Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session (Monday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Guidelines are needed to aid early recognition and treatment of interstitial lung disease in systemic sclerosis (SSc-ILD). This study was conducted to develop expert consensus statements for the identification and management of SSc-ILD.
Methods: Evidence-based consensus statements were established using a modified Delphi process based on a systematic literature analysis. An expert panel of 27 European-based pulmonologists, rheumatologists and internists participated in three rounds of online surveys, a face-to-face discussion and a WebEx meeting, to establish statements and define an SSc-ILD management algorithm.
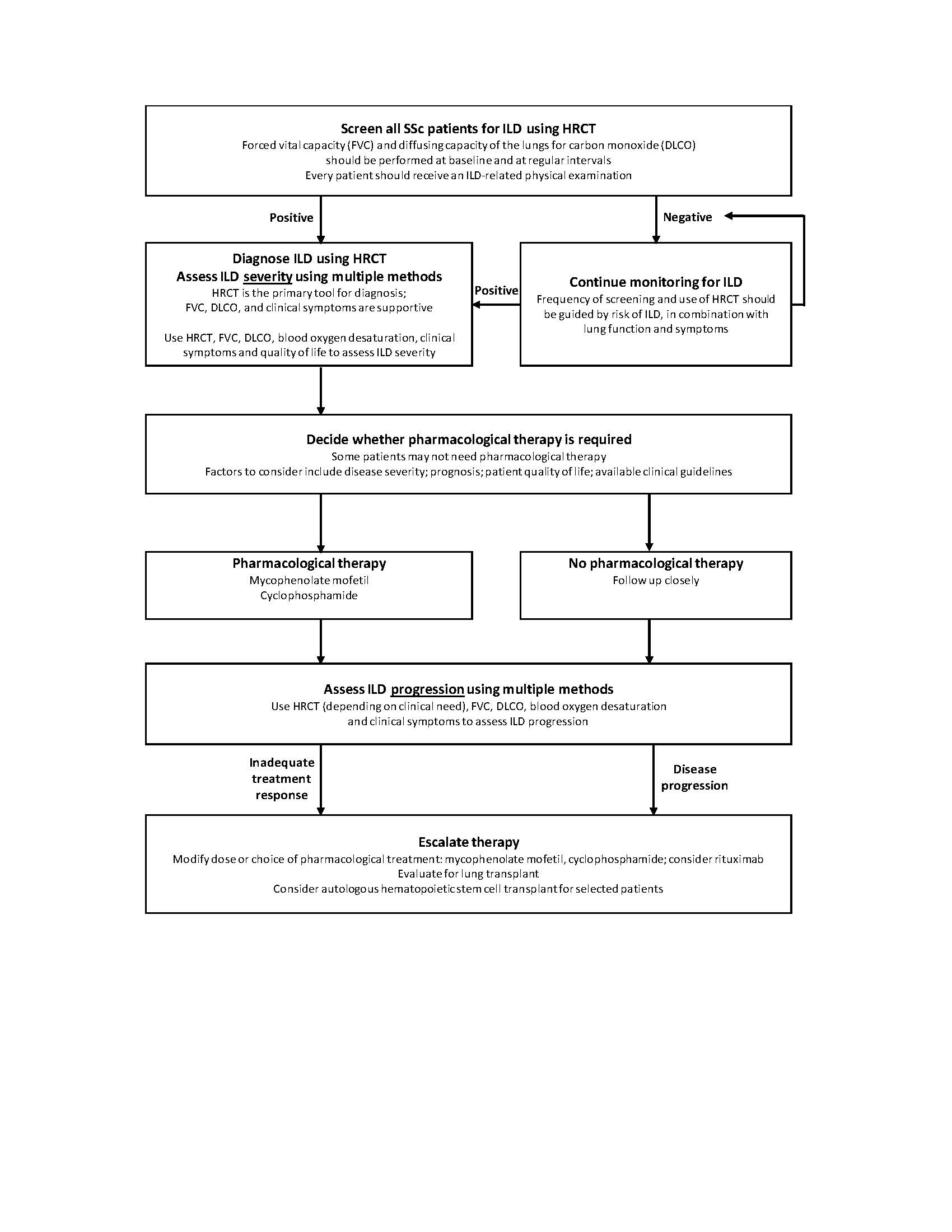
Results: The final evidence-based consensus included detailed statements on screening and risk stratification, diagnosis, assessment of severity, treatment options, monitoring, assessment of progression and treatment escalation. The consensus management algorithm is presented here in an abbreviated form for clinical use (figure).
Conclusion: These evidence-based expert consensus statements, developed using a modified Delphi process, provide important guidance for the identification and management of SSc-ILD in clinical practice.
Acknowledgements: The steering committee members would like to thank the expert panellists who participated in this study: Jérôme Avouac; Gianluca Bagnato; Rafic Barake; Simone Barsotti; Cosimo Bruni; Paolo Carducci; Patricia E Carreira; Ivan Castellví; Francesco Del Galdo; Jörg H W Distler; Ivan Foeldvari; Paolo Fraticelli; Peter M George; Bridget Griffiths; Alfredo Guillén-Del-Castillo; Abdul Monem Hamid; Bernhard Hellmich; Rudolf Horváth; Michael Hughes; Michael Kreuter; Belén López-Muñiz; Florentine Moazedi-Fuerst; Jacek Olas; Suman Paul; Cinzia Rotondo; Manuel Rubio-Rivas; Andrei Seferian; Michal Tomčík; Yurdagül Uzunhan; Ulrich A Walker; and Ewa Więsik-Szewczyk. The steering committee was chaired by John Cole (IQVIA, London, UK); the modified Delphi process was managed by Laura Wilson (IQVIA, Reading, UK). Medical writing support was provided by Rebecca Sutch, PhD, on behalf of AMICULUM Ltd, Oxford, UK.
Funding: Boehringer Ingelheim International GmbH, Germany
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Hoffmann-Vold A, Maher T, Philpot E, Ashrafzadeh A, Distler O. Evidence-based Consensus Statements for the Identification and Management of Interstitial Lung Disease in Systemic Sclerosis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/evidence-based-consensus-statements-for-the-identification-and-management-of-interstitial-lung-disease-in-systemic-sclerosis/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/evidence-based-consensus-statements-for-the-identification-and-management-of-interstitial-lung-disease-in-systemic-sclerosis/