Session Information
Date: Saturday, November 6, 2021
Title: Epidemiology & Public Health Poster I: COVID-19 & Vaccination (0084–0117)
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: Patients with chronic rheumatic diseases are considered to be at increased risk for some infections, with prescribed immunomodulatory (IM) therapies increasing this risk further. It is unclear if patients with RA or PsA receiving IM therapies are at increased risk for SARS-CoV-2 infection, and if they experience more severe COVID-19 clinical outcomes compared with the general population. We describe the characteristics and COVID-19 clinical outcomes in this patient population.
Methods: This descriptive retrospective cohort study (a post-approval safety study of tofacitinib [approved for RA, PsA, and ulcerative colitis (UC) at the time of the study] in the context of the COVID-19 pandemic) used data from the US Optum® deidentified COVID-19 electronic health record dataset (2007–2020). Adults with a COVID-19 diagnosis (≥ 1 diagnosis code or positive SARS-CoV-2 laboratory test [including PCR, antibody, or antigen]) were stratified into 3 cohorts: patients with RA or PsA and evidence of treatment with IM therapy in the 2 yrs prior to COVID-19 diagnosis (RA and PsA cohorts); and patients without a diagnosis of RA, PsA, or UC and no record of IM therapy in the 2 yrs prior to COVID-19 diagnosis (comparator cohort). Baseline (SARS-CoV-2 diagnosis date) demographics, comorbidities, and IM therapy class were evaluated. The incidence proportions (IPs; with 95% confidence intervals) of primary endpoints (hospitalization and intensive care unit [ICU] admission) and COVID-19 clinical manifestations/outcomes of interest were calculated. Logistic regression was used in exploratory analyses to estimate the risk of endpoints, adjusting for demographics (age, sex, race, region), and demographics plus comorbidities.
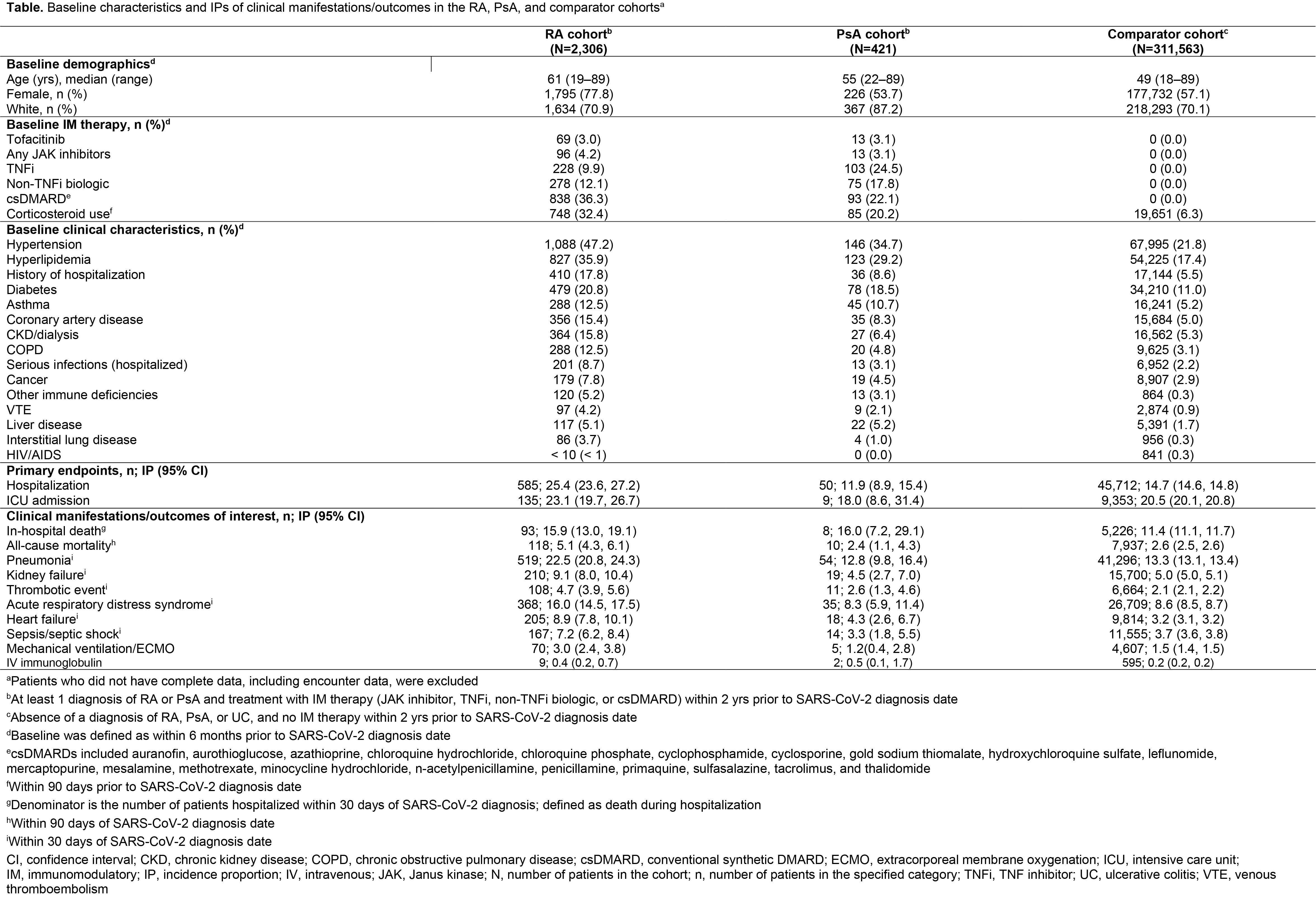
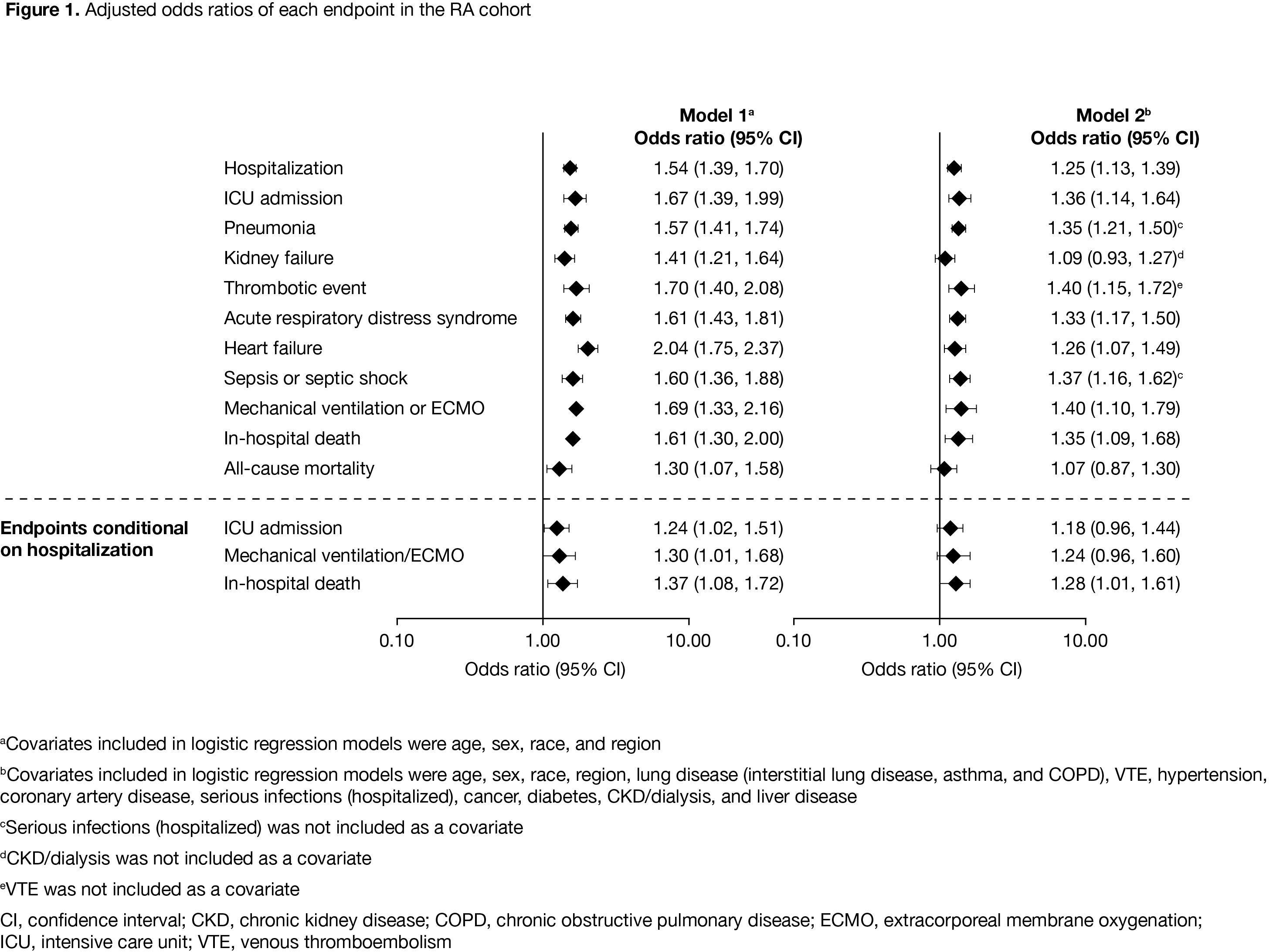
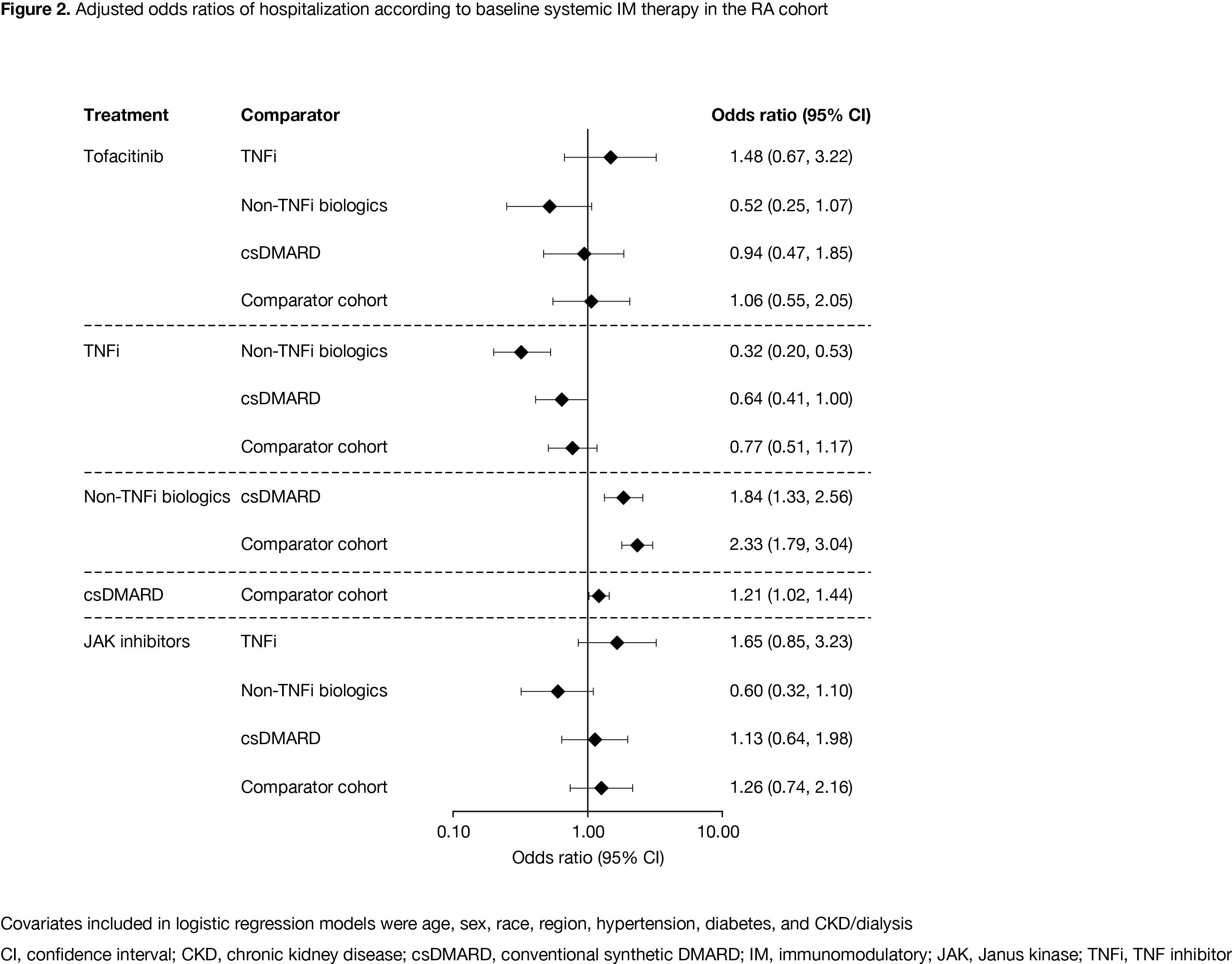
Results: As of December 09, 2020, there were 2,306 patients in the RA cohort, 421 patients in the PsA cohort, and 311,563 patients in the comparator cohort. Compared with the comparator cohort, patients with RA and PsA were older and had a higher prevalence of baseline comorbidities (Table). Crude IP of hospitalization due to COVID-19 was higher in the RA cohort compared with the PsA and comparator cohorts (Table). ICU admission (conditional on hospitalization) was similar in the RA and comparator cohorts. Adjusting for demographics, COVID-19 patients with RA had an increased risk of hospitalization and in‑hospital death, compared with the comparator cohort (Figure 1). The increased risk was also observed when adjusted for demographics plus comorbidities. Risk of hospitalization was lower in COVID-19 patients with RA receiving TNF inhibitors (TNFi) vs non-TNFi biologics and the comparator cohort (Figure 2). In the RA cohort, risk of hospitalization due to COVID-19 was similar between patients receiving tofacitinib and the comparator cohort (Figure 2).
Conclusion: Compared with the comparator cohort, patients with RA were at higher risk of more severe or critical COVID-19; except for non-TNFi biologics, immunosuppressive therapies such as TNFi did not further increase the risk.
Acknowledgments: Study sponsored by Pfizer Inc. Medical writing support was provided by H Findlow, CMC Connect, funded by Pfizer Inc.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Curtis J, Zhou X, Yazdany J, Robinson P, Chen Y, Madsen A, Geier J, Benda B. Evaluation of Patient Characteristics and Clinical Outcomes Among SARS‑CoV‑2‑Diagnosed Patients with and Without RA or PsA Treated with Systemic Therapies: A Retrospective Cohort Study Using US Optum® COVID-19 Electronic Health Record Data [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/evaluation-of-patient-characteristics-and-clinical-outcomes-among-sars%e2%80%91cov%e2%80%912%e2%80%91diagnosed-patients-with-and-without-ra-or-psa-treated-with-systemic-therapies-a-retrospective-coho/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/evaluation-of-patient-characteristics-and-clinical-outcomes-among-sars%e2%80%91cov%e2%80%912%e2%80%91diagnosed-patients-with-and-without-ra-or-psa-treated-with-systemic-therapies-a-retrospective-coho/