Session Information
Date: Saturday, November 12, 2022
Title: Spondyloarthritis Including PsA – Treatment Poster I: AxSpA
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 1:00PM-3:00PM
Background/Purpose: The Phase 3 SELECT-AXIS 2 trial (NCT04169373) assessed the efficacy and safety of upadacitinib (UPA) in patients with non-radiographic axial spondyloarthritis (nr-axSpA). Here, we present a subgroup analysis of the SELECT-AXIS 2 efficacy data stratified by elevated high-sensitivity CRP (hsCRP) and positivity for MRI inflammation in the sacroiliac (SI) joints at screening.
Methods: In SELECT-AXIS 2,1 patients aged ≥18 years with a clinical diagnosis of nr-axSpA, meeting the 2009 Assessment of Spondyloarthritis international Society (ASAS) classification criteria for axSpA, but not the radiologic criterion of the modified New York criteria for AS, and with objective signs of active inflammation on MRI per the ASAS definition (assessed by two primary readers and an adjudicator) and/or hsCRP exceeding the upper limit of normal (ULN, 2.87 mg/L) at screening, were randomized 1:1 to UPA 15 mg once daily or placebo (PBO). The primary endpoint, measured at Week (Wk) 14, was the ASAS40 response. Additional endpoints included Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Score (ASDAS) Low Disease Activity (LDA) with a score ≤2.1, change from baseline (BL) in MRI Spondyloarthritis Research Consortium of Canada (SPARCC) score (SI joints), BASFI, and patients’ assessments of total back pain, all at Wk 14. Prespecified (ASAS40 response) and post hoc (all other endpoints) subgroup analyses were carried out by inflammatory status, with hsCRP ( >ULN vs ≤ULN) and MRI SI joint inflammation status (positive vs negative) at screening as stratification factors. A separate subgroup analysis by BL hsCRP status alone is also presented. Non-response imputation (NRI) with multiple imputation (MI), incorporating MI to handle missing data due to COVID-19, was used for binary outcomes. Mixed model for repeated measures based on as-observed (AO) data was used for continuous outcomes except MRI SPARCC score. Analysis of covariance based on AO data was used for MRI SPARCC score.
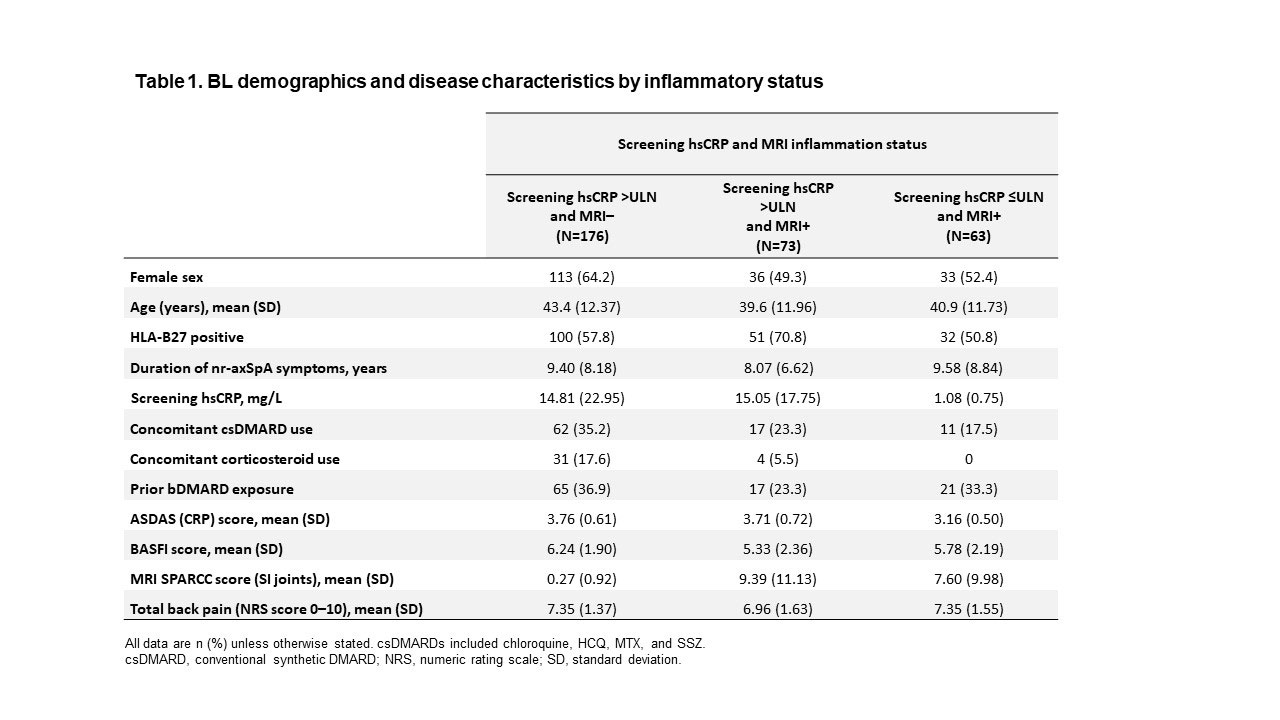
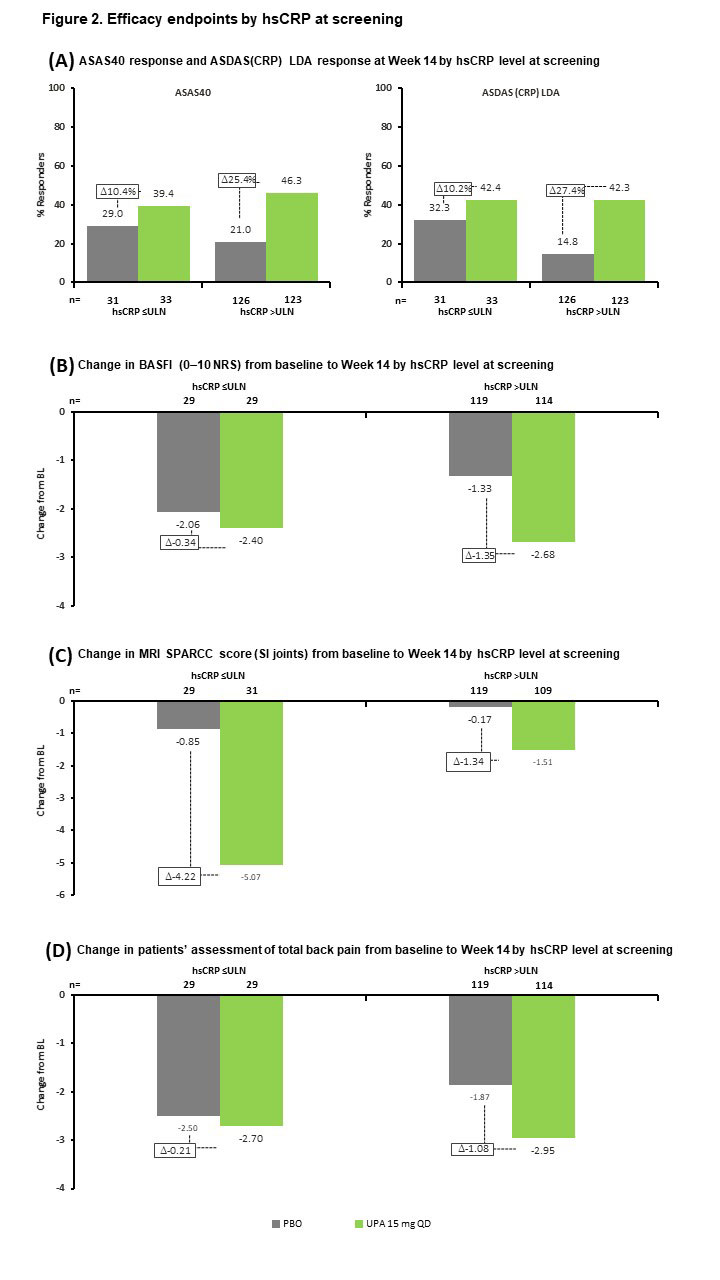
Results: Of 312 patients included in the analysis, 176 (56%) had hsCRP >ULN and were MRI negative (MRI−), 73 (23%) had hsCRP >ULN and were MRI positive (MRI+), and 63 (20%) had hsCRP ≤ULN and were MRI+. BL demographics and disease characteristics were generally similar across subgroups, although the hsCRP >ULN and MRI+ subgroup had a higher frequency of HLA-B27-positive patients and a lower rate of prior biologic DMARD (bDMARD) exposure than the other subgroups (Table 1). UPA was associated with increased ASAS40 and ASDAS LDA rates, and greater reductions in MRI SPARCC score, BASFI, and total back pain from BL, vs PBO across all subgroups at Wk 14 (Figure 1). The treatment difference between UPA and PBO was greatest in the hsCRP >ULN and MRI+ group for all endpoints. When considering BL hsCRP alone, the treatment difference was greater in the hsCRP >ULN group vs the hsCRP ≤ULN subgroup for all endpoints except change from BL in MRI SPARCC score (SI joints) (Figure 2).
Conclusion: In SELECT-AXIS 2, UPA improved outcomes vs PBO in patients with nr-axSpA across all BL inflammation subgroups; the greatest benefit was observed in patients with both elevated CRP levels and evidence of inflammation on MRI at screening.
Reference 1. Deodhar A, et al. Ann Rheum Dis 2022;81(Suppl 1):9. Abstract OP0016
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Maksymowych W, Baraliakos X, Deodhar A, Poddubnyy D, Ganz F, Gao T, Stigler J, Shmagel A, Wung P, Van den bosch F. Efficacy of Upadacitinib in Patients with Non-Radiographic Axial Spondyloarthritis Stratified by Objective Signs of Inflammation at Baseline [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022; 74 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/efficacy-of-upadacitinib-in-patients-with-non-radiographic-axial-spondyloarthritis-stratified-by-objective-signs-of-inflammation-at-baseline/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2022
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/efficacy-of-upadacitinib-in-patients-with-non-radiographic-axial-spondyloarthritis-stratified-by-objective-signs-of-inflammation-at-baseline/