Session Information
Date: Tuesday, November 12, 2019
Title: Epidemiology & Public Health Poster III: OA, Gout, & Other Diseases
Session Type: Poster Session (Tuesday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
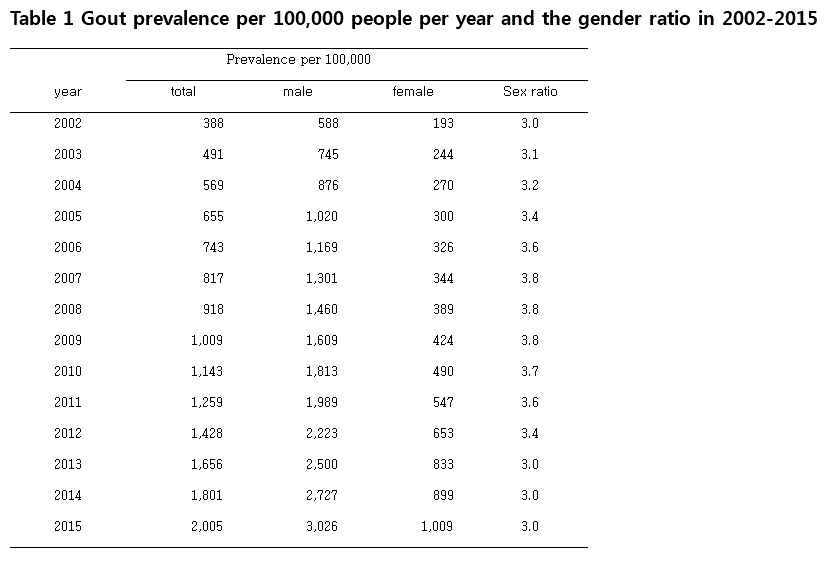
Background/Purpose: Gout is the most common inflammatory arthritis that results from chronic elevation of uric acid levels above the saturation point for monosodium urate crystal formation. However, data on gout incidence, prevalence and management, are sparse, especially in Korean populations. We reevaluated the recent prevalence and incidence of gout in Korean people after our previous study in 2011 (1).
Methods: The National Health Insurance Corporation (NHIC) Database was used to identify patients with gout. We selected the gout patients who were coded as having gout (KCD M10.0) from main diagnosis to 4th additional diagnosis. And we estimated the prevalence (from 2002 to 2015) and the incidence (from 2006 to 2015) for each calendar year.
Results: Prevalence of gout was 0.39% in 2002 and 2.00% in 2015. There was a 5.17 fold increased during over 13 years. Prevalence have increased at all ages, especially at the age of 80 and over. Also, incidence per 100,000 was 361 in 2006 and 797 in 2015, there was 2.21 fold increased during over 10 years. Sex ratio (male:female) was 3.0~3.8:1. When monthly incidence was examined, except for December, it increased as the day warmed and peaked in July and August. In the southern provinces, especially Busan, prevalence and incidence were high. Of those diagnosed with gout in 2012, a total of 30% of those who had been prescribed uric acid lowering agent (allopurinol or febuxostat or benzbromarone) within three years.
Conclusion: In Korea, prevalence and incidence of gout are rapidly increasing. Incidence was higher for males, for older age, for warmer days, and for southern regions. Management of gout in Korea is poor, with only three in ten affected people who have ever been treated with uric acid lowering therapy.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Park J, Song J, Kang M, Lee C. Epidemiology of Gout in South Korea with the National Health Insurance Corporation Database [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/epidemiology-of-gout-in-south-korea-with-the-national-health-insurance-corporation-database/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/epidemiology-of-gout-in-south-korea-with-the-national-health-insurance-corporation-database/