Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 17, 2024
Title: SpA Including PsA – Diagnosis, Manifestations, & Outcomes Poster II
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
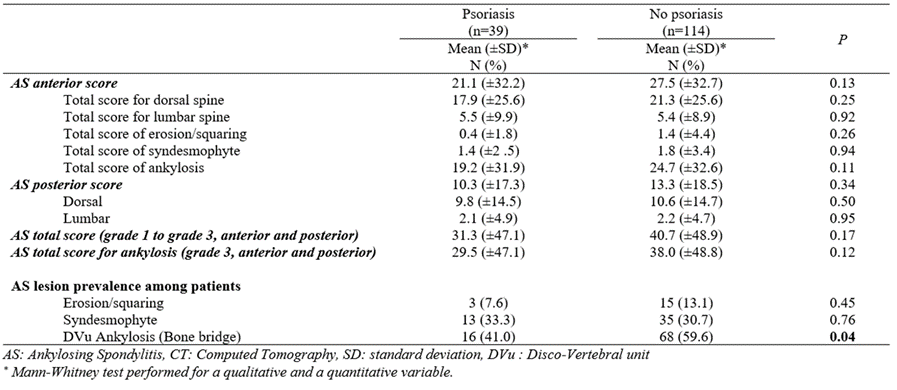
Background/Purpose: To compare, on Thoraco-Abdomino-Pelvic (TAP) computed tomography (CT), structural spinal involvement of the dorsal and lumbar segments in ankylosing spondylitis with (AS-Pso) and without psoriasis (AS).
Methods: Retrospective study including AS patients followed between 2008 and 2021, responding to modified New York criteria for radiographic sacroiliitis. Patients performed a pelvic x-ray and a CT-TAP within a delay of 12 months. From C7 to S1, structural evaluation was performed opportunistically on TAP-CT from reconstructed sagittal slices. The 18 disco-vertebral units (DVu) were evaluated and each vertebra anterior corner was graded as grade 1 for erosion/squaring, grade 2 for syndesmophytes and grade 3 for bone bridge. The anterior score ranged from 0 to 108 (sum of the grades). The posterior segment evaluated only facet ankylosis (as present = grade 3; or absent = grade 0) and the posterior score ranged from 0 to 108 (sum of the grades). The total CT-score (anterior and posterior) ranged from 0 to 216 with excellent intra readers reliabilities (ICCs >0.90).
Results: Finally, 153 patients had a sacroilitis on X-ray (83.6% bilateral). Their median age was 55 years [49;62] and they were mostly male gender (70.4%), smokers (66.6%), with HLA-B27+ (77.4%) and CRP > 5 mg/l. The median disease duration was 13 years [6;26]. Pso was present in 39 patients with a higher proportion of women (43.6% vs. 24.6%: p=0.024) and less tobacco users (48.8% vs. 73.8% p=0.011). In 153 patients, the most prevalent anterior lesion was bone bridge (54.9%), followed by syndesmophytes (31.3%), then erosions/squaring (11.7%). Spinal ankylosis predominated at the dorsal segment and syndesmophytes at the lumbar spine (p< 0.0001). All CT-scores were numerically higher in AS patients compared to AS-Pso patients but did not achieve a statistically significant difference (Table). No difference was observed for posterior ankylosis between both groups (p=0.34). For the 153 patients, the total-CT score showed association with age (value=0.216; p=0.009), male gender (value=0.233; p=0.002) disease duration (value=0.308; p=0.0001), and CRP >5 mg/l (value=0.20; p=0.007) in multivariate analysis. For the 39 AS-Pso patients the for total-CT score showed a trend with disease duration and CRP > 5 mg/l (value = 0.29; p=0.86) and (value = 0.29 p=0.08) respectively in multivariate analysis.
Conclusion: On TAP-CT, presence of psoriasis in AS patients did not modify significantly structural damages on lumbar and dorsal segments. More severe lesions were depicted at the dorsal segment, region difficult to be assessed on radiograph. As for radiograph, variables associated with structural lesions on X-ray were also associated.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
MENNINI A, Loeuille D, Chary-Valckenaere I, Morizot C, LAFFAIRE M. Evaluating Spine Structural Damage on a Single CT in Patients with Ankylosing Spondylitis, and According to the Presence of Skin Psoriasis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/evaluating-spine-structural-damage-on-a-single-ct-in-patients-with-ankylosing-spondylitis-and-according-to-the-presence-of-skin-psoriasis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/evaluating-spine-structural-damage-on-a-single-ct-in-patients-with-ankylosing-spondylitis-and-according-to-the-presence-of-skin-psoriasis/