Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Submissions (ACR)
Background/Purpose Several models have been proposed to refer patients (pts) with possible axial spondyloarthritis (axSpA) from primary care to the rheumatologist. Aim of the study was to evaluate performance of referral models for axSpA in the SPondyloArthritis Caught Early (SPACE) cohort.
Methods Ten referral models were found in literature and tested in the Leiden SPACE cohort, including pts with back pain (≥3 months, ≤2 years, onset <45 years; n=192) referred to the rheumatology outpatient clinic of the LUMC. Imaging was omitted from all models if included as a referral parameter, as it is unfeasible for screening in primary care. [table 1]

Performance of the models was evaluated (sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value, positive likelihood ratio) using classification by ASAS axSpA criteria as external standard. For pts not fulfilling the ASAS criteria who are referred, post-test probability for axSpA was calculated based on the LR product for presence of SpA features. A LR product ≥78 equals a post-test probability ≥80% and was used as cut-off for probable axSpA. Pts who were incorrectly not referred met the ASAS axSpA criteria by fulfilling the clinical arm only or the imaging arm (imaging arm only or both arms). [table 2]
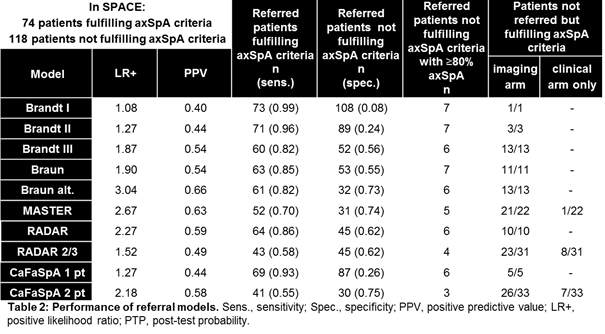
Results In total, 74/192 pts fulfilled ASAS axSpA criteria; 48 with positive imaging (n=15 radiographic sacroiliitis). Most models performed well regarding sensitivity/specificity. Braun alt. model has the most balanced sensitivity/specificity and highest LR+. All models that include HLA B27 miss axSpA pts with positive imaging, 14-23% with radiographic sacroiliitis (depending on the model). PPV of the models is low, indicating that many pts are referred despite not fulfilling axSpA criteria. However, 6-16% (depending on the model) of these pts have a post-test probability ≥80% for axSpA. This reflects that these pts are rightly referred, despite not fulfilling the axSpA criteria.
Conclusion Most referral models performed well in the SPACE cohort. However, this cohort includes pts already referred from primary care, probably causing overestimation of performance of all models. All models miss pts fulfilling the ASAS imaging arm, 14-23% of which have radiographic sacroiliitis, which is highly undesirable. Moreover, large numbers of pts referred unnecessarily might lead to a burden for health care systems. Further studies should be conducted in primary care to evaluate these models in their target population.
References
1Brandt ARD 2007;66:1479-84
2Braun Rheum 2013;52:1418-24
3Poddubnyy J Rheum 2011;38:2452-60
4Sieper ARD 2013;72:1621-7
5Weel AC&R 2013-09-19
Disclosure:
O. Abawi,
None;
R. van den Berg,
None;
D. van der Heijde,
None;
F. van Gaalen,
None.
« Back to 2014 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/evaluation-of-referral-models-for-axial-spondyloarthritis-in-primary-care-in-the-spondyloarthritis-caught-early-cohort/
