Session Information
Date: Tuesday, November 9, 2021
Title: RA – Treatments Poster III: RA Treatments & Their Safety (1674–1710)
Session Type: Poster Session D
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: Optimal dosing of methotrexate (MTX) for individual rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients to achieve adequate disease control remains challenging. Assessment of erythrocyte MTX-polyglutamates (PGs) levels has been used as a tool to monitor clinical response of RA patients in the first 3-12 months of treatment and MTX-PG2-4 as well as total MTX-PGs were associated with lower DAS28 over 9 months. However, data per route of administration and from earlier time points, including MTX-PG6 levels are lacking.
We investigated the pharmacokinetics and -dynamics of erythrocyte MTX-PG accumulation in RA patients receiving oral or subcutaneous MTX in the early phase (1, 2, 3 months) and later stage (6 months) of MTX treatment.
Methods: In a clinical prospective cohort study (MeMo study: NTR7149), newly diagnosed RA patients were treated with oral (n=24) or subcutaneous (n=22) MTX mostly according to the COBRA-light schedule (start 10 mg MTX, increased to 25 mg MTX in 8 weeks, with prednisolone). At 1, 2, 3 and 6 months after start of therapy, blood was collected and individual MTX-PGs (MTX-PG1 – MTX-PG6) were analyzed in erythrocytes using a validated UHPLC-MS/MS method with labeled internal standards. (De Rotte 2015) Dosing, concomitant treatments and DAS28-ESR assessments were in conformity with clinical practice. Adverse events were recorded. We used a linear mixed model analysis to assess the association between MTX-PG levels and DAS28-ESR (per group and total), with corrections for age, baseline DAS28, eGFR, MTX dose (1 month before sampling), smoking and BMI.
Results: 46 consecutive patients were included in this study of which 76% female, mean age was 57.8 years, BMI was 25.8, 20% were smokers, mean baseline DAS28-ESR was 3.5. MTX dose at baseline was 10.5 mg (SD: 1.5) for both groups, 15.4 (4.4) and 16.8 (1.8) at 1 month and 22.8 (3.9), 22.4 (5.2) at 2 months, 20.1 (6.3) and 20.8 (5.6) at 3 months and 19.0 (6.5) and 18.6 (8.6) at 5 months for oral and subcutaneous use, respectively. On average, patients starting subcutaneous MTX had significantly higher levels of long chain MTX-PGs (MTX-PG3-6) in erythrocytes when compared to patients in the oral MTX group at 1 and 2 months (Figure 1B and 1C, Table 1). Similarly, erythrocyte MTX-PG1-6 and MTX-PG3 concentrations were significantly higher in subcutaneous MTX-users at month 1 compared to the oral group (median 68.6 nmol/L (IQR:40.5) vs 51.9 (55.6) and 17.4 (11.1) vs 11.2 (15.6), respectively (Figure 1B and 1C, Table 1). This difference remained present at month 2. Erythrocyte MTX-PG accumulation reached a plateau after 3 months.
Apart from small positive and negative correlations, no (clinically) significant relation between MTX-PG concentrations and DAS28 was observed during the first 6 months of treatment; DAS28 decreased with 1.2 in the oral group and 1.6 in the subcutaneous group.
Side effects, mostly headache and dizziness were similar in both groups and not correlated with MTX-PG levels.
Conclusion: This study demonstrated significantly higher accumulation of long-chain and total MTX-PGs following subcutaneous versus oral MTX administration in the first 3 months. Early phase erythrocyte MTX-PG analyses may hold promise for optimization of individual patient MTX dose scheduling.
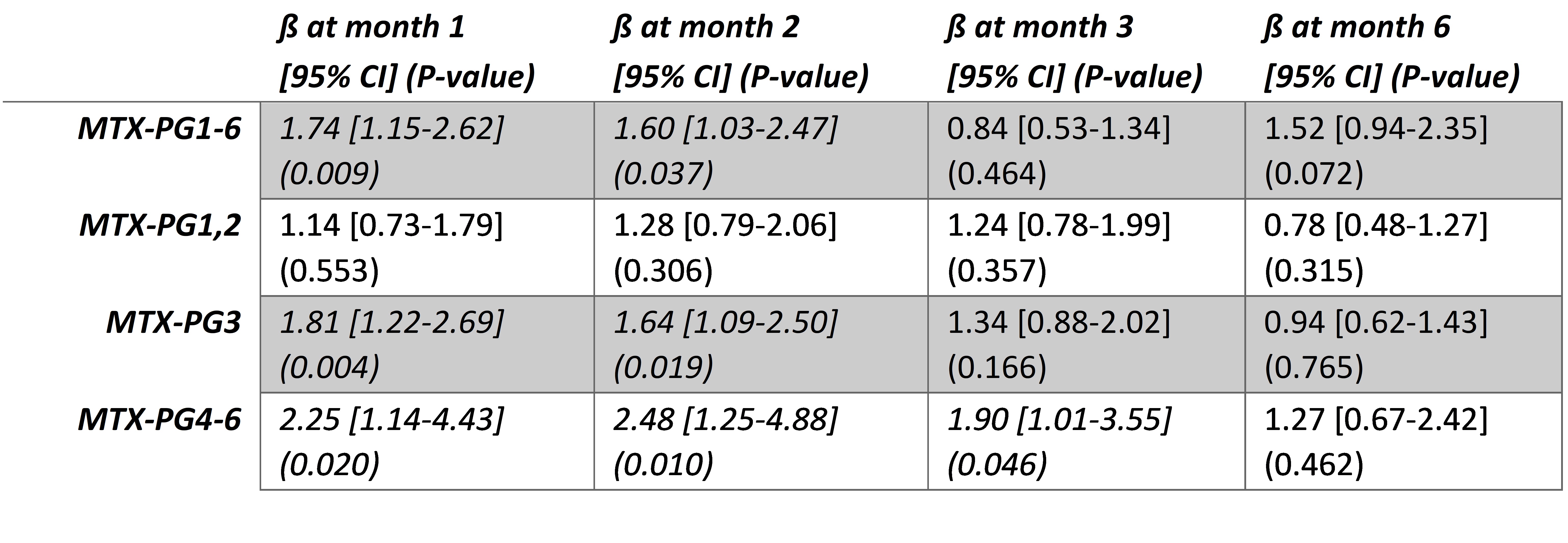 Table 1. Linear regression of MTX-PG levels and administration route, corrected for age, baseline DAS28, smoking, BMI, eGFR and MTX dose.
Table 1. Linear regression of MTX-PG levels and administration route, corrected for age, baseline DAS28, smoking, BMI, eGFR and MTX dose.
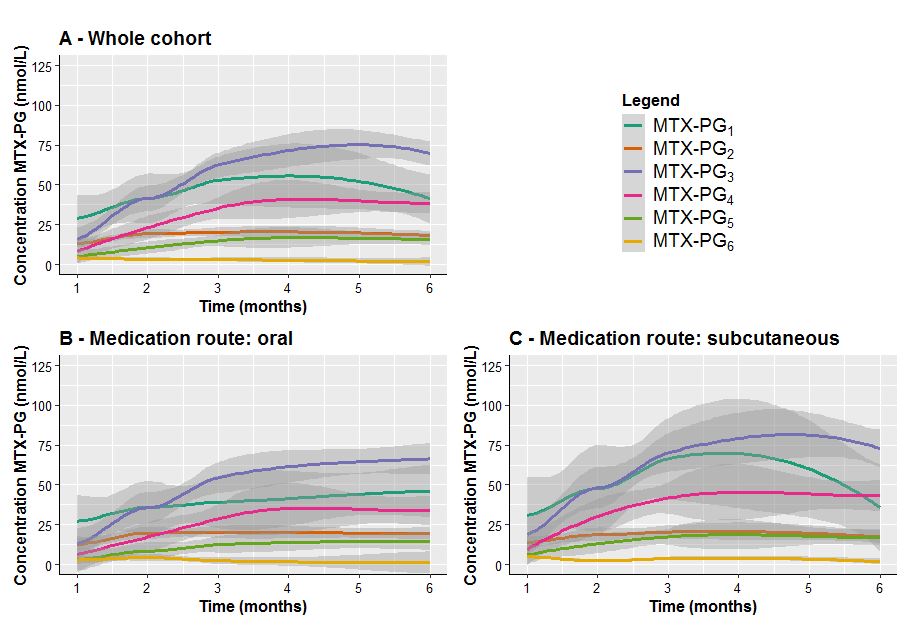 Figure 1. Erythrocyte individual MTX-PG accumulation in RA patients (A) during the first 6 months of oral (B) or subcutaneous (C) MTX administration. At 6 months, 18 patients using oral and 18 patients using subcutaneous MTX were still continuing MTX treatment. Means (colored lines) and standard errors (shaded areas) are depicted (Loess regression).
Figure 1. Erythrocyte individual MTX-PG accumulation in RA patients (A) during the first 6 months of oral (B) or subcutaneous (C) MTX administration. At 6 months, 18 patients using oral and 18 patients using subcutaneous MTX were still continuing MTX treatment. Means (colored lines) and standard errors (shaded areas) are depicted (Loess regression).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Hebing R, Mahmoud S, Lin M, Muller I, Heil S, Lems W, Nurmohamed M, de Jonge R, Jansen G. Erythrocyte Methotrexate Polyglutamates Are Substantially Higher After Subcutaneous Methotrexate Treatment in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients in the First Months of Treatment [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/erythrocyte-methotrexate-polyglutamates-are-substantially-higher-after-subcutaneous-methotrexate-treatment-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-patients-in-the-first-months-of-treatment/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/erythrocyte-methotrexate-polyglutamates-are-substantially-higher-after-subcutaneous-methotrexate-treatment-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-patients-in-the-first-months-of-treatment/
