Session Information
Date: Monday, November 9, 2015
Title: Rheumatoid Arthritis - Small Molecules, Biologics and Gene Therapy Poster II
Session Type: ACR Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: It is well documented that epithelium
turnover is markedly increased in the affected joints of rheumatoid arthritis
(RA). This causes disruption of the well organized supramolecular
architectures of the basal lamina composed of a network of collagen IV and
other components such as laminins, nidogens or perlecan. The aim of
this study was to 1) investigate the circulating levels of MMP-degraded
collagen type IV fragments in RA and 2) if TCZ may reduce the epithelial
turnover of the RA pathogenesis.
Methods: The LITHE biomarker study (n =682) was a phase III double-blind, placebo
(PBO)-controlled, parallel group study of 4- and 8-mg/kg TCZ in combination with methotrexate
(MTX). The biomarker C4M, a competitive ELISA assay evaluating fragments of
type IV collagen, was tested in serum from baseline and week 4, 16, 24, and 52.
A dose-dependent effect was investigated and the differences between groups
were evaluated by Mann-Whitney test. Early response was
evaluated at week 16 as 7-20% improvement in swollen/tender joint counts; and ACR50 was evaluated
at week 52.
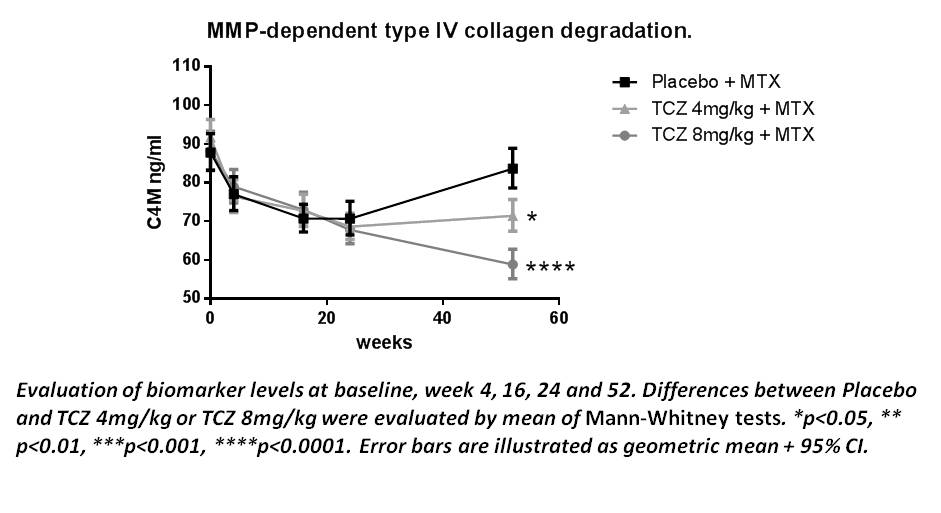
Results: All of the 3 patient groups experienced a
decrease of C4M from baseline to week 16 of roughly 20%. At this point there
were no significant differences between the C4M levels of the placebo group
compared to treatment groups. This level seemed to be stabile from week 16-24
for all of the 3 groups. Interestingly, from week 24-52 C4M in the placebo
group significantly increased (p<0.0001) from a geometric mean of 70.7ng/ml
to 83.6ng/ml. The C4M level of the patient group receiving TCZ 4mg/kg was
steady with a geometric mean of 68.6 at week 24 and 71.4 at week 52. Patients
in the TCZ 8mg/kg had a significant decrease (p=0.0017) from a geometric mean
of 67.8 to 58.8 from week 24-52.There was a significant difference in C4M level
between placebo and treatment groups at week 52 (p<0.05).
Conclusion: The differences of C4M between the 3 treatment groups
at week 52, indicate a dose-dependent reduction of epithelial
degradation as an effect of treatment over time. Furthermore, the decrease of
C4M from baseline to week 16 in all of the 3 treatment groups, suggests that
MTX has an additional effect on top of that of TCZ.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Gudman NS, Byrjalsen I, Musa K, Kehlet SN, Karsdal MA, Bay-Jensen AC. Epithelial Changes in Response to Tocilizumab Combined with Methotrexate in Rheumatoid Arthritis: Evaluated on Circulating Fragments of Type IV Collagen [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015; 67 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/epithelial-changes-in-response-to-tocilizumab-combined-with-methotrexate-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-evaluated-on-circulating-fragments-of-type-iv-collagen/. Accessed .« Back to 2015 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/epithelial-changes-in-response-to-tocilizumab-combined-with-methotrexate-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-evaluated-on-circulating-fragments-of-type-iv-collagen/