Session Information
Date: Saturday, November 16, 2024
Title: Muscle Biology, Myositis & Myopathies – Basic & Clinical Science Poster I
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Myocarditis in idiopathic inflammatory myopathies (IIM) is poorly understood despite its association with poor outcomes such as heart failure and sudden cardiac death. It is important to detect myocarditis early to potentially escalate immunosuppressive treatment. The purpose of this study was to determine whether multiparametric cardiac MRI can better quantify and detect myocarditis including subclinical disease in IIM.
Methods: We performed a prospective pilot study of patients with IIM (excluding inclusion body myositis) within first year of disease onset to rigorously screen for myocarditis with cardiac biomarkers including high-sensitivity troponin-I and pro-BNP, EKG, echocardiogram, and multiparametric cardiac MRI. Clinically suspected myocarditis was defined by the 2013 European Society of Cardiology (ESC) for clinically suspected myocarditis and confirmed by the 2018 Lake Louise Criteria for myocarditis on cardiac MRI. Advanced multiparametric parameters on cardiac MRI such as T1 and T2 maps, and extracellular volume fraction (ECV) and quantification of late gadolinium enhancement were obtained. Differences in clinical characteristics and multiparametric values were compared between patients with and without a myocarditis using student’s t-tests and Fischer’s exact test as appropriate
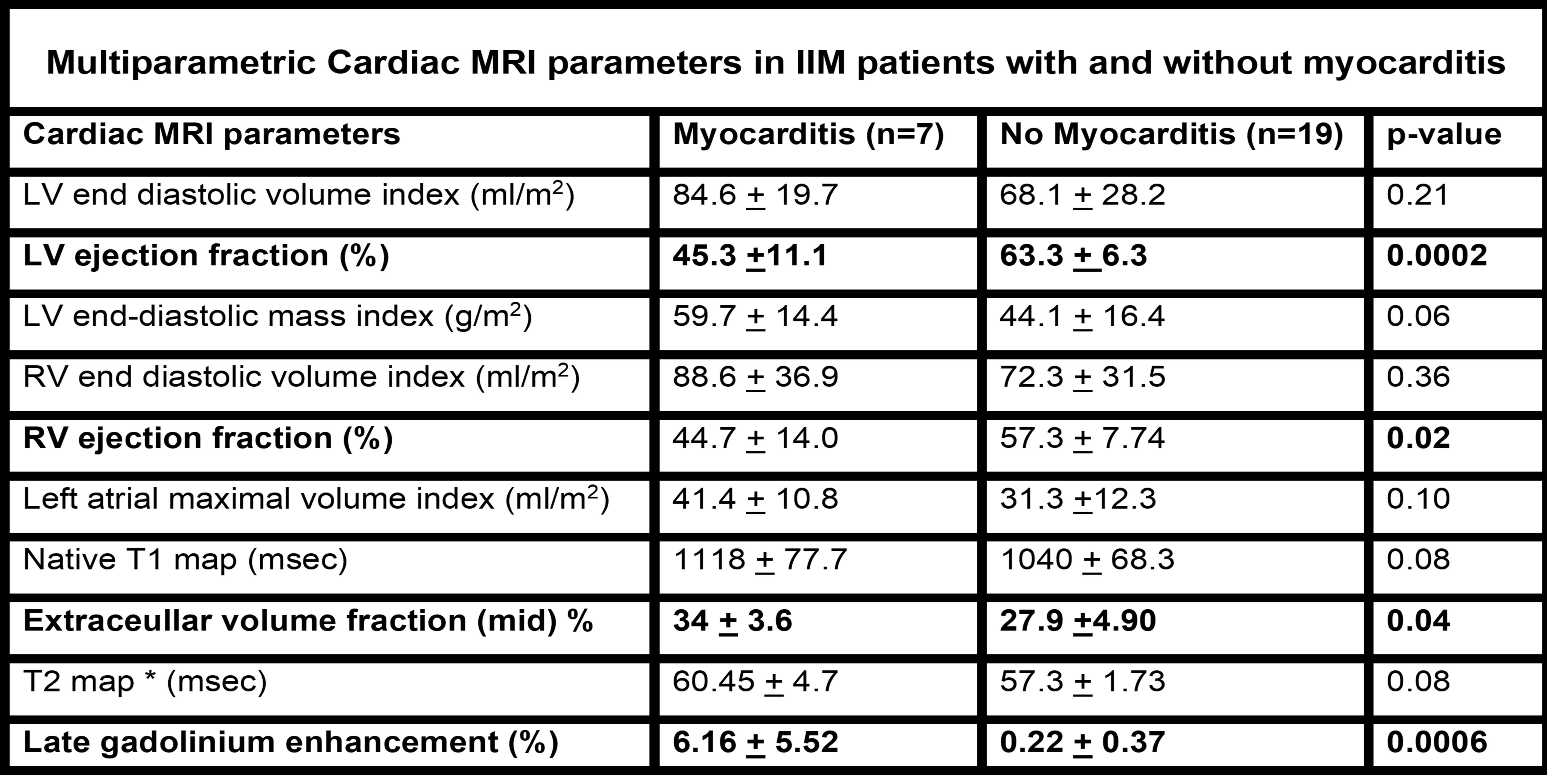
Results: 26 patients with myositis were screened for myocarditis and 7 of 26 (26%) met the ESC criteria for clinically suspected myocarditis and the 2018 Lake Louise Criteria for myocarditis on cardiac MRI. The most common IIM subgroup that that had myocarditis was the overlap IIM with scleroderma (5 of 7, 71%) and anti-synthetase syndrome (ASyS) (2 of 7, 29%). When compared to those without myocarditis, anti-Ku was more prevalent in those with myocarditis (p=0.003), while cardiac events such as heart failure (EF< 50%) or arrhythmia were more prevalent in those with myocarditis (42.8% vs. 6.2%, p=0.02). Multiparametric cardiac MRI demonstrated that IIM patients with myocarditis had elevated T1, T2, and ECV maps when compared to those without myocarditis, and late gadolinium enhancement (LGE) was higher in those with myocarditis compared to those without myocarditis (6.16 + 5.52 % vs. 0.22 + 0.37%, p=0.0006) (Table 1). Interestingly, the greatest degree of LGE ( >5%) was found in those who were anti-Ku positive. Among IIM patients without myocarditis, T1 and T2 map values were elevated compared to historical healthy controls indicating subclinical myocardial edema(T1map values: 1040 + 68.3 vs 963.9 + 32.5 ,p=0.0012 and T2 map values: 57.3 + 1.73 vs 52.8 + 4.4, p=0.0004).
Conclusion: In this preliminary study of myocarditis in IIM with disease onset within 1 year, myocarditis was associated with a higher frequency of poor outcomes. Advanced multiparametric CMR quantified the extent and burden of myocarditis by assessing myocardial edema and fibrosis using T1 and T2 maps, ECV, and quantification of LGE. Overall, T1 and T2 maps were higher even in those without myocarditis highlighting that low grade myocardial edema may be present even in those without symptoms or elevated cardiac biomarkers
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Paik J, Ayoumi S, Zandieh G, Calhoun C, Connolly C, Christopher-Stine L, Mecoli C, Albayda M, Tiniakou E, Gilotra N, Zimmerman S, Venkatesh B. Enhanced Detection of Myocarditis in Idiopathic Inflammatory Myopathies Utilizing Multiparametric Cardiac Magnetic Resonance Imaging [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/enhanced-detection-of-myocarditis-in-idiopathic-inflammatory-myopathies-utilizing-multiparametric-cardiac-magnetic-resonance-imaging/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/enhanced-detection-of-myocarditis-in-idiopathic-inflammatory-myopathies-utilizing-multiparametric-cardiac-magnetic-resonance-imaging/