Session Information
Date: Tuesday, November 7, 2017
Title: Fibromyalgia, Soft Tissue Disorders, Regional and Specific Clinical Pain Syndromes Poster II
Session Type: ACR Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Fibromyalgia is a widespread chronic pain syndrome (FMS) the pathogenesis of which remains incompletely understood. FMS patients demonstrate an altered profile of chemokines relative to healthy controls (HC).(1) An interplay between glial and neuro-glial cells involving an extensive cytokines/chemokines network has been suggested as a potential key mechanism underlying chronic pain.(2,3) Eotaxin-2 is a potent chemoattractant for eosinophils, basophils and lymphocytes, distributed in a variety of tissues, including human brain.(4)
The aim of the current study was to compare serum levels of eotaxin-2 between FMS patients and HC and to examine a potential correlation between eotaxin-2 levels and clinical parameters of FMS.
Methods: 50 patients fulfilling ACR 2010 diagnostic criteria for FMS and 15 HC were recruited. Patients filled out questionnaires to asses and document severity of symptoms of FMS and depression, including the widespread pain index (WPI), the symptom severity scale (SSS), the fibromyalgia impact questionnaire (FIQ), and the Beck depression inventory (BDI). Serum levels of Eotaxin-2 (ELISA) were determined in all participants. High sensitive CRP (hs-CRP) was measured in the FMS group. Data were statistically analyzed with SPSS (version 20) and the significance level was set to P value of 0.05.
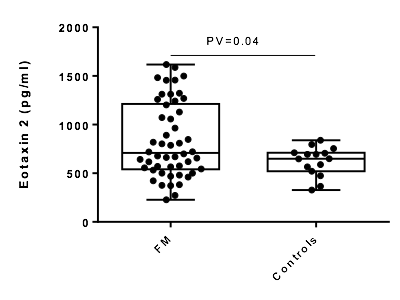
Results: The FMS cohort included predominantly females (84%), mean age 49 yo, mean disease duration of 6 years, with the following characteristics (means): WPI 12.5 (±4.2), SSS 9.1 (±1.9), FIQ 63.9 (±16.9), BDI 20 (±11). FMS patients exhibited significantly higher eotaxin-2 serum levels (pg/ml) vs HC: 833 (±384) vs 622 (±149), p-value 0.04, respectively. (Figure 1)
Mean hsCRP levels among FMS patients were 4.8±6 mg/dl, a value not indicative of acute inflammation, and no correlation was found between the eotaxin-2 and hs-CRP levels. Further, no correlation was found between Eotaxin-2 /hs-CRP levels and severity measures of FMS or depression.
Conclusion: Significantly increased levels of Eotaxin-2 were demonstrated in FMS compared with HC, with no correlation observed between Eotaxin-2 and hsCRP levels. Further, no correlation was found between FMS activity and Eotaxin-2 levels. Thus, Eotaxin-2 does not appear to be a candidate for a disease activity biomarker. Further research is warranted into the role of this chemokine in the pathophysiology of the FMS.
Figure 1. Serum concentration of eotaxin-2 in patients with FMS vs controls
References:
1. Zhang Z. Exp Biol Med 2008,233.
2.García JJ. Ann Clin Bioch 2014, 51.
3. Ji R-R. PAIN 2013, 154.
4. Kitaura M. J Biol Chem. 1996;271.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Furer V, Hazan E, Mor A, Segal M, Katav A, Aloush V, Elkayam O, George J, Ablin JN. Elevated Levels of Eotaxin-2 in Serum of Fibromyalgia Patients [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017; 69 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/elevated-levels-of-eotaxin-2-in-serum-of-fibromyalgia-patients/. Accessed .« Back to 2017 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/elevated-levels-of-eotaxin-2-in-serum-of-fibromyalgia-patients/