Session Information
Date: Monday, November 14, 2022
Title: SLE – Diagnosis, Manifestations, and Outcomes Poster III: Outcomes
Session Type: Poster Session D
Session Time: 1:00PM-3:00PM
Background/Purpose: Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Disease Activity Index-2000 (SLEDAI-2K) Glucocorticoid Index (SLEDAI-2KG) is a novel valid index able to measure disease activity while accounting for prednisone usage. Previous studies examining disease activity and Health-related quality of life (HRQoL) have been inconsistent, with most finding no association between the two. Given that SLE patients report lower HRQoL compared to the general population, establishing a better understanding between disease activity and its impact on HRQoL may improve patients’ health outcomes.
This study had 2 aims:
1) Ascertain the association of the novel index, SLEDAI-2KG with the 36-Item Short Form Survey (SF-36), and
2) Compare the performances of the SLEDAI-2K and SLEDAI-2KG in determining poor HRQoL based on normative Canadian population data.
Methods: This is a single centre cross-sectional retrospective analysis of 1357 patients treated from 1994 to 2020. Data from SLEDAI-2K, SLEDAI-2KG and SF-36 at the first visit in the cohort were analysed. Descriptive statistics were used to describe patients’ baseline characteristics.
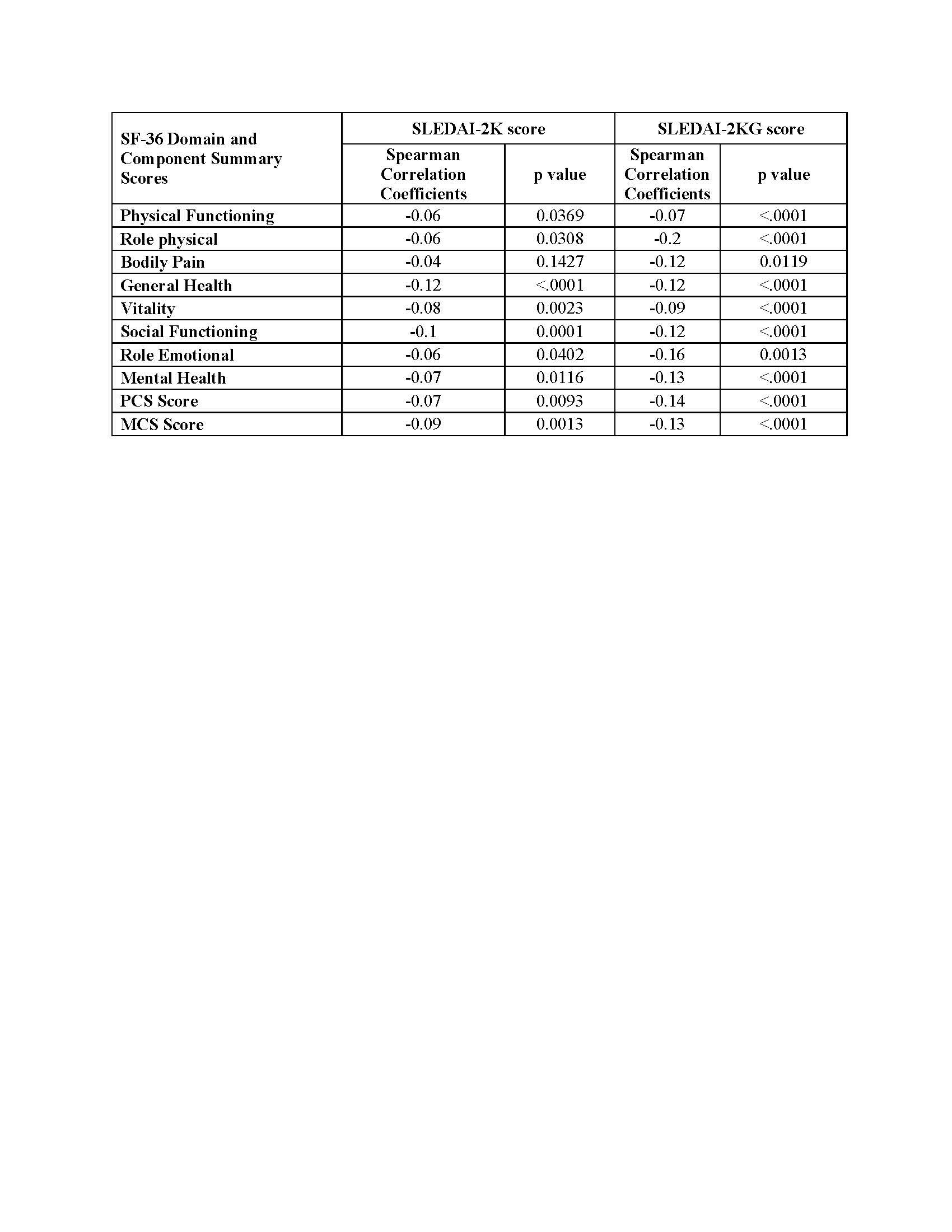
Aim 1: We hypothesised that SLEDAI-2K and SLEDAI-2KG would have none to low correlations with SF-36 domains but that SLEDAI-2KG would show better correlations. Spearman correlations were determined between disease activity indices and SF-36 domains.
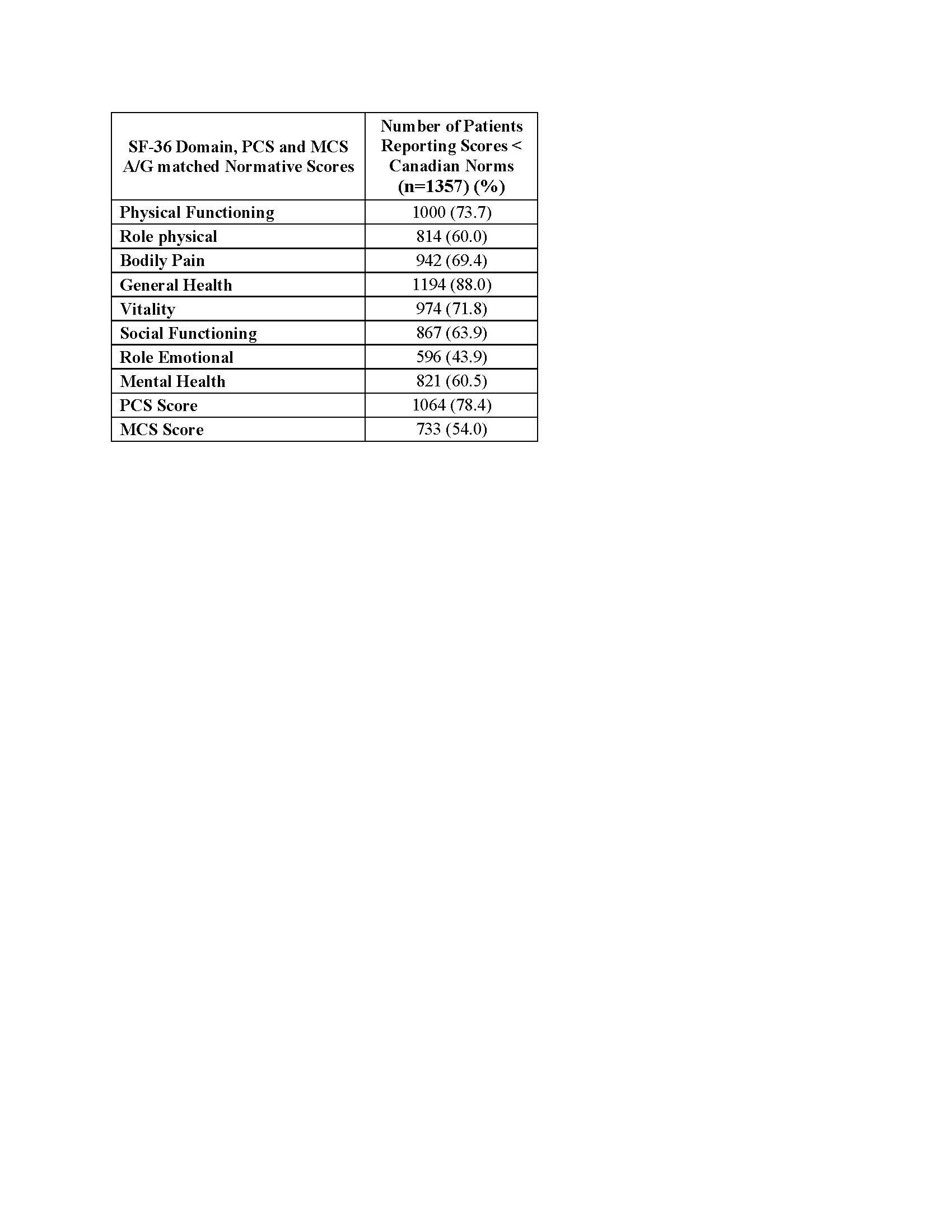
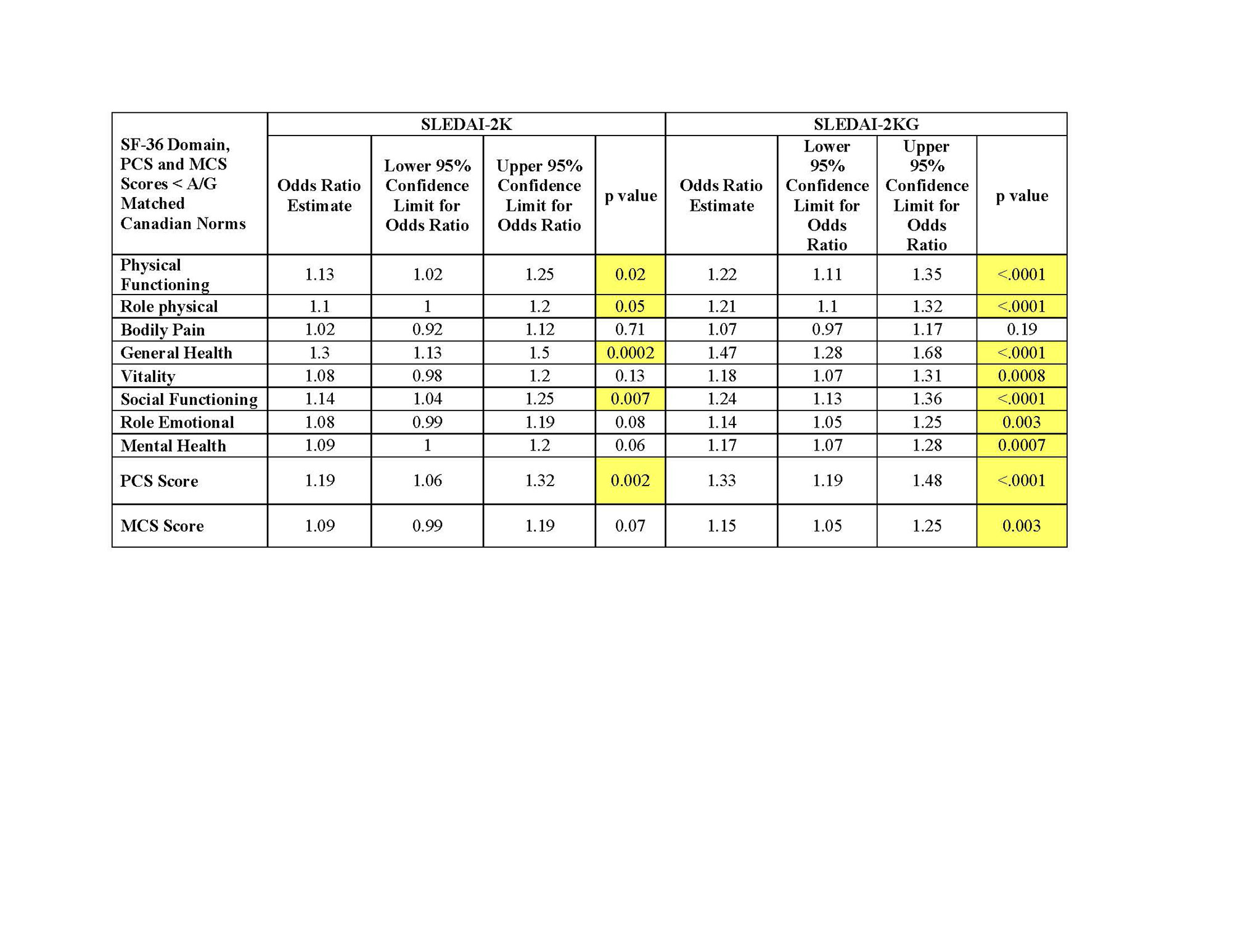
Aim 2: Age and gender (A/G) matched SF-36 scores based on Canadian population norms were determined and HRQOL was then categorized as below or equal to or above Canadian norms. Univariate logistic regressions were performed using either SLEDAI-2K or SLEDAI-2KG as the sole independent variable to evaluate the association with normative scores.
Results: 1357 SLE patients (88.5% female) were included in the study. Mean age and duration of SLE at the 1st visit were 38.0 ± 13.6 and 8.5 ± 5.2 years respectively. 854 (62.9%) patients were treated with prednisone at mean doses of 12.0 ± 11.6 mg/day (Table 1). SLEDAI-2KG scores were in general 2 points higher than SLEDAI-2K scores (6.5 ± 5.9 and 4.5 ± 4.7 respectively).
There were weak negative correlations (r < 0.3) with both SLEDAI-2K and SLEDAI-2KG and the 8 SF-36 domain and physical (PCS) and mental (MCS) component summary scores, ranging from -0.06 to -0.12 and -0.07 to -0.20 respectively. Correlation coefficients of SLEDAI-2KG with SF-36 were approximately double those of SLEDAI-2K but remained < 0.3.
When dichotomizing SF-36 scores based on Canadian A/G matched norms, the majority of patients reported scores less than (54.0-88.0%) normative values across all SF-36 domains, PCS and MCS, with exception of the Role Emotional domain (43.9%) (Table 2).
In univariate analyses, an increase of 1 in the SLEDAI-2KG score was associated with higher odds of SF-36 scores less than Canadian norms compared with SLEDAI-2K (14-47% vs. 10-30% respectively) (Table 3).
Conclusion: Both SLEDAI-2K and SLEDAI-2KG scores weakly correlated with SF-36. SLEDAI-2KG, compared with SLEDAI-2K, was more likely to identify SLE patients with poorer HRQoL across all SF-36 domains. These results might serve as a more comprehensive guide for determining disease prognosis and treatment decisions to improve HRQoL in SLE.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Cheng A, Strand V, Su J, Anderson N, Simon L, Touma Z. Evaluation of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Disease Activity Index 2000 (SLEDAI-2K) vs. SLEDAI-2K Glucocorticoids (SLEDAI-2KG) on Patient Health-Related Quality of Life (HRQoL) in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE) [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022; 74 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/evaluation-of-systemic-lupus-erythematosus-disease-activity-index-2000-sledai-2k-vs-sledai-2k-glucocorticoids-sledai-2kg-on-patient-health-related-quality-of-life-hrqol-in-systemic-lupus-erythe/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2022
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/evaluation-of-systemic-lupus-erythematosus-disease-activity-index-2000-sledai-2k-vs-sledai-2k-glucocorticoids-sledai-2kg-on-patient-health-related-quality-of-life-hrqol-in-systemic-lupus-erythe/