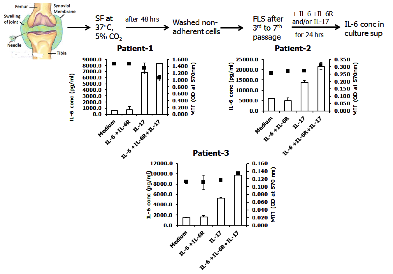
Methods: Arthritis was induced with oral feeding of salmonella enterica followed by ankle microbleeding in the ankle joints of F759 mice. Sera IL-6 along with IL-6 mRNA and STAT3 phosphorylation in synovium were measured. Further,exosomes isolated from sera of salmonella infected and control mice and were injected into the joints of mice, and measured the expression of proinflammatory cytokine, chemokines and growth factor. On the other hand, sera and synovial fluid of patients with ReA multiple cytokines, chemokines and growth factors were also measured. Finally, synovial fibroblasts (FLS) were cultured to purity and stimulated with IL-6, IL-17, IL-6 plus IL-17 and IL-6 were measured to see synergistic activation.
Results: IL-6 in sera of arthritic mice were significantly higher (p<0.05) than control mice along with increase STAT3 phophorylation in the synovium. Though, oral infection itself not sufficient to induce arthritis but if infection is followed by microbleeding then it significantly induces the arthritis in these mice (Fig-1). Further, exosomes from salmonella infected mice induced arthritis in ankle joint and significantly increased IL-6 expression (p<0.05). Similarly, in comparison to IL-6 and IL-17 alone these cytokines synergistically induced more IL-6 production from FLS isolated from ReA patients (Fig-2). Finally, we found that SF concentrations of effectors of inflammation amplifiers like IL-6, CCL-20, PLGF and FGF-basic were significantly higher in patients with ReA/uSpA as compared to osteoarthritis patients. Further, levels of these factors were also high in SF compared to sera in ReA patients.
Conclusion: Data of mice and patients support that synovitis in ReA is perpetuated by inflammation amplifier or synergistic induction of IL-6 and IL-17.
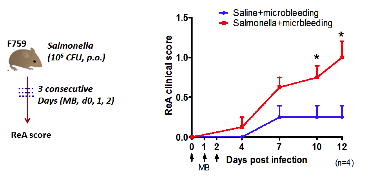 Figure 1: Oral infection of Salmonella followed by microbleeding into the ankle joint induces clinical symptoms of arthritis.
Figure 1: Oral infection of Salmonella followed by microbleeding into the ankle joint induces clinical symptoms of arthritis.
Figure 2: Activation of FLS isolated from ReA patients with IL-6 and IL-17 alone and synergistically with both cytokines and measurement of IL-6 level in culture supernatant.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Misra R, Kumar S, Singh R, Singh A, Kamimura D, Chaurasia S, Aria Y, Austria T, Mukherjee R, Ravindran B, Agarwal V, Murakami M. Existence of IL-6 and IL-17 Mediated Inflammation Amplifier Loop in Reactive Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017; 69 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/existence-of-il-6-and-il-17-mediated-inflammation-amplifier-loop-in-reactive-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to 2017 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/existence-of-il-6-and-il-17-mediated-inflammation-amplifier-loop-in-reactive-arthritis/