Session Information
Session Type: ACR Concurrent Abstract Session
Session Time: 4:30PM-6:00PM
Background/Purpose: Joint destruction in rheumatoid arthritis
(RA) progresses via the hyperproliferation of the
synovium and secretion of MMP-3/RANKL from fibroblast-like synoviocytes
(FLS). In tumors, we previously reported that the expression of mitochondria-related
genes is low and increased numbers of mitochondria enhance cell
apoptosis. However, the relationship between mitochondrial biogenesis and joint destruction in RA remains unclear. To
elucidate this relationship, we measured the expression levels of mitochondria-related genes and mitochondrial DNA in
RA-FLS and osteoarthritic (OA)-FLS. We then tested the effects of AICAR
(5-Aminoimidazole-4-carboxamide ribonucleotide), an enhancer of mitochondrial biogenesis, on MMP-3/RANKL secretion in RA-FLS and on joint
destruction in collagen-induced arthritis (CIA) mice.
Methods: Quantitative
PCR was used to assess the expression levels of mitochondria-related mRNA (PGC-1a,
NRF-1, and TFAM) and number of mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA)
in RA- and OA-FLS. The effect of AICAR (2 mM) on
mitochondrial biogenesis in RA-FLS was assessed in the same way. Cell
viability was assessed using WST assay, and MMP-3/RANKL secretion was measured using an immunoassay (immunoblot
and ELISA) with/without IL-1b or TNFa stimulation. For evaluating the effect of
AICAR (500 mg/kg) on joint destruction in CIA mice, micro-CT was used.
Results: The expression of NRF-1 and TFAM and
the levels of mtDNA were lower in RA-FLS than in OA-FLS (Fig. 1). In RA-FLS, the levels of mtDNA
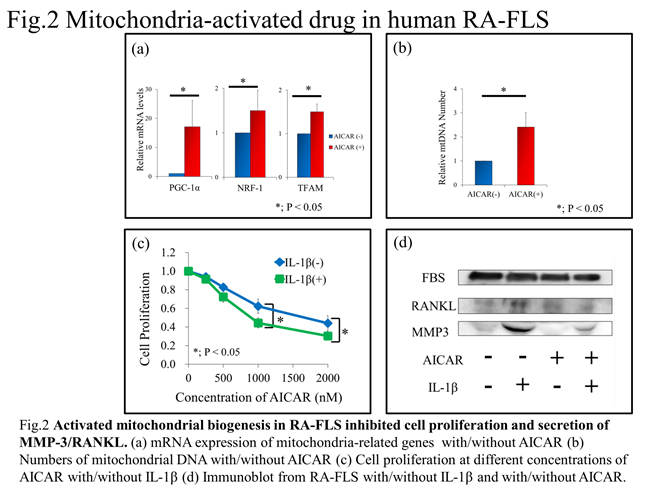
and mRNA expression of mitochondria-related genes were enhanced by AICAR
(Fig. 2a, 2b). AICAR inhibited cell viability and IL-1b– or TNFa-induced
MMP-3/RANKL secretion in
inflammation-induced RA-FLS (Fig. 2c, 2d). Moreover,
AICAR reduced the arthritis score and joint destruction in CIA mice (Fig. 3).
Conclusion: Downregulation of mitochondrial biogenesis is
related to the disease state of RA, and enhancement of mitochondrial biogenesis resulted in the suppression
of disease activities of RA, such as reducing RA-FLS viability, secretion
of MMP-3/RANKL from RA-FLS, and joint destruction in CIA mice. A novel
therapeutic approach by changing mitochondrial biogenesis is
proposed.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Ueha T, Sakai Y, Morishita M, Maeda T, Fukuda K, Inoue M, Harada R, Minoda M, Miura Y, Hashiramoto A, Kurosaka M. Enhancement of Mitochondrial Biogenesis Inhibits Cell Proliferation and MMP-3/RANKL Secretion in Rheumatoid Arthritis Fibroblast-like Synovial Cells and Joint Destruction in Arthritis Model Mice [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015; 67 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/enhancement-of-mitochondrial-biogenesis-inhibits-cell-proliferation-and-mmp-3rankl-secretion-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-fibroblast-like-synovial-cells-and-joint-destruction-in-arthritis-model-mice/. Accessed .« Back to 2015 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/enhancement-of-mitochondrial-biogenesis-inhibits-cell-proliferation-and-mmp-3rankl-secretion-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-fibroblast-like-synovial-cells-and-joint-destruction-in-arthritis-model-mice/