Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Submissions (ACR)
Background/Purpose: In the clinical development program of the oral Janus kinase inhibitor tofacitinib for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis (RA), small mean increases in serum creatinine (SCr) (<4 μmol/L least mean squares difference from placebo [PBO] for tofacitinib 5 and 10 mg twice daily [BID] at Month 3) were observed and plateaued early. Further analyses using pooled data from five Phase 3 and two long‑term extension (LTE) studies suggested that tofacitinib had a small and reversible effect on mean SCr in patients (pts) with RA; the mean SCr changes plateaued, remained within normal limits and did not appear to be associated with acute renal failure or progressive worsening of renal function in the LTE studies. This study aimed to assess changes in measured glomerular filtration rate (mGFR) with tofacitinib relative to PBO in pts with active RA.
Methods: In this double-blind, PBO-controlled, Phase 1 study (NCT01484561) RA pts were randomized 2:1 to oral tofacitinib 10 mg BID in Period 1 (P1) then PBO BID in Period 2 (P2) (tofacitinib→PBO); or oral PBO BID in both P1 and P2 (PBO→PBO). P1 and P2 were 6-7 and 4‑5 weeks in duration, respectively. Each pt underwent mGFR evaluations by iohexol serum clearance at 4 time points (run-in, pre-dose 1 in P1, end of P1, and end of P2); estimated GFR (eGFR) was calculated using the Cockcroft-Gault equation. The primary endpoint was the geometric mean change in mGFR from baseline to end of P1. Secondary endpoints included the geometric mean change in mGFR from baseline to end of P2 and from end of P1 to end of P2, change in eGFR and SCr, RA clinical efficacy and safety.
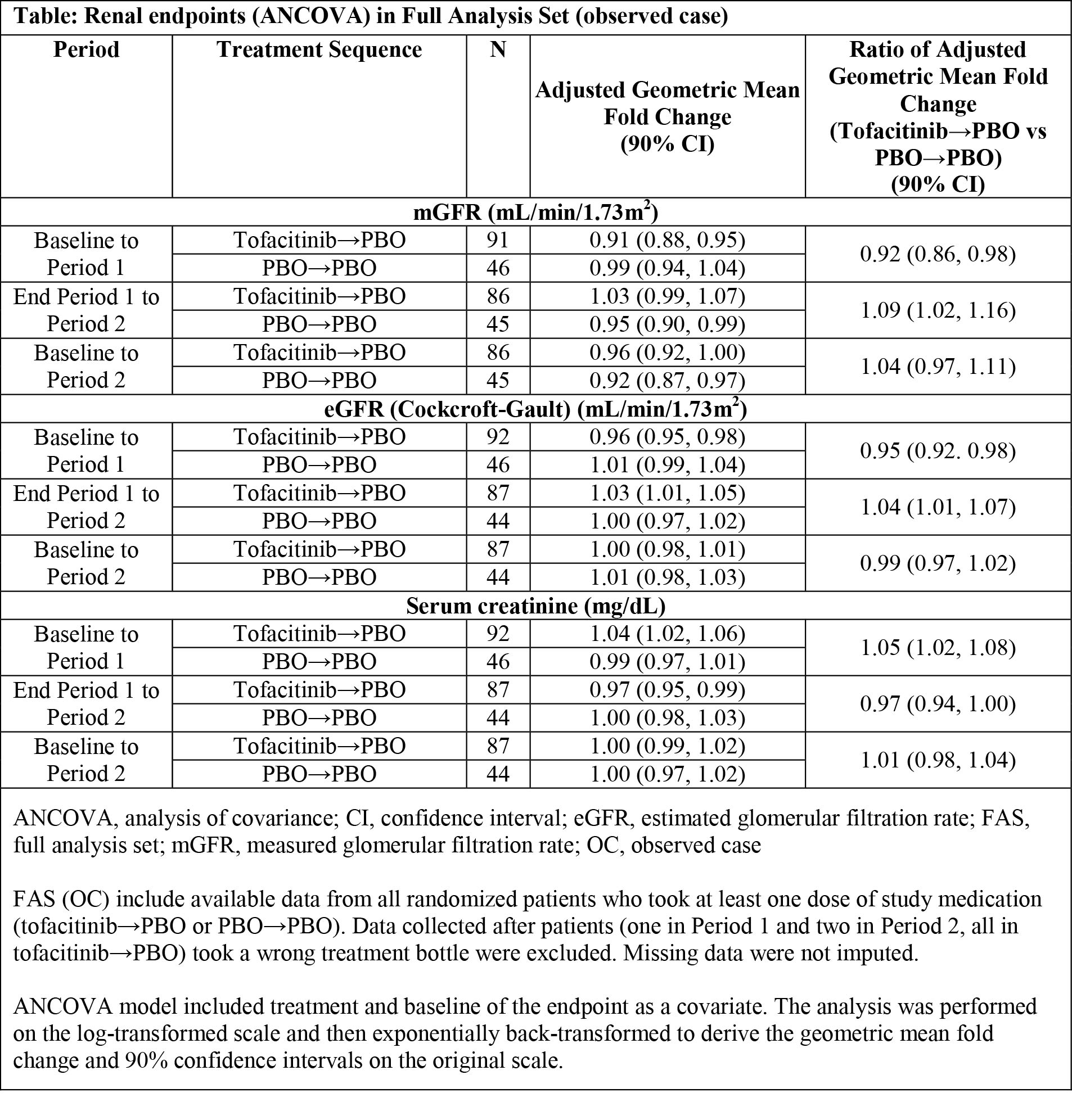
Results: 148 pts were randomized to tofacitinib→PBO (N=97) and PBO→PBO (N=51). Baseline characteristics were similar between groups. In tofacitinib→PBO, tofacitinib treatment in P1 was associated with a reduction of 8% (90% confidence interval [CI]: 2%, 14%) from baseline in geometric mean mGFR vs PBO→PBO. The reduction in geometric mean mGFR associated with tofacitinib in P1 reversed on PBO in P2, and there was no difference vs PBO→PBO in the adjusted geometric mean fold change of mGFR at the end of the study (tofacitinib→PBO: PBO→PBO: 1.04; 90% CI: 0.97, 1.11). Similar results were observed for eGFR and SCr (Table). Of note, during P2 there was a 5% reduction (90% CI: 1%, 10%) in mGFR (but not eGFR) in PBO→PBO. Clinical efficacy and safety were consistent with prior studies.
Conclusion: This study suggests that small mean increases in SCr and mean decreases in eGFR in pts with RA treated with tofacitinib may occur in parallel with small mean decreases in mGFR, and that changes in these parameters with short-term tofacitinib treatment appear reversible after discontinuation. Safety monitoring will continue in ongoing and future clinical trials and routine pharmacovigilance.
1. Isaacs JD et al. Ann Rheum Dis 2012; 71 (Supplement 3): 672.
2. Wollenhaupt J et al. Arthritis Rheum 2013; 65(suppl 10): S993.
Disclosure:
J. Kremer,
Pfizer Inc,
2,
Pfizer Inc,
5;
A. J. Kivitz,
Pfizer Inc,
2,
Pfizer Inc,
5,
Pfizer Inc,
8;
J. A. Simon Campos,
None;
E. L. Nasonov,
None;
H. Tony,
None;
B. Vlahos,
Pfizer Inc,
1,
Pfizer Inc,
3;
C. Hammond,
Pfizer Inc,
1,
Pfizer Inc,
3;
J. Bukowski,
Pfizer Inc,
1,
Pfizer Inc,
3;
H. Li,
Pfizer Inc,
1,
Pfizer Inc,
3;
S. Schulman,
Pfizer Inc,
1,
Pfizer Inc,
3;
S. Raber,
Pfizer Inc,
1,
Pfizer Inc,
3;
A. Zuckerman,
Pfizer Inc,
1,
Pfizer Inc,
3;
J. Isaacs,
Pfizer Inc,
2,
Pfizer Inc,
5.
« Back to 2014 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/evaluation-of-the-effect-of-tofacitinib-on-measured-glomerular-filtration-rate-in-patients-with-active-rheumatoid-arthritis/