Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session (Monday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Uveitis is one of the most frequent extra articular manifestation of spondyloarthritis (SpA). Biological therapy, especially monoclonal TNF inhibitors, are useful to prevent and to treat refractory non-infectious uveitis. However, other biologics had been related to paradoxical uveitis. Our aim was to assess a) the epidemiological and clinical features of uveitis associated to SpA and b) its relationship with biological treatment used in SpA.
Methods: We set up an observational study of patients who developed uveitis form a cohort of 255 consecutive unselected patients with axial SpA (axSpA) classified according to the ASAS criteria. They were divided into: a) ankylosing spondylitis (AS) according to New York modified criteria (n= 193) b) non-radiographic axSpA (nr-axSpA) (n= 62). All these patients were followed in a single reference University Hospital.
Results: We studied 255 patients with axSpA axSpA (151 men / 104 women); mean age 37.8 ± 10.6 years. In 36 (14.2%) patients at least one episode of uveitis was observed after a follow-up 12.4 ± 4.5 years. The underlying axSpA diseases were AS (n=31) and nr-axSpA (n= 5). The mean age at onset of uveitis was 45.7±14.2 years. Uveitis was diagnosed in 5 patients before SpA diagnosis. In the remaining patients (n=31) it was detected after a median of 6 [2-15] years of follow-up after SpA diagnosis. Pattern of uveitis was anterior and acute in all cases, and unilateral in 83%. None of them presented intermediate or posterior uveitis. Median of anterior chamber cells was 1 [1-2] cells. Comparison of baseline characteristics and clinical features between patients who developed uveitis and those who did not is shown in Table 1. Almost all patients who developed uveitis were HLAB27 positive. In these patients a lower frequency of enthesitis and inflammatory bowel disease was observed.
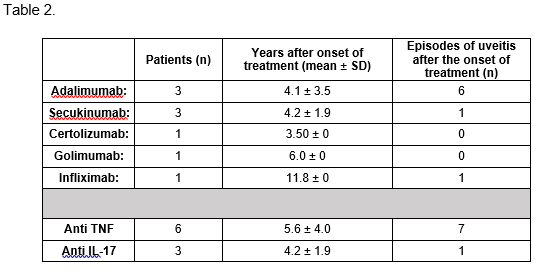
Cumulative incidence of uveitis episodes related to each biological agent is shown in Table 2. Patients treated with secukinumab developed 2.72 episodes of uveitis/100 patients/year, meanwhile those who received monoclonal anti TNF presented 2.53 episodes/100 patients / year.
Conclusion: The most frequent clinical pattern of uveitis in patients with SpA was acute unilateral anterior uveitis which appeared in most patients after 6 years of follow-up. Almost all of them were HLA B27 positive. No differences were found in cumulative incidence between secukinumab and monoclonal anti-TNF.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Gonzalez-Mazon I, Sanchez-Bilbao L, Rueda-Gotor J, MARTINEZ-LOPEZ D, PRIETO- PENA D, Calderón-Goercke M, Martín-Varillas J, Atienza-Mateo B, Gonzalez-Gay M, Blanco R. Epidemology, Clinical Features and Relationship to Biological Therapy of Uveitis in Axial Spondyloarthritis: Single Center University Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/epidemology-clinical-features-and-relationship-to-biological-therapy-of-uveitis-in-axial-spondyloarthritis-single-center-university-study/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/epidemology-clinical-features-and-relationship-to-biological-therapy-of-uveitis-in-axial-spondyloarthritis-single-center-university-study/