Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 3:00PM-4:30PM
Background/Purpose: Juvenile idiopathic arthritis (JIA) categories of enthesitis-related arthritis (ERA) and juvenile psoriatic arthritis (JPsA) represent pediatric counterparts of adult non-radiographic axial spondyloarthritis and psoriatic arthritis, respectively.1,2 JUNIPERA, a 2-year, randomized, double-blind, placebo (PBO)-controlled trial demonstrated significantly longer time to flare with secukinumab (SEC) vs PBO with sustained improvement of signs and symptoms up to week (wk) 104.3 The effect of SEC on axial and peripheral manifestations in active ERA and JPsA patients (pts) is presented here.
Methods: Pts (2–18 years of age) with active disease (both ≥3 active joints and ≥1 active enthesitis site) were treated with open-label (OL) subcutaneous SEC (75/150 mg in pts < 50/ ≥50 kg) in treatment period (TP) 1. SEC was administered at baseline (BL) and wks 1–4, 8, and 12. Responders at wk 12 (pts who achieved at least JIA-ACR30 response) were randomized into the double-blinded, withdrawal TP2 to continue SEC or PBO every 4 wks until a disease flare or up to wk 100. The time to flare in ERA and JPsA pts in TP2 is reported here. JIA-ACR responses, resolution of enthesitis and dactylitis, Juvenile Arthritis Disease Activity Score (JADAS)-27, and axial, peripheral, and skin manifestations were also assessed.
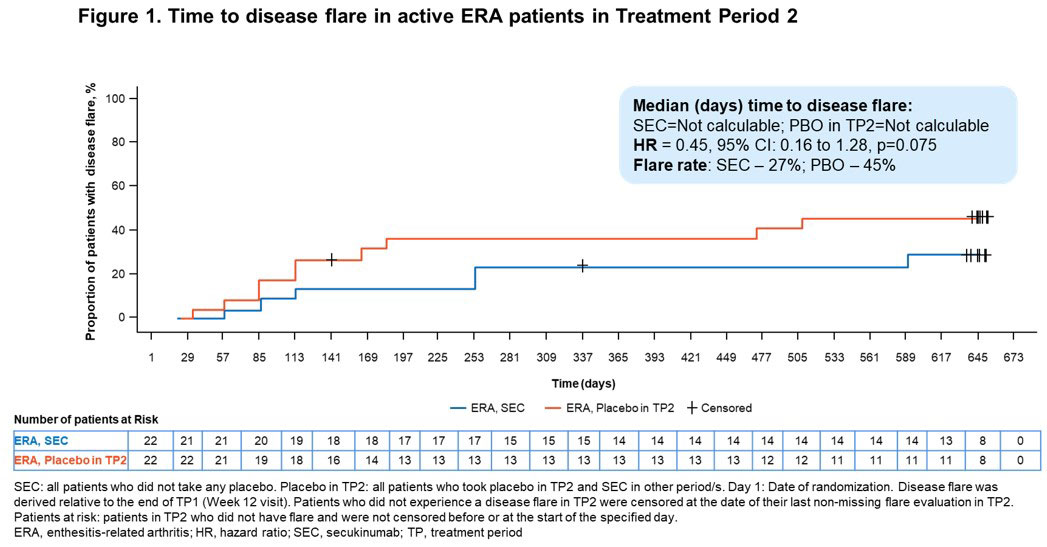
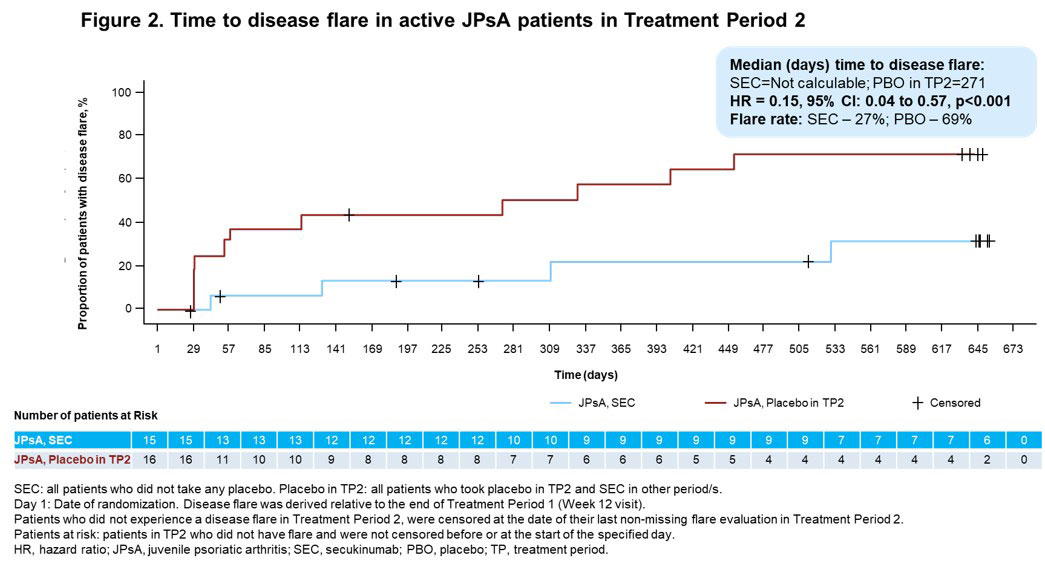
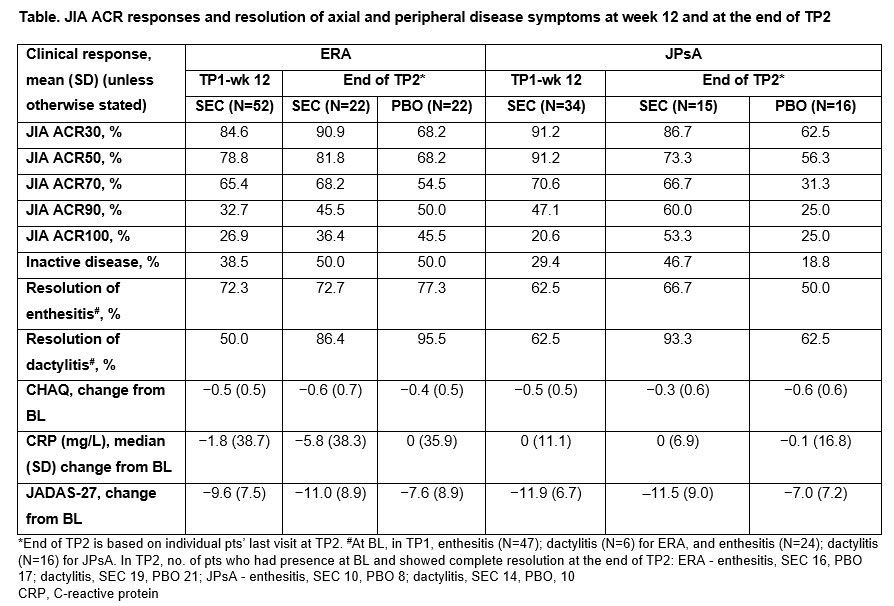
Results: A total of 52/86 (60.5%) pts with ERA (mean age, 13.7 years; male, 78.8%) and 34/86 (39.5%) pts with JPsA (mean age, 12.2 years; male, 47.1%) were enrolled in the OL TP1. The relative risk reduction of experiencing a disease flare in TP2 in ERA and JPsA pts is provided in Figures 1 and 2, respectively. Improvements in JIA-ACR responses, inactive disease and resolution of enthesitis and dactylitis were observed in ERA and JPsA pts with SEC treatment at wk 12 and at the end of TP2 (Table). Axial symptoms in ERA with SEC and PBO treatment at the end of TP2 were: modified Schober’s test, 100% and 100%; inflammatory back pain, 100% and 50%; Flexion, ABduction, External Rotation (FABER) test, 100% and 83.3%; and clinical sacroiliitis, 100% and 50%. Pts who had Childhood Health Assessment Questionnaire score=0 at the end of TP2 with SEC and PBO treatment were 9 each in ERA and 8 each in JPsA. JPsA pts with mild-to-moderate skin psoriasis (7/15; investigator’s global assessment [2011 modified version; IGA mod 2011]) at BL showed improvements in overall psoriatic skin manifestations at wk 12 (13/15): clear (n=8, 53.3%) and almost clear (n=5, 33.3%).
Conclusion: In pts with active ERA and JPsA, SEC demonstrated a longer time to disease flare and a reduction of flare risk compared with PBO up to wk 104 and exhibited rapid and sustained improvement of axial, peripheral and skin manifestations.
References
1. Pagnini I, et al. Front Med. 2021;8:6673052.
2. Zisman D, et al. J Rheumatol. 2018;94:11–16.
3. Brunner H, et al. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021;73 (suppl 10).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Brunner H, Chertok E, Dehoorne J, Horneff G, Kallinich T, Louw I, Alessio M, Compeyrot-Lacassagne S, Lauwerys B, Martin N, Marzan K, Knibbe W, Martin R, Zhu X, whelan s, Pricop L, Lovell D, Martini A, Ruperto N. Efficacy of Secukinumab in Enthesitis-related Arthritis and Juvenile Psoriatic Arthritis Subtypes of Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis: Results from a Randomized, Phase 3 Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022; 74 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/efficacy-of-secukinumab-in-enthesitis-related-arthritis-and-juvenile-psoriatic-arthritis-subtypes-of-juvenile-idiopathic-arthritis-results-from-a-randomized-phase-3-study/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2022
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/efficacy-of-secukinumab-in-enthesitis-related-arthritis-and-juvenile-psoriatic-arthritis-subtypes-of-juvenile-idiopathic-arthritis-results-from-a-randomized-phase-3-study/