Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session (Monday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Vascular involvement is one of the major causes of morbidity and mortality in Behcet’s Disease (BD) patients. Immunosuppressive (IS) agents are the mainstay of vascular BD (VBD) treatment, however up to one third of patients relapse under conventional ISs. In this case series, we present the results of tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNFα) inhibitor use for the treatment of VBD patients who were refractory to conventional ISs and corticosteroids.
Methods: This retrospective multicenter study included 27 refractory VBD patients treated with TNFα inhibitor agents. All data were acquired from patient charts.
Activity was assessed by the treating clinician according to clinical manifestations, imaging findings and acute-phase reactant results. Complete remission was defined as no new signs and symptoms of vascular disease assessed by physician and corticosteroid dose under 10 mg/day at the third month of treatment. Partial response was defined as an improvement of clinical and laboratory parameters and at least 50% reduction of initial corticosteroid dose at the third month.
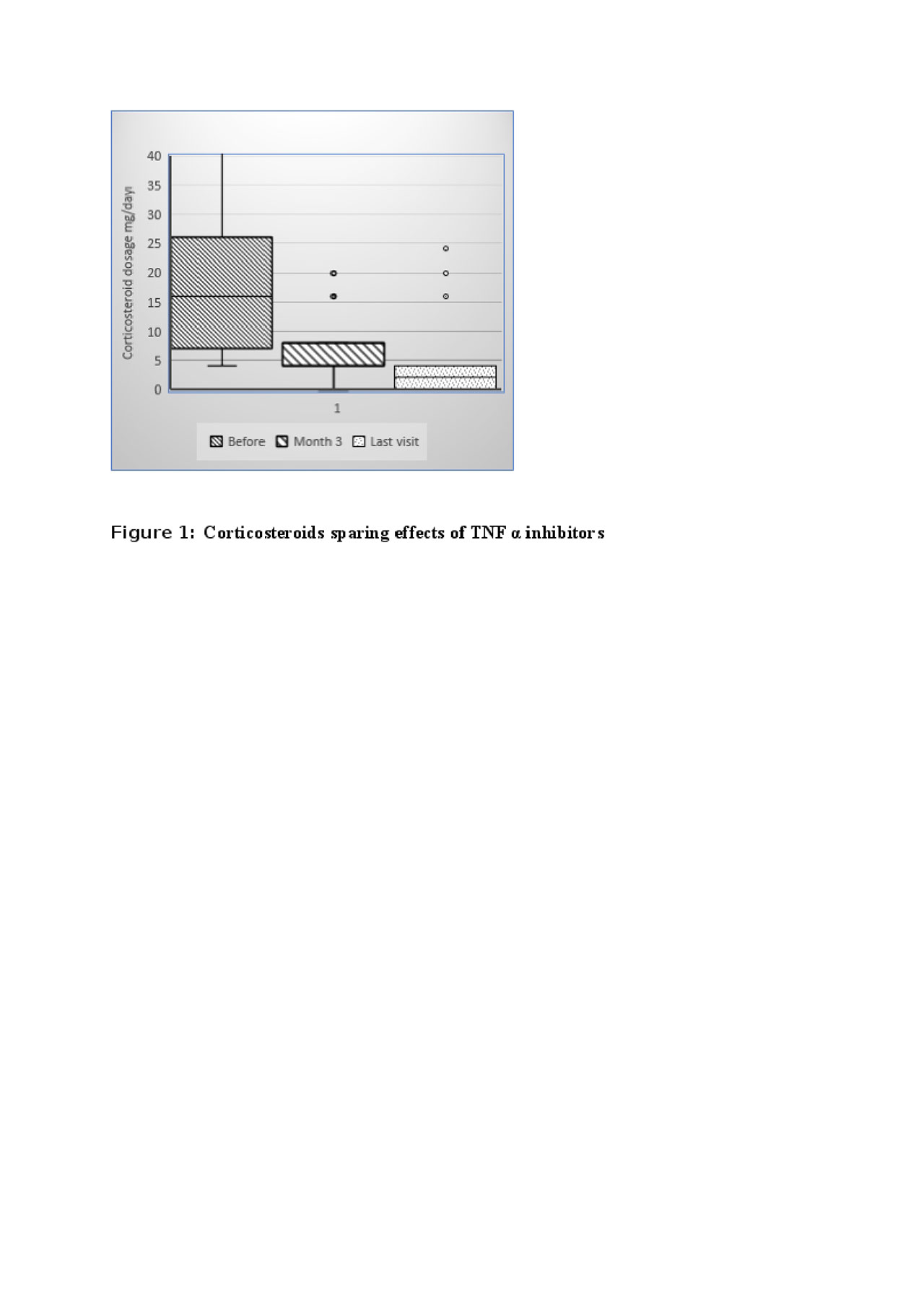
Results: Infliximab was the first choice of TNFα inhibitor in 24 and adalimumab in 3 patients. Complete clinical remission was achieved in 22 (80%) patients within 3 months of the initiation of TNFα inhibitors. The median daily dose of corticosteroids significantly decreased at 3 months. (Figure 1) and stopped in 7 patients during follow-up without any relapse. Also, 89% of patients discontinued or maintained 4 mg or lower daily of methylprednisolone dosage at the last visit. Fifteen patients received concomitant immunosuppressive (all was azathioprine) together with a TNFα inhibitor. A trend towards a higher rate of complete remission was observed with concomitant IS use compared to monotherapy of TNFa inhibitors (93% vs 67%, p=0.09). Also, duration of first TNFα inhibitor drug survival was also 12.5 (1-43) months and 24 (4-67) months for monotherapy and concomitant IS user groups, respectively (p >0.05) (Figure 2) Three patient had vascular relapses under the treatment of TNFα inhibitors (2 Infliximab, 1 Adalimumab). Serious side effects were observed in 2 patients (1 pneumonia and 1 tuberculosis). TNFα inhibitors were stopped with sustained remission in 2 patients (after 24 and 37 months of treatment). One of the patients relapsed 6 months after cessation of TNFα inhibitor. After median 14 (3-67) months of follow-up period under TNFα inhibitors, 23 patients were still under TNFα inhibitors and all were in remission.
Conclusion: TNFα inhibitors seem a highly effective option for remission-induction of refractory VBD with an acceptable safety data. Concomitant IS use may achieve higher complete remission rates as compared to TNFα inhibitor monotherapy. Comparative efficacy and safety of biological agents for VBD require further prospective, randomized controlled studies with a longer duration of follow-up.
-The median daily dose at baseline was 16 -4-64- mg vs 4 -0-20- mg at 3 months -p=0.000- and 2 -0-20- mg at last visit -p=0.000-, respectively-
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Aksoy A, Yazici A, Omma A, Cefle A, Onen F, Tasdemir U, Ergun T, Direskeneli H, Alibaz-Oner F. Efficacy of TNF α Inhibitors for Refractory Vascular Behcet’s Disease: A Multicenter Observational Study of 27 Patients [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/efficacy-of-tnf-%ce%b1-inhibitors-for-refractory-vascular-behcets-disease-a-multicenter-observational-study-of-27-patients/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/efficacy-of-tnf-%ce%b1-inhibitors-for-refractory-vascular-behcets-disease-a-multicenter-observational-study-of-27-patients/