Session Information
Date: Tuesday, November 12, 2019
Title: RA – Diagnosis, Manifestations, & Outcomes Poster III: Comorbidities
Session Type: Poster Session (Tuesday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Interstitial lung disease (ILD) as an extra-articular manifestation of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) leads to significant morbidity and mortality. As data is limited, this study aims to investigate the efficacy of mycophenolate mofetil (MMF) in the treatment of RA associated ILD.
Methods: This retrospective chart review identified patients with a clinical diagnosis of RA and ILD at a single tertiary academic medical center who were treated with MMF for at least 3 months between 1/01/2005 and 12/31/2018. Patients were identified by diagnosis codes, then reviewed to confirm clinical diagnoses and to collect data on concurrent therapies, pulmonary function, infections and hospitalizations.
Results: Twenty six patients were identified; 17 female (65.4%) and 23 Caucasian (88.5%) with a mean age of 57.8 at the time of diagnosis of RA. RF was positive in 20 (76.9%), ACPA in 16 (61.5%) and 10 (38.5%) were seropositive for both, while 3 (11.5%) patients were seronegative. The mean time to diagnosis of ILD after diagnosis of RA was 40.6 months with a range of -50 to 504 months. Seven (26.9%) patients had an ILD diagnosis prior to RA.
Fourteen (53.8%) patients had usual interstitial pneumonia (UIP), 5 (19.2%) nonspecific interstitial pneumonia (NSIP), 3 (11.5%) organizing pneumonia (OP), and 4 (15.4%) had other forms such as mixed UIP and NSIP. The average duration of MMF therapy was 24.9 months with an average maximum daily dose of 2163.5mg. Eleven (42.3%) patients were concurrently on rituximab (RTX), 1 (3.85%) on methotrexate, 1 (3.85%) on certolizumab, and 1 (3.85%) on sulfasalazine. Fifteen (57.7%) patients were on prednisone ≥10mg daily and 6 (23.1%) were on < 10mg daily for at least one month.
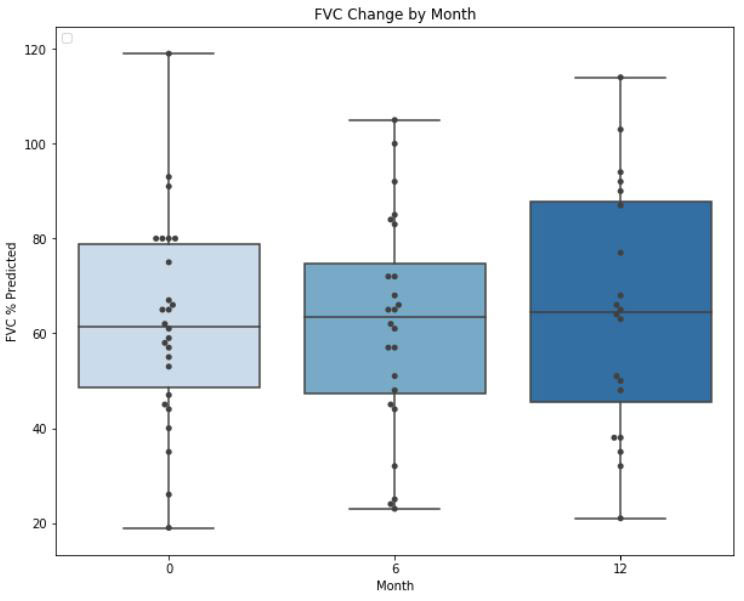
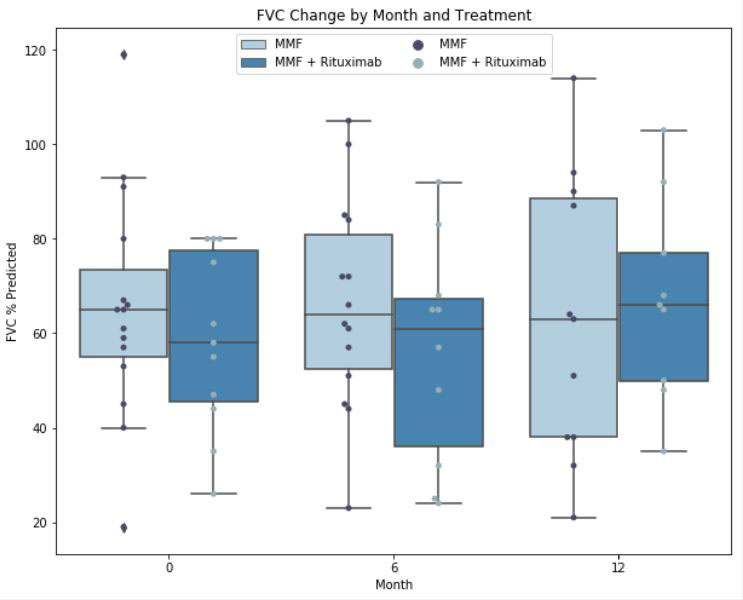
Average FVC for all patients was 62.4 ± 21.9% predicted at the time of initiation of MMF, 61.9% ± 23.0 predicted at 6 months (p=0.95), and 64.8% ± 25.9 predicted at 12 months (p=0.67). In aggregate, 13 (50%) patients on MMF had stable or improved FVC over the 12-month period, of whom 6/13 (46.2%) were on concurrent RTX. Six of 11 (54.5%) patients on combination MMF and RTX had stable or improved FVC over the 12-month period.
There were 26 hospitalizations in 8 (30.8%) patients; 17 (65.4%) for infections, 3 (11.5%) for respiratory failure, and 6 (23.1%) for cardiovascular events. Twenty four (92.3%) hospitalizations were in the combination MMF and RTX treatment group, including all infection related admissions. There were 10 outpatient infections treated with antimicrobials. There were 8 (30.8%) deaths; 6 were in the MMF and RTX combination group. Two deaths were from infection and ILD, 2 from infection, 2 from cardiac disease, 1 from ILD, and 1 from myasthenia gravis crisis.
Conclusion: In this cohort of 26 RA patients with ILD, treatment with MMF as mono or combination therapy with RTX was associated with a stable or improved FVC in 50% of patients at 12-month. About 55% of patients on combination MMF and RTX showed stability or improvement in FVC. Patients treated with MMF compared to combination MMF and RTX had similar FVC values at the end of the study period, however, the combination therapy had more hospital admissions and infections. Further studies are needed to better understand the efficacy and safety of MMF or combination therapy with RTX in RA associated ILD.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Amos J, Kendall J, Moran R, Krause M, Schmidt P, Hall C, Hamblin M, Maz M. Efficacy of Mycophenolate Mofetil in the Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis Associated Interstitial Lung Disease [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/efficacy-of-mycophenolate-mofetil-in-the-treatment-of-rheumatoid-arthritis-associated-interstitial-lung-disease/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/efficacy-of-mycophenolate-mofetil-in-the-treatment-of-rheumatoid-arthritis-associated-interstitial-lung-disease/