Session Information
Date: Tuesday, October 23, 2018
Title: Rheumatoid Arthritis – Treatments Poster III: Biosimilars and New Compounds
Session Type: ACR Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Recent randomized clinical trials (RCTs) have shown similar efficacy of biosimilar agents compared to reference agents. Is the efficacy of reference biologic agents different in pivotal RCTs and in recent RCTs comparing these agents vs biosimilar ?
To compare the reference agent efficacy (infliximab, etanercept, adalimumab, rituximab) in pivotal RCTs (reference agent vs. placebo), with their efficacy in non-inferiority RCTs (reference agent vs. biosimilar), in rheumatoid arthritis (RA).
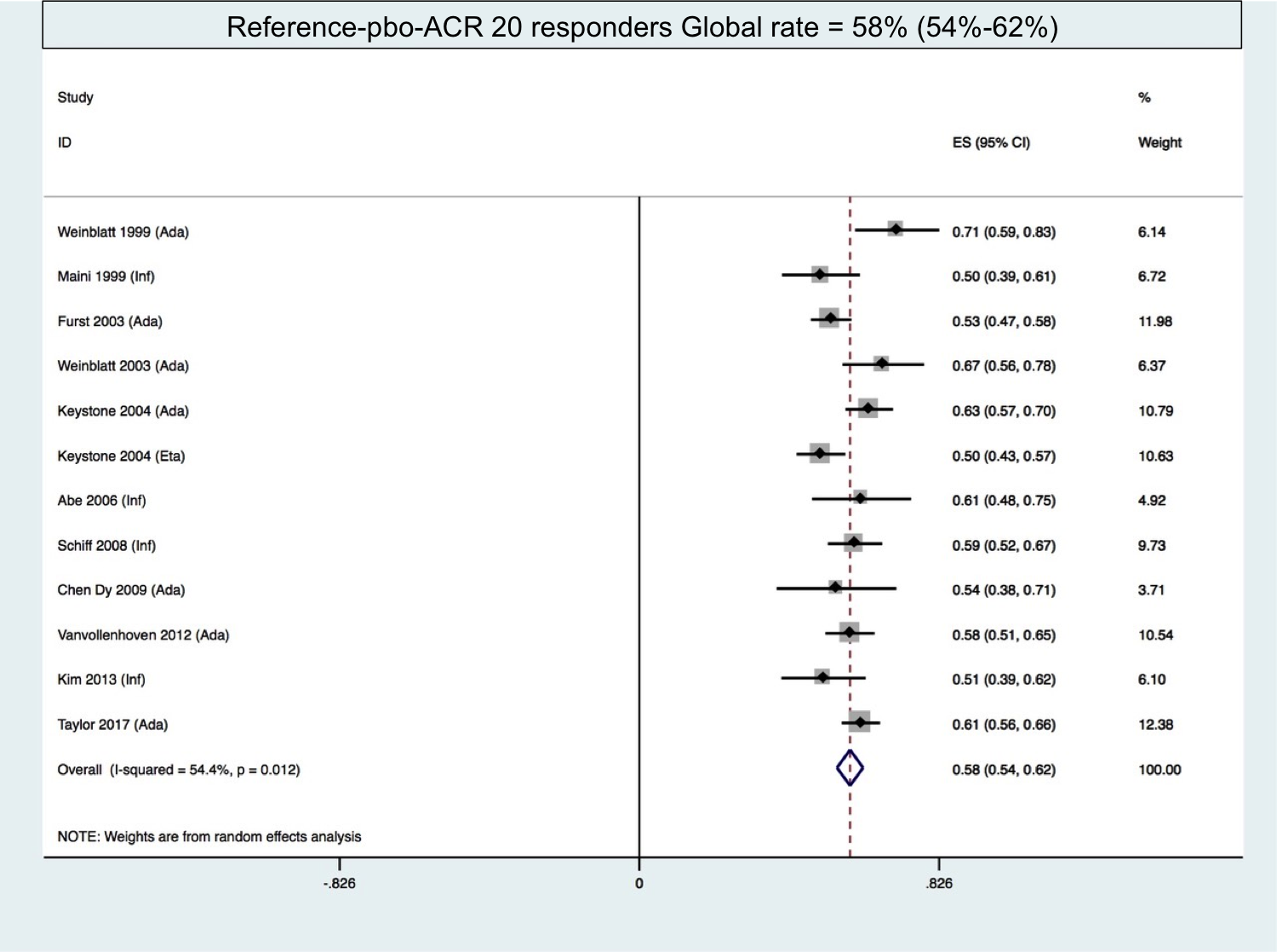
Methods: We searched in MEDLINE and EMBASE (until march 2018) for randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled (Reference-pbo group) or biosimilar controlled trials (Reference-bs group) in rheumatoid arthritis. We included the RCTs in methotrexate/disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drug incomplete or inadequate responders (MTX/DMARD-IR). RCTs in monotherapy, in MTX-naive patients, and biologics incomplete or inadequate responders (bDMARD-IR) were excluded. The primary endpoint was the American College of rheumatology 20% response criteria (ACR 20) of reference agents. We calculated the global rate of ACR 20 responders in Reference-pbo group and in Reference-bs group by performing a meta-analysis using the inverse variance approach with fixed or random effect model according to heterogeneity estimation.
Results: We included 22 articles within the 783 found: 12 in Reference-pbo group, 10 in Reference-bs group. We excluded Rituximab because Rituximab-bs trials (3) were only in bDMARD-IR patients. Global rate of ACR 20 response of the reference biologic agents is 58% (54%-62%) in Reference-pbo group and 70% (64%-76%) in Reference-bs group. Global rate of ACR 50 response of the reference biologic agents is 34% (30%-39%) and 44% (37%-51%) in Reference-pbo and Reference-bs groups, respectively. The time frame was comparable in the two groups: mostly 24 weeks. The inclusion criteria in both groups were similar. The characteristics of the population (disease duration , disease activity, seropositivity % and MTX dose) in both groups were similar.
Conclusion: The efficacy of reference agents is better in recent non-inferiority RCTs where all patients were treated with the reference agents or its biosimilar, than in pivotal RCTs where the patients could potentially be treated with the biologic agents or a placebo. Inclusion criteria or characteristics of the population in these different trials seem comparable. We believe that a nocebo effect could explain this difference.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Lopez L, Richez C, Truchetet ME, Bannwarth B, Barnetche T, Schaeverbeke T. Efficacy of the Reference Biologic Agents in Two Different Types of Randomized Clinical Trials: 1/ the Ones Comparing Their Efficacy Vs. Placebo and 2/ the Ones Comparing Their Efficacy Vs. Biosimilar in Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Systematic Review of Literature and Meta-Analysis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018; 70 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/efficacy-of-the-reference-biologic-agents-in-two-different-types-of-randomized-clinical-trials-1-the-ones-comparing-their-efficacy-vs-placebo-and-2-the-ones-comparing-their-efficacy-vs-biosimilar/. Accessed .« Back to 2018 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/efficacy-of-the-reference-biologic-agents-in-two-different-types-of-randomized-clinical-trials-1-the-ones-comparing-their-efficacy-vs-placebo-and-2-the-ones-comparing-their-efficacy-vs-biosimilar/