Session Information
Date: Friday, November 6, 2020
Title: SLE – Diagnosis, Manifestations, & Outcomes Poster I: Clinical Manifestations
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Multiple indices are available to measure disease activity in SLE patients, but are often considered too complex and time consuming for use in routine clinical practice. The Lupus Foundation of America-Rapid Evaluation of Activity in Lupus (LFA-REAL)1 is a simplified assessment which provides multiple anchored visual analog scales (range 0–100 mm) for individual symptoms, the sum of individual scores derives an overall disease activity assessment. Moreover, it includes both a clinician- and a patient-reported outcome component for tandem assessments of disease activity. The aim of this study was to analyze the performance of the LFA-REAL as an SLE disease activity measure and to compare it with other clinician- and patient-reported outcome measures in a single-center Italian cohort.
Methods: This is a cross-sectional study that enrolled SLE patients (diagnosed based on 1997 ACR criteria). Disease activity was evaluated using the SELENA-SLEDAI score and organ damage using the SLICC/DI. During the visit, both the clinician and the patient completed the LFA-REAL for the assessment of disease activity. Moreover, each patient completed the following patient reported outcome measures (PROs): SLAQ, SF-36, FACIT-Fatigue, LIT. We evaluated the correlation between clinician LFA-REAL and SELENA-SLEDAI and between patient LFA-REAL and the PROs. ROC curve analysis was applied to compare LFA-REAL with the definition of active disease (SELENA-SLEDAI >4) and low disease activity state (LLDAS)2.
Results: We enrolled 110 consecutive adult SLE patients (90.9% female, 97.3% Caucasian, mean age 45.06±11.8 years, median disease duration 14 years (IQR 7-21)). Median SELENA-SLEDAI at enrollment was 2 (IQR 0-3). Baseline characteristics of the cohort are summarized in Table 1. The mean clinician total LFA-REAL was 15±27.7 mm, while the mean patient total LFA-REAL was 127.3±114.0 mm; clinician and patient LFA-REAL were significantly correlated (r= 0.36, p< 0.001). We found a moderate correlation between clinician LFA-REAL and SELENA-SLEDAI (r=0.31, p< 0.001), while patient LFA-REAL was strongly associated with the SLAQ score (r= 0.88, p< 0.0001) and with the scores of all other PROs, as reported in Table 2. Clinician LFA-REAL was highly accurate in defining active disease (SELENA-SLEDAI >4) by ROC analysis (area under the curve 0.929). A clinician LFA-REAL of at least 33 mm demonstrated the optimal trade-off of sensitivity (83.33%) and specificity (81.73%) in detecting active disease. Conversely, we found that clinician LFA-REAL performed less well against the definition of LLDAS (area under the curve 0.690).
Conclusion: In our SLE cohort, clinician LFA-REAL demonstrated a good correlation with SELENA-SLEDAI and patient LFA-REAL showed strong correlations with multiple PROs, including the SLAQ score. Therefore, the LFA-REAL may be a valuable simplified screening tool to rapidly identify active patients in routine clinical practice.
1 Askanase A et al., Lupus Sci Med. 2015. PMID: 25861457; 2 Franklyn K et al., Ann Rheum Dis 2016. PMID 26458737.
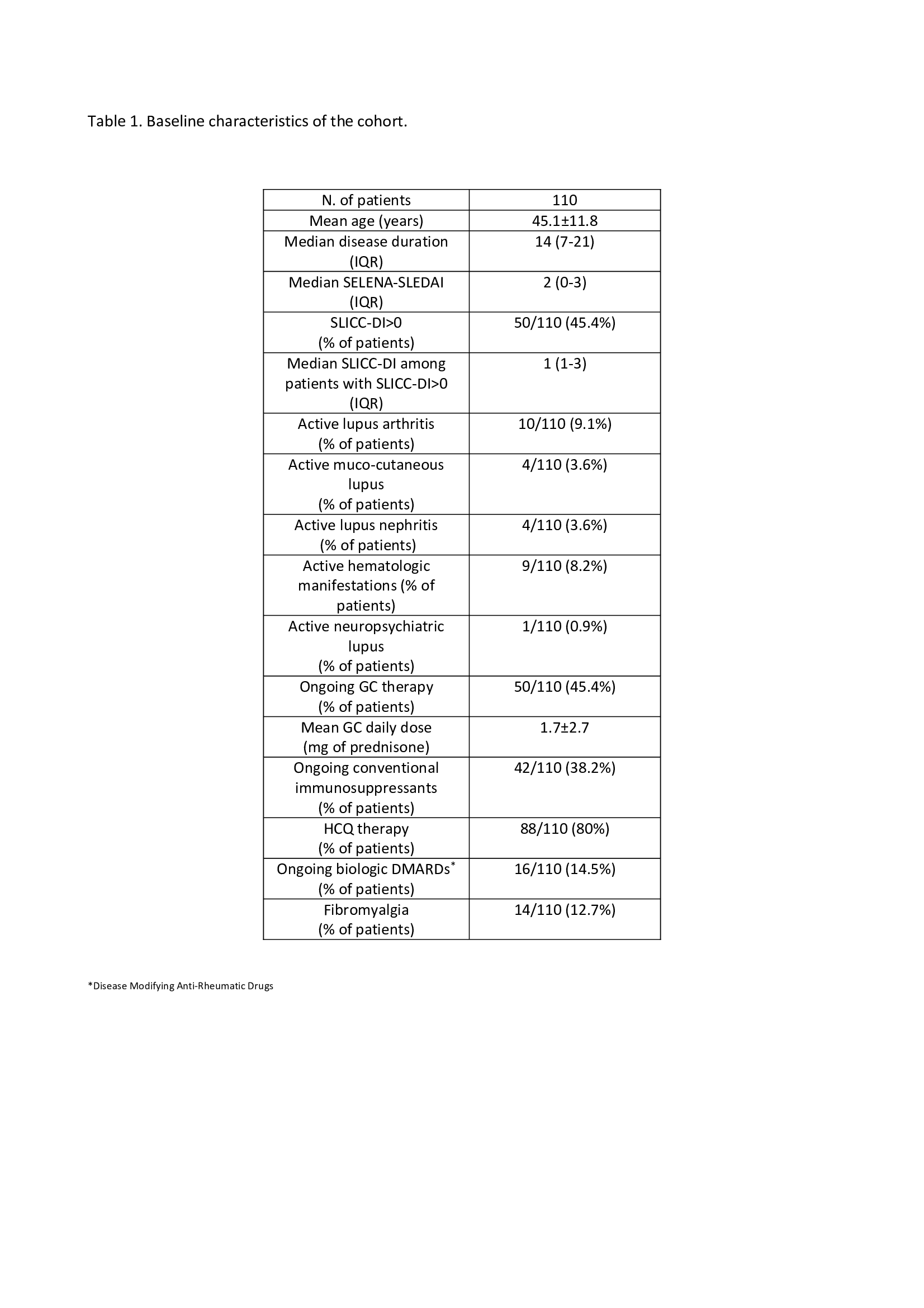 Table 1. Baseline characteristics of the cohort.
Table 1. Baseline characteristics of the cohort.
 Table 2. Correlation between patient LFA-REAL and PROs.
Table 2. Correlation between patient LFA-REAL and PROs.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Elefante E, Tani C, Signorini V, Poli V, Stagnaro C, Parma A, Zucchi D, Carli L, Ferro F, Askanase A, Mosca M. Evaluation of the Lupus Foundation of America-Rapid Evaluation of Activity in Lupus as a Measure of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE) Disease Activity from the Clinician and the Patient Perspective: Experience from an Italian Cohort [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/evaluation-of-the-lupus-foundation-of-america-rapid-evaluation-of-activity-in-lupus-as-a-measure-of-systemic-lupus-erythematosus-sle-disease-activity-from-the-clinician-and-the-patient-perspective/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/evaluation-of-the-lupus-foundation-of-america-rapid-evaluation-of-activity-in-lupus-as-a-measure-of-systemic-lupus-erythematosus-sle-disease-activity-from-the-clinician-and-the-patient-perspective/
