Session Information
Date: Tuesday, November 15, 2016
Title: Muscle Biology, Myositis and Myopathies - Poster II: Clinical
Session Type: ACR Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: In order to enable meaningful clinical care and research, accurate algorithms are needed to identify patients with dermatomyositis (DM). In this study, we aimed to evaluate DM case-finding algorithms in a large health administrative database.
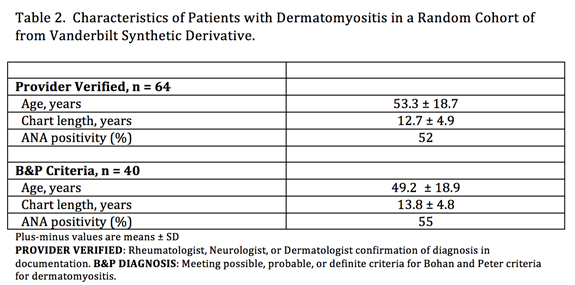
Methods: 100 patients were randomly selected from the Vanderbilt Synthetic Derivative, a de-identified version of the medical record, using the International Classification of Diseases version 9 (ICD9) code for DM: 710.3. We developed 13 algorithms using combinations of frequency of ICD9 code, clinic encounter (defined as two ICD9 codes at least three months apart in one year), provider specialty (Rheumatology, Neurology, or Dermatology), use of immunosuppressant medications (prednisone alone or other immunosuppressants), Current Procedural Terminology code (for electromyogram or skin or muscle biopsy), and creatine kinase level over 600 IU/L. Diagnosis was confirmed by manual review of the de-identified chart using documented diagnosis of DM or DM sine myositis by rheumatologist, dermatologist, or neurologist as the gold standard. Age, ANA status, chart length, and number and type of Bohan and Peter (B&P) criteria were extracted from each chart. Patients with DM sine myositis or incomplete medical records were excluded from analysis of test characteristics with B&P criteria.
Results: Of the 100 patients reviewed, sixty-four were diagnosed as having DM by provider documentation and forty met threshold for diagnosis of as least “possible” DM by B&P criteria. Table 1 shows the algorithm characteristics, including positive predictive value (PPV), cohort sensitivity, and specificity in both subsets of patients. Table 2 shows characteristics of DM patients found with the algorithms. An algorithm of clinic encounter and prednisone dose of at least 20mg daily had the highest PPV and specificity in each group (PPV: 95.3, 96.8; specificity: 94.4, 97). Provider specialty and immunosuppressant medications separately had high sensitivity in each group (sensitivity > 95%).
Conclusion: An algorithm of clinic encounter with prednisone dosage of at least 20mg daily had the highest PPV. An algorithm of 3 or more instances of ICD9 code 710.3had well performing test characteristics as well, with cohort sensitivity and positive predictive value. These algorithms can be used to identify cohorts of patients with rare disease in electronic medical records or administrative database and enable further study of outcomes and quality improvement. 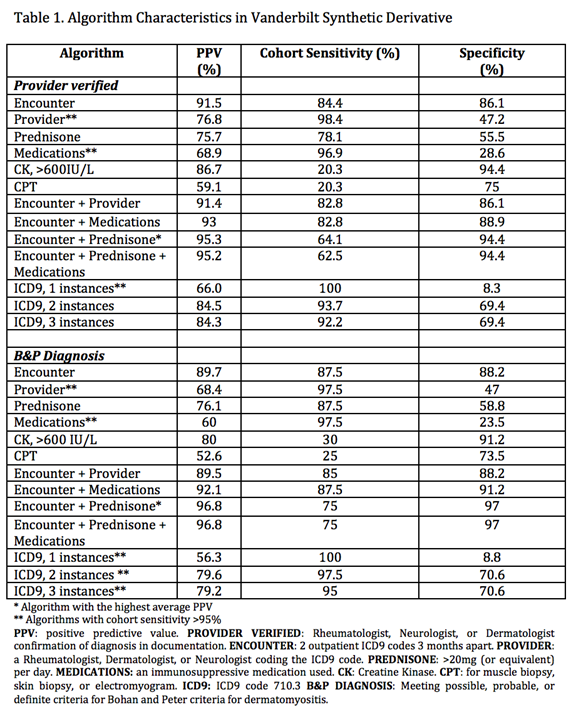
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Byram K, Annapureddy N. Evaluation of Case-Finding Algorithms for Identification of Patients with Dermatomyositis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016; 68 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/evaluation-of-case-finding-algorithms-for-identification-of-patients-with-dermatomyositis/. Accessed .« Back to 2016 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/evaluation-of-case-finding-algorithms-for-identification-of-patients-with-dermatomyositis/