Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 1:00PM-3:00PM
Background/Purpose: Interstitial lung disease (ILD) is a leading cause of morbidity and mortality in patients with RA. To date, there are no specific treatments available for patients with RA-ILD. Several arguments suggest a potential role of the JAK-STAT signaling transduction pathway in the RA-ILD physiopathogenesis. Our objective was to test for association JAK-STAT pathway related genes rare coding variants with ILD in patients with RA.
Methods: In this candidate case-control genetic association study, RA-ILD patients were compared to RA-noILD patients. All cases fulfilled the 2010 EULAR-ACR and/or 1987 ACR revised criteria for RA. The ILD status was established by chest HRCT that were centrally reviewed by an experienced reader. Whole exome sequencing (WES) was performed, followed by a restricted analysis in JAK-STAT pathway candidate genes extracted from the Gene Ontology database. Two JAK-STAT related genes lists were generated, the first included 110 genes and a second restricted to 9 genes (STAT1, STAT2, STAT3, STAT4, STAT5, TYK2, JAK1, JAK2 and JAK3) for sensitivity analyses. Analyses were restricted to rare variants predicted to be deleterious: 1) variants with a minor allele frequency < 0.1% in non-Finnish Europeans of gnomAD, 2) variants predicted to have a high impact in the protein or to change protein effectiveness, 3) variants with a CADD score ≥ 15. Burden tests were performed using a logistic regression in 163 RA-ILD vs. 232 RA-noILD.
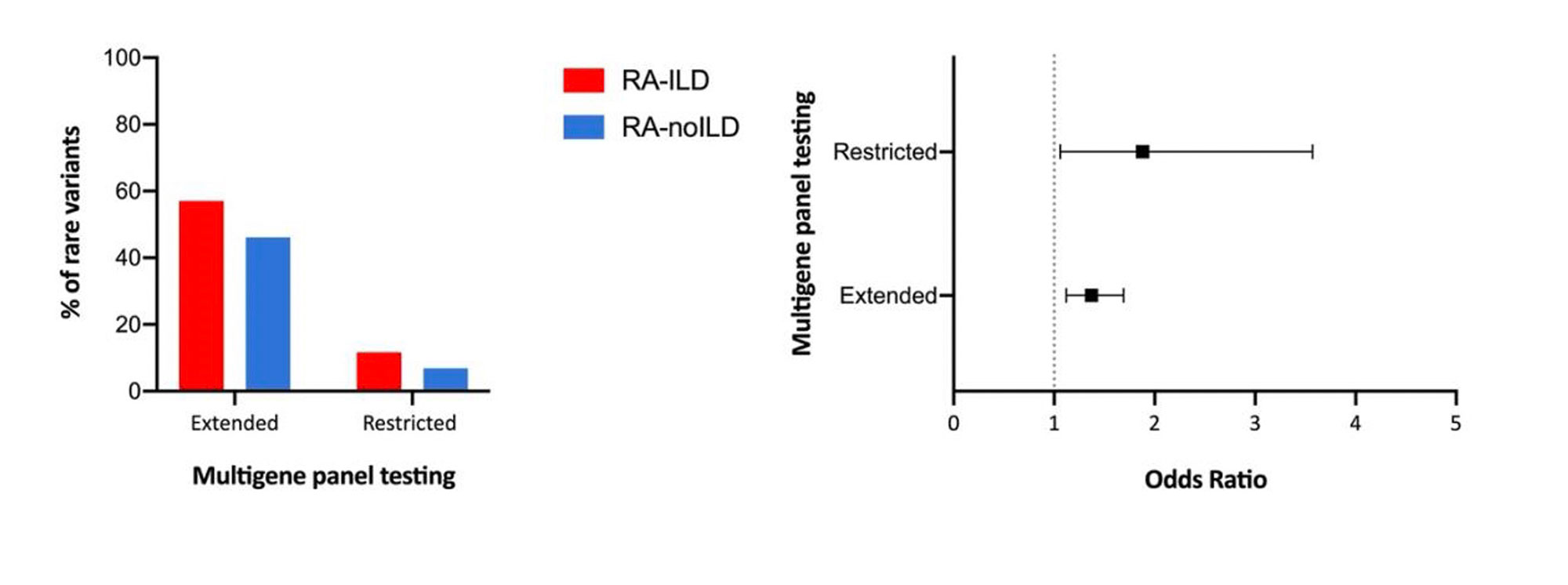
Results: 163 patients with RAILD and 235 with RA-noILD were included in the study. Briefly, RA-ILD patients were more frequently men (81.7% vs. 55.8%), elder at RA onset (64.3 ± 10.9 y/o vs. 44.1 ± 12.7 y/o) and more frequently smokers (60.0% vs. 48.4%). Restricted analysis on the 110 JAK-STAT candidates genes revealed an excess of rare variants in patients with RA-ILD when compared to patients with RA-noILD: 57.06% vs. 46.12%; OR=1.37 95% CI [1.12-1.69], P=2.56×10-3 (Table1, Figure1). The sensitive analyze restricted to STAT1, STAT2, STAT3, STAT4, STAT5, TYK2, JAK1, JAK2 and JAK3 found significant excess of rare variants in patients with RA-ILD: OR=1.88 95% CI [1.06-3.57], P=0.04 (Table1, Figure1).
Conclusion: This discovery step study found an excess of rare variants predicted to be deleterious within JAK-STAT pathway related genes in patients with RA-ILD compared to patients with RA-noILD. These findings suggest that the JAK-STAT pathway could play a physiopathogenic role in the occurrence of RA-ILD.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Juge P, Gazal S, Borie R, Wemeau L, Debray M, Ottaviani S, Marchand Adam S, Richez C, Nunes H, Richette P, Kannengiesser C, Avouac J, Sibilia J, Flipo R, Cottin V, Schaeverbeke T, Soubrier M, Saidenberg-Kermanac’h N, Valeyre D, Boileau C, Crestani B, Dieude P. Excess of Rare Deleterious Variants Within JAK-STAT Pathway – Related Genes in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis Associated Interstitial Lung Disease [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022; 74 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/excess-of-rare-deleterious-variants-within-jak-stat-pathway-related-genes-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-associated-interstitial-lung-disease/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2022
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/excess-of-rare-deleterious-variants-within-jak-stat-pathway-related-genes-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-associated-interstitial-lung-disease/