Session Information
Date: Monday, November 8, 2021
Title: Health Services Research Poster II: Care Models and Innovation (1061–1082)
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: The COVID-19 pandemic impacted everyday practice pattern of health care in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients. The objective was to evaluate the implementation of a tele-consultation program in adult population with RA
Methods: This was an analytical observational study-prospective cohort (Clinical trials NCT04768413) that evaluated the effectiveness of a teleconsultation model compared with a face-to-face consultation model in RA adult patients. Patients were followed 12 weeks (Jul-Oct 2020) at a RA center of excellence in Colombia. Simple random sampling was done. Two groups were included: Group A, patients who assisted to tele-consultation care and Group B, those who wish to continue with the usual face-to-face consultation. Data regarding activity of disease (Week 0,6,12) [Patient Activity Scale (PAS) in both groups and DAS28 in group B], and Quality of life [EQ-5D-3L], disability [Health Assessment Questionnaire (HAQ)], therapeutic adherence [Morisky-Green Adherence Scale (MGLS)] and self-care capacity [Appraisal of Self-care Agency Scale -Revised (ASA-R)] was evaluated (weeks 0-12). Outcomes regarding COVID-19 were evaluated. Bivariate analysis was done (StataV-13; P-value< 0.05)
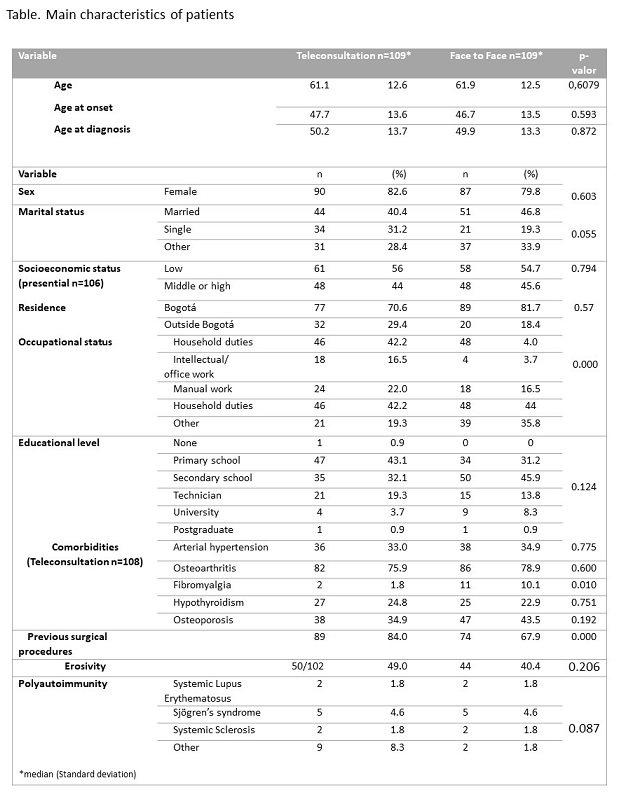
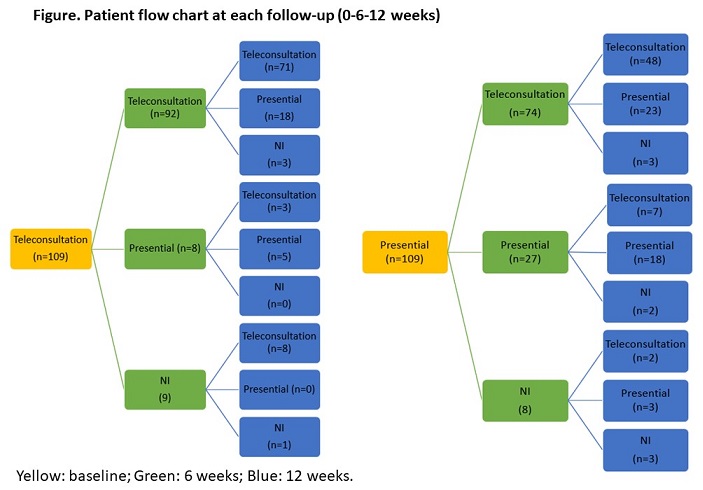
Results: 218 adults were included: (109 in Group A and 109 in Group B). The groups did not differ in general characteristics (See Figure-Table). In Group A: (n=71), no statistically significant differences were observed in the median scores of VAS global, VAS pain, PAS, HAQ, EQ-5D and ASA-R, while increase in adherence was demonstrated (MGLS, without statistical significance), during follow-up. In Group B: (n=18), a significant decrease in adherence (MGLS, p= 0,019) and increase in self-care (ASA-R, p= 0,0077) were found, no other differences were found (including DAS-28). A third group was conformed by patients (n=129) that transited between the two models during follow-up (See figure). An increase in in self-care (ASA-R) was demonstrated in the group presential >remote >presential (p=0,0001), the same result was documented in the group presential >remote >presential, with a decrease in adherence (p=0,033). 7 patients developed COVID-19 (one patient hospitalized/group A and one patient died/mixed model)
Conclusion: The teleconsultation model favors that patients remain without deteriorating their commitment to RA, without major differences compared to the face-to-face model. It is important to know these results due to the impact they have given the changes that will follow in the care of RA patients due the current pandemic. Studies with a longer follow-up period are required to corroborate the results
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Santos-Moreno P, Casanova R, Rodríguez-Vargas G, Villareal L, Rubio J, Chávez-Chávez J, Rivera-Triana D, Castiblanco-Montañez R, Hernández-Zambrano S, Rojas-Villarraga A. Evaluation of a Non-Face to Face Multidisciplinary Health Care Model in a Population with Rheumatoid ArthritisVulnerable to Covid-19 in a Health Emergency Situation [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/evaluation-of-a-non-face-to-face-multidisciplinary-health-care-model-in-a-population-with-rheumatoid-arthritisvulnerable-to-covid-19-in-a-health-emergency-situation/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/evaluation-of-a-non-face-to-face-multidisciplinary-health-care-model-in-a-population-with-rheumatoid-arthritisvulnerable-to-covid-19-in-a-health-emergency-situation/