Session Information
Date: Monday, November 14, 2016
Title: Rheumatoid Arthritis – Small Molecules, Biologics and Gene Therapy - Poster II
Session Type: ACR Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
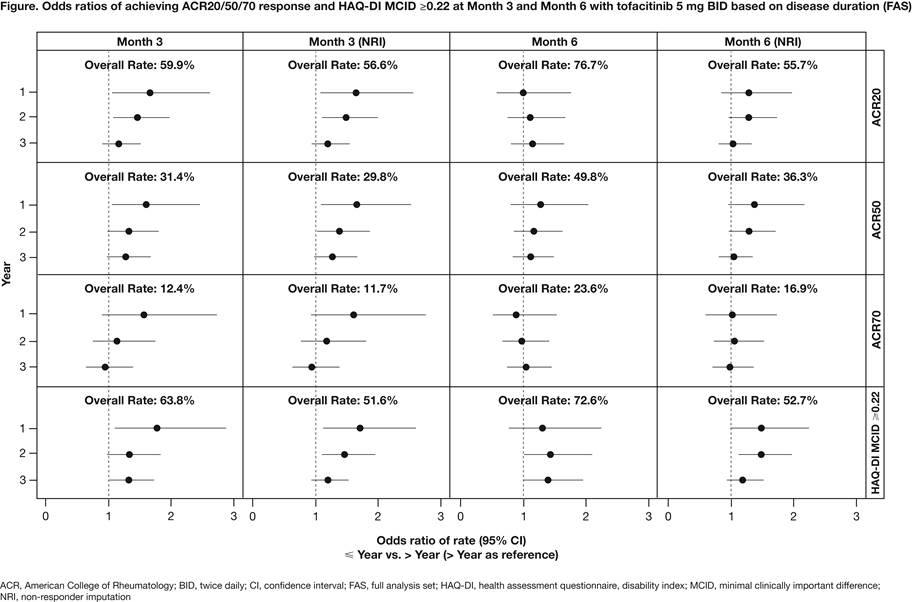
Background/Purpose: Tofacitinib is an oral Janus kinase inhibitor for the treatment of RA. This post-hoc analysis of data from Phase 3 studies investigated the efficacy of tofacitinib in patients (pts) according to RA duration (early vs late).
Methods: Pts from 5 placebo-controlled Phase 3 studies (ORAL Step [NCT00960440]; ORAL Scan [NCT00847613]; ORAL Solo [NCT00814307], ORAL Sync [NCT00856544]; ORAL Standard [NCT00853385]) of tofacitinib as monotherapy or with background DMARDs were included. This analysis included pts who were inadequate responders (IR) to ≥1 DMARDs randomized to tofacitinib 5 mg or 10 mg BID, placebo or adalimumab (ORAL Standard); results for tofacitinib 5 mg BID are presented. Pts were evaluated according to RA duration at baseline (years [yr]): ≤1 vs >1; ≤2 vs >2; ≤3 vs >3. For each subset pair, at Month 3 and Month 6 we evaluated proportions of pts achieving ACR20/50/70 response, Disease Activity Score (ESR) (DAS 28-4[ESR]) <2.6 (remission), DAS28-4(ESR) ≤3.2 (low disease activity), HAQ-DI minimal clinically important difference (MCID) ≥0.22, 0.30, 0.50, and 0.80, and mean changes from baseline in DAS28-4(ESR) and HAQ-DI scores. Odds ratios (ORs [for rates]) and mean differences (for change from baseline) were calculated with corresponding 95% CIs, and 2-sided p values (‘>’ category as reference). Non-responder imputation (NRI) was applied for rates. Pts meeting criteria for rescue (failed to achieve ≥20% improvement from baseline at Month 3 in applicable studies) had NRI applied or were excluded from mean change analyses at Month 6.
Results: At Month 3, significantly greater OR for ACR20, ACR50, HAQ-DI MCID ≥0.22, and ≥0.30 were shown for ≤1 vs >1 yr and ≤2 vs >2 yr subsets (Figure). HAQ-DI MCID ≥0.50 and ≥0.80 were significantly greater for ≤1 vs >1 yr, ≤2 vs >2 yr, and ≤3 vs >3 yr subsets. For all other efficacy outcomes, ORs were not statistically significant between subsets at Month 3. Mean changes from baseline in DAS28-4(ESR) were significantly greater for ≤1 vs >1 yr and ≤2 vs >2 yr subsets at Month 3 (Table). Mean changes from baseline in HAQ-DI at Month 3 was significantly greater for ≤1 vs >1 yr, ≤2 vs >2 yr, and ≤3 vs >3 yr subsets. In general, higher responses were seen at Month 3 in pts with early vs late RA disease duration.
Conclusion: In this analysis, a trend was observed indicating that DMARD-IR pts with earlier disease duration at treatment initiation respond better to tofacitinib 5 mg BID than pts with late disease duration. Results suggest that initiating tofacitinib earlier in the disease may yield greater treatment response and thereby reduce the time pts experience active disease.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Hall S, Nash P, Rischmueller M, Wiid Z, Witcombe D, Gruben D, DeMasi R, Lukic T. Efficacy of Tofacitinib in Patients Who Are Inadequate Responders to Disease-Modifying Antirheumatic Drugs According to Early Versus Late Duration of Rheumatoid Arthritis: Post-Hoc Analysis of Data from Phase 3 Trials [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016; 68 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/efficacy-of-tofacitinib-in-patients-who-are-inadequate-responders-to-disease-modifying-antirheumatic-drugs-according-to-early-versus-late-duration-of-rheumatoid-arthritis-post-hoc-analysis-of-data-fr/. Accessed .« Back to 2016 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/efficacy-of-tofacitinib-in-patients-who-are-inadequate-responders-to-disease-modifying-antirheumatic-drugs-according-to-early-versus-late-duration-of-rheumatoid-arthritis-post-hoc-analysis-of-data-fr/