Session Information
Date: Wednesday, October 24, 2018
Title: 6W012 ACR Abstract: Systemic Sclerosis & Rel D/O III:Cohort Study, Biomarkers, & Response(2934–2939)
Session Type: ACR Concurrent Abstract Session
Session Time: 9:00AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: Treatment with the IL-6 receptor inhibitor tocilizumab (TCZ) in early progressive systemic sclerosis (SSc; focuSSced trial; NCT02453256) resulted in numeric improvements in skin sclerosis and clinically meaningful forced vital capacity (FVC) results at week 48 (data on file). The combined response index for SSc (ACR CRISS), a composite outcome measure for trials in SSc,1 is a 2-step process that assigns a probability of improvement for each patient (pt) ranging from 0 [no improvement] to 1 [marked improvement]. Step 1 assesses clinically meaningful decline in cardio-pulmonary-renal involvement with a probability of 0. For remaining pts, the probability of improvement examines change from baseline in 5 variables: modified Rodnan skin score, FVC%, pt and physician global assessments (PtGA, MDGA), and HAQ-DI. CRISS distinguished between TCZ and placebo (PBO) in the faSScinate trial.2 We prospectively assessed the performance of ACR CRISS, an exploratory outcome in focuSSced, at week 48; this is the first time ACR CRISS has been prospectively evaluated in a phase 3 trial in SSc.
Methods: Pts ≥18 years of age with active SSc were randomly assigned 1:1 to TCZ 162 mg or PBO subcutaneously every week for 48 weeks. Step 1 for ACR CRISS was captured prospectively with blinded review of adverse events (AEs) and serious AEs between medical monitors and the lead investigator. Step 2 was calculated as defined.1 The van Elteren test was used to assess whether differences existed between TCZ and PBO groups in the ACR CRISS score in its continuous form. The analysis included all pts who received study treatment, stratified by baseline IL-6 levels (<10; ≥10 pg/mL) with no imputation for missing data.
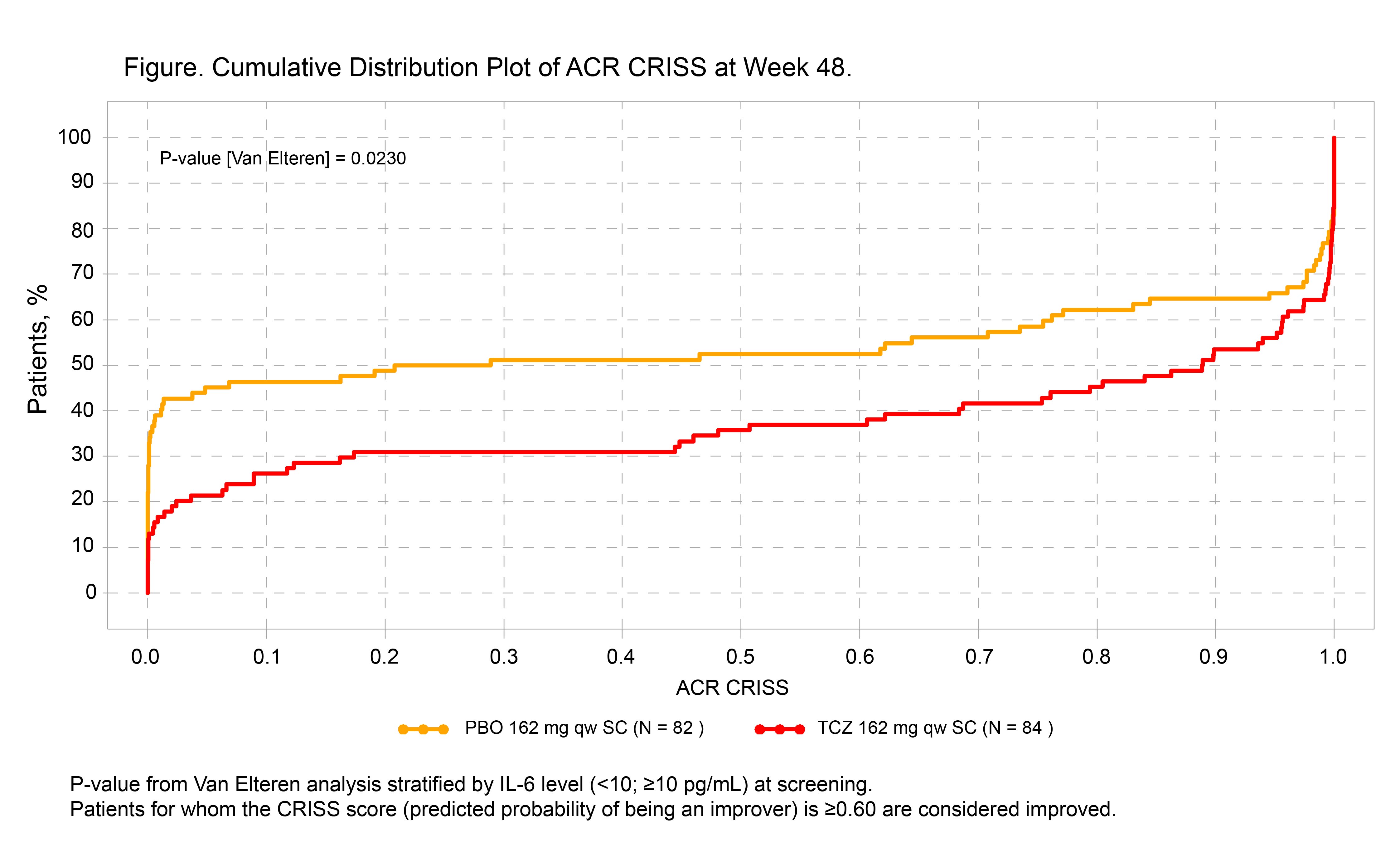
Results: In total, 210 pts (104 TCZ, 106 PBO) received study treatment; 13 pts in the PBO group and 6 in the TCZ group met the predefined definition of worsening cardio-pulmonary-renal involvement (step 1) and were given a score of 0. Using the ACR CRISS as a continuous measure, scores favored TCZ over PBO at week 48: median (IQR), 0.89 (0.09-1.00) vs 0.25 (0.00-0.99) (p = 0.023; Figure). In the binary form of CRISS, 51% of pts in the TCZ group vs 37% in the PBO group achieved the cutoff of ≥0.60 at week 48 (difference, 13.9; 95% CI, 1.0-26.8; p = 0.035).
Conclusion: In analysis of patient-level data from the focuSSced trial, more pts had cardio-pulmonary-renal involvement in the PBO group than in the TCZ group (captured by step 1). Additionally, step 2 CRISS score distinguished TCZ from PBO. The focuSSced study validates the ACR CRISS end point for the first time in an independent prospective clinical trial and highlights the importance of step 1 as an indicator of reduced organ progression during 48 weeks of treatment. References: 1. Khanna D et al. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016; 299-311. 2. Khanna D et al. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017;69(suppl 10). Abstract 2981. Acknowledgment: focuSSced clinical trial investigators.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Khanna D, Lin CJF, Spotswood H, Siegel J, Jahreis A, Denton CP, Furst DE. Evaluation of American College of Rheumatology Provisional Composite Response Index in Systemic Sclerosis (ACR CRISS) in a Phase 3 Randomized Controlled Trial [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018; 70 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/evaluation-of-american-college-of-rheumatology-provisional-composite-response-index-in-systemic-sclerosis-acr-criss-in-a-phase-3-randomized-controlled-trial/. Accessed .« Back to 2018 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/evaluation-of-american-college-of-rheumatology-provisional-composite-response-index-in-systemic-sclerosis-acr-criss-in-a-phase-3-randomized-controlled-trial/