Session Information
Date: Monday, November 13, 2023
Title: Abstracts: Systemic Sclerosis & Related Disorders – Basic Science
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 4:00PM-5:30PM
Background/Purpose: Type I interferon (IFN-1) signature is a hallmark of patients with systemic sclerosis (SSc). However, its significance in clinical stratification and contribution to deterioration still need to be better understood.
Methods: For hypothesis generation, we performed single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNAseq) on skin biopsies (SSc=4, control =2) using the BD Rhapsody platform. Two publicly available datasets of skin scRNAseq were used for validation (GSE138669: dcSSc=12, control=10; GSE195452: dcSSc=52, lcSSc=41, control =54). IFN-1 signature was mapped, functionally investigated in a bleomycin plus IFNα2-adeno-associated virus (IFNA2-AAV) induced model, and verified in an SSc cohort (n=61).
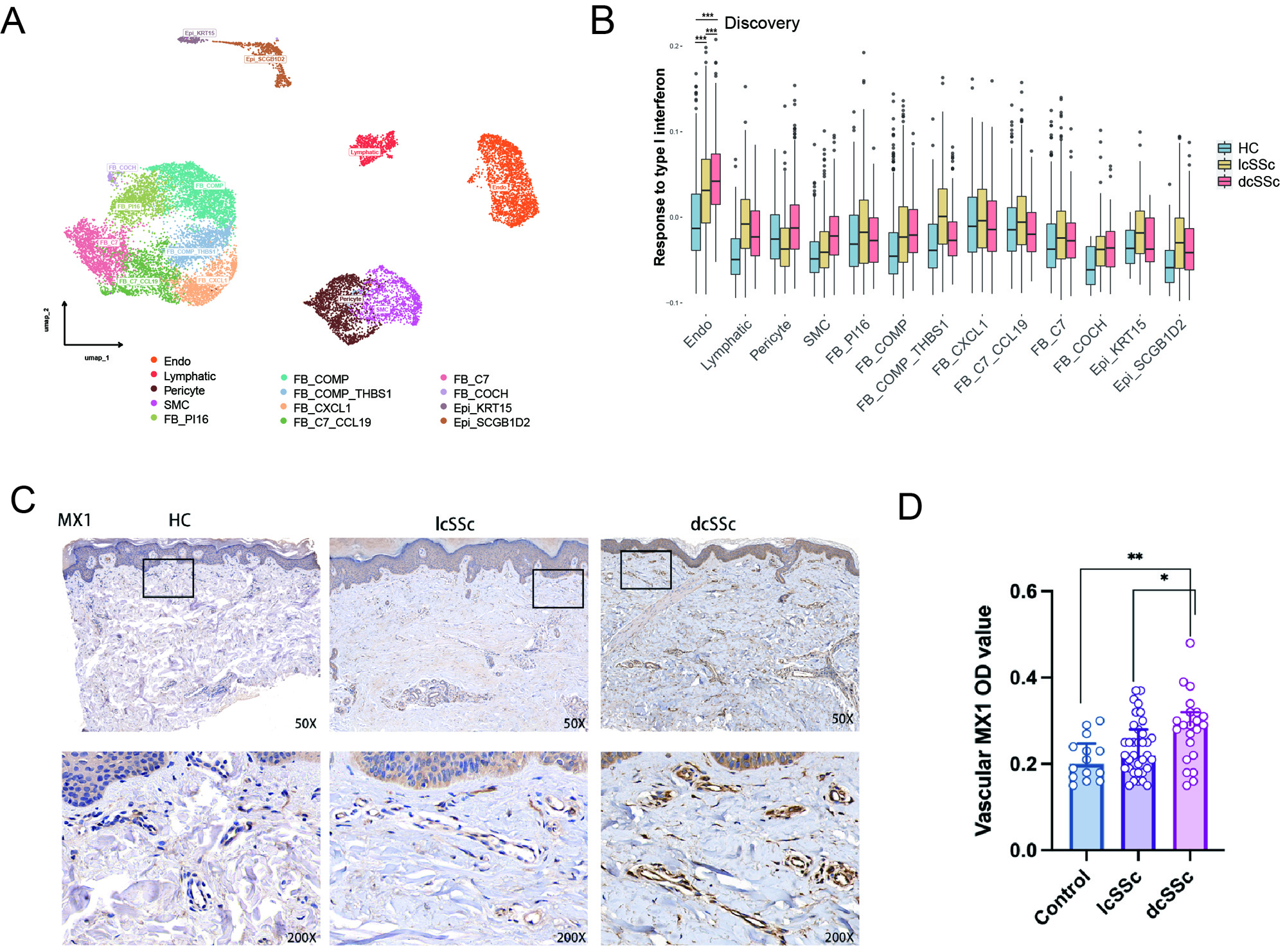
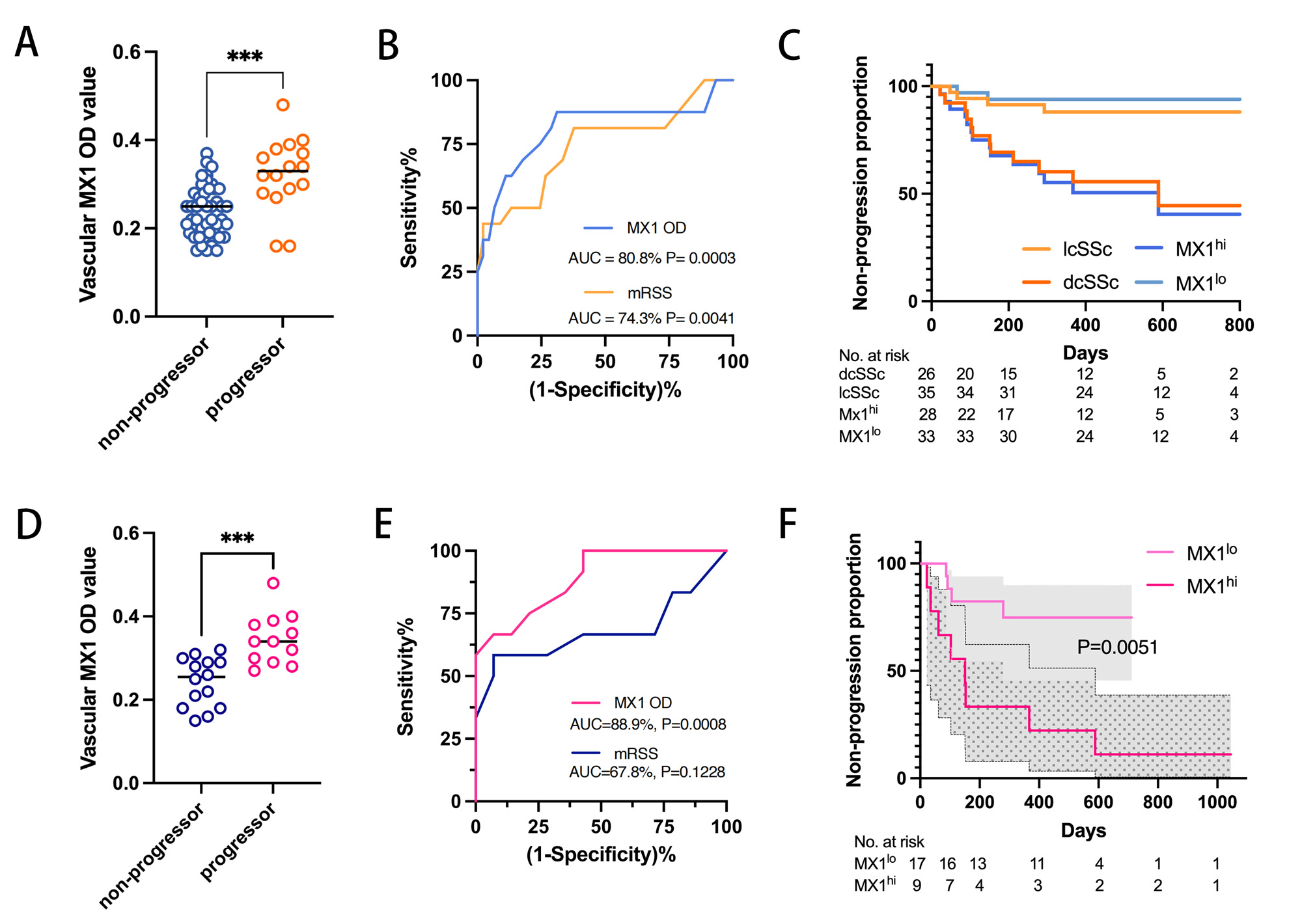
Results: The discovery and validation datasets shared findings. The endothelial cells (EC) had the most prominent IFN-1 response among dermal non-immune cells. EC IFN-1 signature was increased both in SSc vs. control and in dcSSc vs. lcSSc. Among EC subclusters, the elevation of IFN-1 signature in dcSSc patients compared to control was still true in capillary, post-capillary venule, and venule ECs in all datasets. Endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EndoMT) scores increased in parallel. IFNA2-AAV deteriorated bleomycin-induced dermal fibrosis, EndoMT, and perivascular fibrosis and caused blood vessel loss with EC apoptosis. Vascular MX1, an IFN-1 response protein, was significantly increased both in total SSc skin and in dcSSc vs. lcSSc. To predict disease progression in 6-34 months, the baseline vascular MX1 performed similarly to skin score in total SSc and was superior in the dcSSc subpopulation.
Conclusion: The EC IFN-1 signature distinguished SSc skin subtypes and disease progression and may contribute to vasculopathy and fibrosis.
(A)Umap plot exhibiting the identified 13 clusters in dermal stromal cells.
(B)Response to type I interferon scores calculated by GSVA method in each celltype.
(C)Immunohistochemical staining of MX1 in dcSSc, lcSSc, and HC skin.
(D)Qualification of vascular MX1 OD value.
(A)Vascular MX1 OD value in progressor and non-progressor among all SSc patients.
(B)ROC curves of the predictive values for vascular MX1 OD value (blue) and mRSS (yellow) in all SSc patients.
(C)Kaplan–Meier analysis of non-progression in patients with low and high vascular MX1 expression as well as patients with lcSSc and dcSSc .
(D)Vascular MX1 OD value in progressor and non-progressor among dcSSc patients.
(E)ROC curves of the predictive values for vascular MX1 OD value (red) and mRSS (purple) in dcSSc group.
(F)Vascular MX1 distinguished disease worsening eddectively in Cox regression for dcSSc.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Yin H, Distler O, Li B, Yan Q, Lu L. Endothelial Response to Type I Interferon Contributes to Vasculopathy and Fibrosis and Predicts Disease Progression of Systemic Sclerosis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/endothelial-response-to-type-i-interferon-contributes-to-vasculopathy-and-fibrosis-and-predicts-disease-progression-of-systemic-sclerosis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/endothelial-response-to-type-i-interferon-contributes-to-vasculopathy-and-fibrosis-and-predicts-disease-progression-of-systemic-sclerosis/