Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 10, 2019
Title: RA – Diagnosis, Manifestations, & Outcomes Poster I: Risk Factors, Predictors, & Prognosis
Session Type: Poster Session (Sunday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Seropositive arthralgia is defined as joint pain in patients positive for rheumatoid factor (RF) or anti-citrullinated protein antibodies (ACPA). In some individuals it is a precursor to rheumatoid arthritis (RA). The factors which determine progression and outcomes in seropositive arthralgia patients remain to be fully defined. Our aim was to evaluate outcomes and prognostic factors, including arthroscopic findings, in a cohort of patients with seropositive arthralgia.
Methods: We performed a prospective study of consecutive patients with seropositive arthralgia. All patients were seropositive for RF and/or ACPA. Demographic and clinical characteristics were collected on all patients. Synovial biopsy was performed by needle arthroscopy in all patients, and macroscopic and histologic features recorded. The degree of synovitis and vascularity were recorded on a 0–100-mm visual analog scale. Diagnosis at last follow-up was recorded in all patients. Mann-Whitney U test was used to compare groups. GraphPad Prism Version 8 and IBM SPSS Statistics Version 24 were used for data analysis.
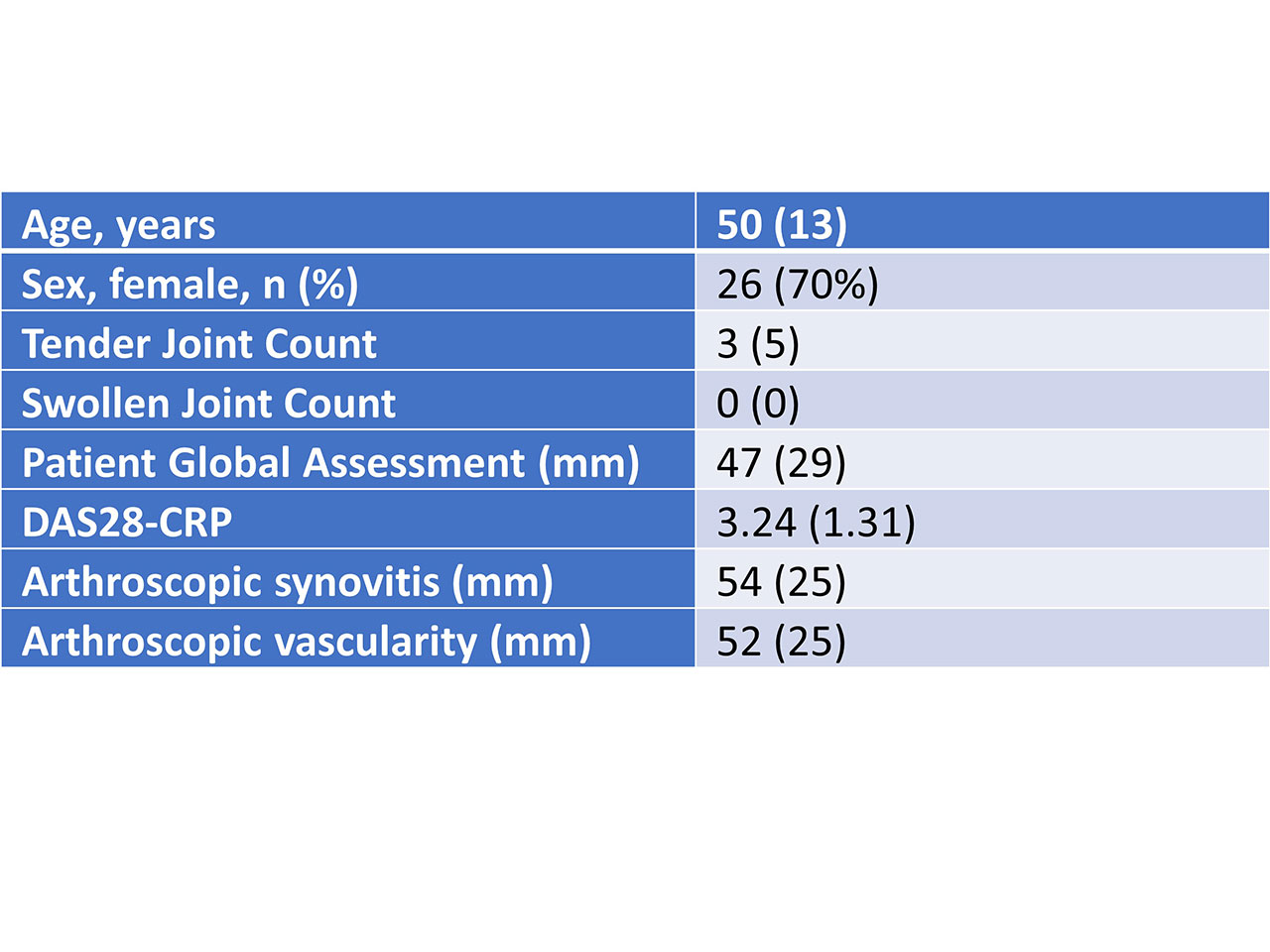
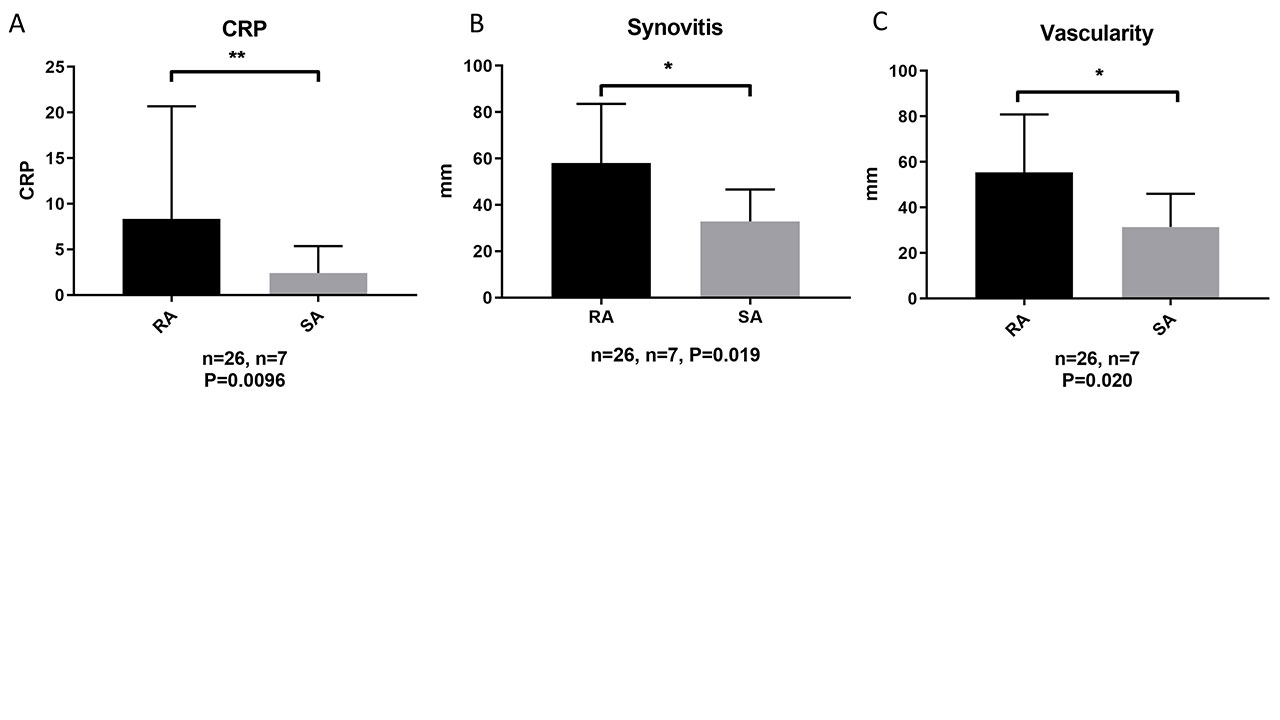
Results: 37 patients were recruited. Mean (SD) age was 50 (13) years. 26 (70%) were female. 31 (84%) were positive for RF and 32 (86%) for ACPA with 26 (70%) dual positive. Mean (SD) follow-up was 38 (13) months. Baseline characteristics are shown in Table 1. Final diagnosis was RA in 26 (70%), psoriatic arthritis in 2 (5%), connective tissue disease in 1 (3%), calcium pyrophosphate arthritis in 1 (3%), and remained seropositive arthralgia in 7 (19%). Baseline CRP was significantly higher in patients who developed RA than those who remained seropositive arthralgia, median (SD) 3.50 (2.00, 8.25) vs 1.00 (1.00, 2.00) mg/dL (p=0.0096), Figure 1. Baseline macroscopic synovitis and vascularity at arthroscopy were both significantly higher in those who developed RA than in those who remained as seropositive arthralgia, median (IQR) 60 (30, 80) vs 40 (20, 40) mm (p=0.021), and median (IQR) 50 (30, 73) vs 40 (20, 40) mm (p=0.021), Figure 1. Baseline DAS28-CRP, tender joint count, swollen joint count, and patient global assessment were not different between the groups. Baseline synovial cell immunophenotyping did not predict final diagnosis.
Conclusion: Elevated baseline CRP and arthroscopically determined macroscopic synovial inflammation and vascularity predict the development of RA in patients with seropositive arthralgia.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Low C, Conway R, Young F, Molloy E, Mongey A, Wilson G, Fearon U, Veale D. Evolution of Seropositive Arthralgia over Time: Predictors of Evolution to Rheumatoid Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/evolution-of-seropositive-arthralgia-over-time-predictors-of-evolution-to-rheumatoid-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/evolution-of-seropositive-arthralgia-over-time-predictors-of-evolution-to-rheumatoid-arthritis/