Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 10, 2019
Title: 3S084: Systemic Sclerosis & Related Disorder – Clinical I: Therapeutics & Outcomes (863–868)
Session Type: ACR Abstract Session
Session Time: 2:30PM-4:00PM
Background/Purpose: Systemic sclerosis (SSc) causes scleroderma renal crisis (SRC) and chronic kidney disease (CKD). A previous open label trial of bosentan suggested possible benefit for CKD following SRC [1]. Here we report the results of a placebo-controlled trial of zibotentan, a highly selective endothelin A receptor antagonist, in SSc associated CKD.
Methods: ZEBRA-1 was a double-blind randomised placebo-controlled trial in SSc with CKD (eGFR 45-60 ml/min) comparing oral zibotentan 10 mg/day and placebo over 26 weeks with final safety assessment at 52 weeks (Clinical Trials NCT02047708). Efficacy was assessed by eGFR with safety a key secondary endpoint. Candidate urinary molecular markers of SSc-associated CKD were measured. Variables were compared by non-parametric Mann-Whitney U test. Pharmacokinetics (PK) were explored in ZEBRA-1 and an additional single escalating dose PK substudy (ZEBRA-2) undertaken in patients (n=8) on haemodialysis.
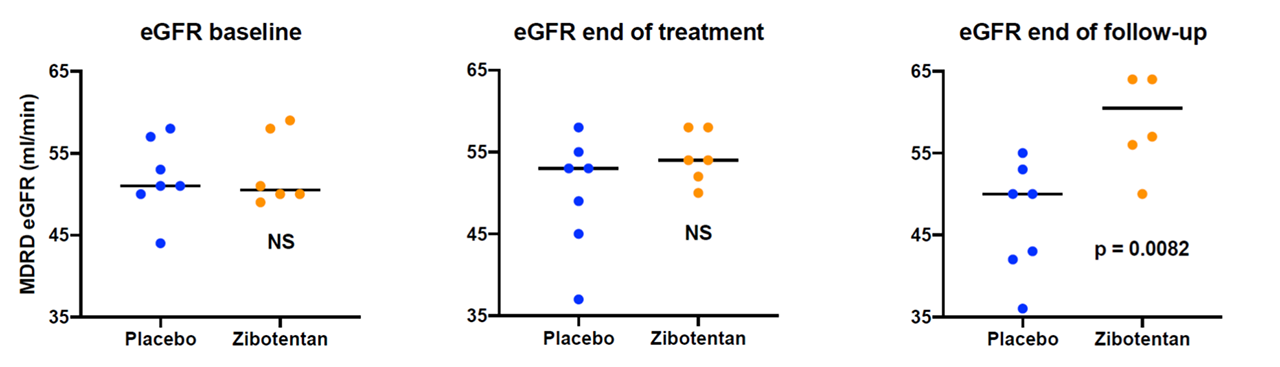
Results: 16 patients consented to enter ZEBRA-1. There were 3 screen failures due to renal function being ineligible on re-testing. 7 patients received placebo and 6 zibotentan. Baseline renal function was well matched between treatment groups (median eGFR in placebo 51 (44-58); zibotentan 50.5 (49-59)). Renal function was equal at 26 weeks (placebo 53 (37-58); zibotentan 54 (50-58)) but eGFR significantly improved in the active treatment group at 52 weeks (placebo 50 (36-55) zibotentan 60.5 (50-74), p=0.0082) (see Figure 1).
Our previous work identified elevated urinary MCP-1: creatinine ratio as a marker of SSc-CKD [2]. Interestingly, levels declined on zibotentan but not in placebo. Thus, median baseline urinary MCP1/creatinine (pg/mg/L) was 7.1 (5.2-21.9) in placebo arm and 5.4 (3.1-28.9) for zibotentan, increased to 8.8 (6.3-33.5) at 26 weeks on placebo and reduced to 4.4 (2.9-11.2) on zibotentan. At 52 weeks MCP-1/creatinine for placebo arm was 7.5 (6.4-15.8) and was significantly lower at 4.5 (4.1-6.0; p=0.0095) after zibotentan.
There were 46 reported adverse events (AE) (26 placebo and 20 active treatment) in ZEBRA-1 in 11 patients (6 placebo and 5 zibotentan). Of the 46 reported AE, 6 were serious (3 in each arm). PK confirmed zibotentan levels within therapeutic range in ZEBRA-1 and suggested feasible dose regimen for dialysis patients (ZEBRA-2).
Conclusion: This is the first placebo-controlled interventional trial in renal SSc. Zibotentan was generally well tolerated. Compared with placebo, zibotentan treatment over 26 weeks was associated with improved eGFR at 52 weeks and fall in urinary MCP1:creatinine, a candidate marker for SSc kidney disease. Whilst preliminary, these results suggest targeting endothelin A in SSc associated CKD may be beneficial.
References
- Penn H, et al. Targeting the endothelin axis in scleroderma renal crisis: rationale and feasibility. QJM. 2013 Sep;106(9):839-48
- Stern E, et al. Monocyte Chemoattractant Protein-1 (MCP-1, CCL2) Is a potential local marker of renal involvement in scleroderma [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015; 67 (suppl 10).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Stern E, Host L, Escott K, Gilmour P, Wanjiku I, Ochiel R, Burns A, Unwin R, Ong V, Denton C. Evaluation of the Highly Selective Endothelin a Receptor Antagonist Zibotentan in Systemic Sclerosis Associated Chronic Kidney Disease [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/evaluation-of-the-highly-selective-endothelin-a-receptor-antagonist-zibotentan-in-systemic-sclerosis-associated-chronic-kidney-disease/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/evaluation-of-the-highly-selective-endothelin-a-receptor-antagonist-zibotentan-in-systemic-sclerosis-associated-chronic-kidney-disease/