Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Ivarmacitinib (SHR0302), a selective Janus kinase 1 inhibitor, has demonstrated efficacy in patients with moderate-to-severe rheumatoid arthritis (RA). This post-hoc study aimed to evaluate the efficacy of Ivarmacitinib stratified by baseline patient characteristics.
Methods: This post-hoc analysis was based on data from a phase III clinical trial (NCT04333771, Liu J, Jiang Y, Zhang S, et al. Ivarmacitinib, a selective Janus kinase 1 inhibitor, in patients with moderate-to-severe active rheumatoid arthritis and inadequate response to conventional synthetic DMARDs: results from a phase III randomised clinical trial. Ann Rheum Dis. Published online November 27, 2024. doi:10.1136/ard-2024-226385). Patients were randomized to receive Ivarmacitinib 4 mg (n=189), Ivarmacitinib 8 mg (n=189) or placebo (n=188) for the initial 24-week treatment period. After week 24, patients on placebo switched to Ivarmacitinib 4mg, while the other groups continued their initial regimen until 52 weeks. Efficacy outcomes were analyzed by subgroups based on demographic factors, disease characteristics, and treatment history.
Results: At week 24, both Ivarmacitinib 4 mg and 8 mg demonstrated significantly higher American College of Rheumatology (ACR) criteria improvement of 20% (ACR20) response rate compared to placebo across all subgroups, including age, sex (except for males who received Ivarmacitinib 8 mg), disease duration, ACR functional class (grades Ⅱ and Ⅲ), C-reactive protein (CRP), 28-joint Disease Activity Score-CRP (DAS28-CRP), and prior exposure to biologic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs). By week 52, both Ivarmacitinib 4 mg (e.g., 93.8% in males) and 8 mg (e.g., 90.9% in patients with ACR functional class of I and 86.5% in patients with RA duration < 3 years) achieved high ACR20 response rates across all subgroups. Patients who switched from placebo at week 24 also achieved substantial benefits in week 52 ACR20 response across subgroups (Table 1). Regarding safety, the incidences of adverse events were generally comparable between Ivarmacitinib 4 or 8 mg versus placebo across all subgroups.
Conclusion: Ivarmacitinib provides consistent efficacy across various subgroups in patient with moderate-to-severe RA.
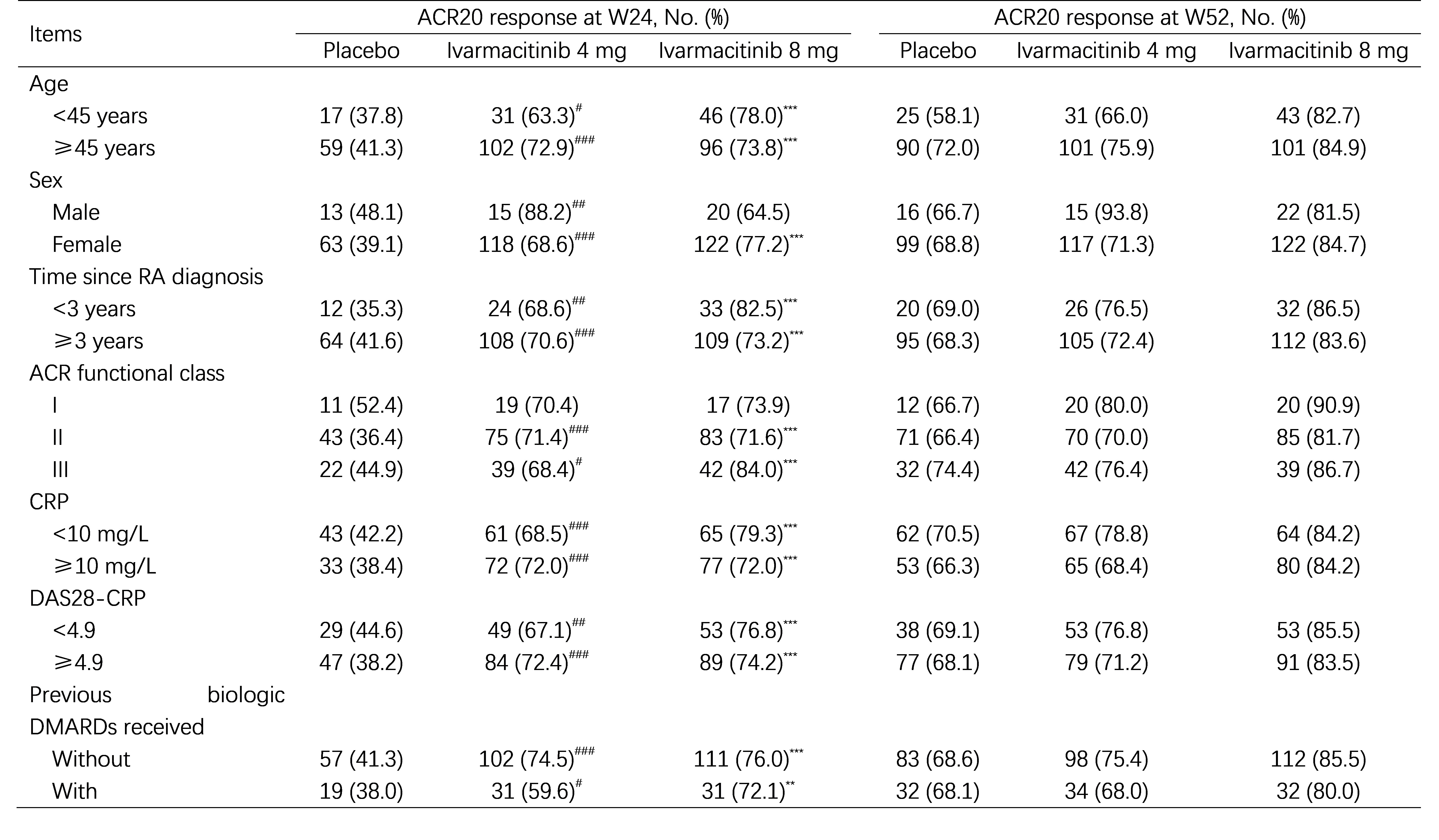 Table 1. Comparison of ACR20 response at W24 and W52 based on subgroups.
Table 1. Comparison of ACR20 response at W24 and W52 based on subgroups.
*, P < 0.05 between placebo vs. Ivarmacitinib 8 mg; **, P < 0.01 between placebo vs. Ivarmacitinib 8 mg; ***, P < 0.001 between placebo vs. Ivarmacitinib 8 mg. #, P < 0.05 between placebo vs. Ivarmacitinib 4 mg; ##, P < 0.01 between placebo vs. Ivarmacitinib 4 mg; ###, P < 0.001 between placebo vs. Ivarmacitinib 4 mg.
ACR20, American College of Rheumatology criteria improvement of 20%; W24, 24 weeks; W52, 52 weeks; RA, rheumatoid arthritis; ACR, American College of Rheumatology; CRP, C reactive protein; DAS28, 28-joint Disease Activity Score; DMARDs, disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Xue Y, Wei B, Huang X, Ding R. Efficacy of Ivarmacitinib in Patients with Moderate-to-severe Rheumatoid Arthritis Stratified by Baseline Characteristics: A Post-hoc Study of a Phase III Clinical Trial [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/efficacy-of-ivarmacitinib-in-patients-with-moderate-to-severe-rheumatoid-arthritis-stratified-by-baseline-characteristics-a-post-hoc-study-of-a-phase-iii-clinical-trial/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/efficacy-of-ivarmacitinib-in-patients-with-moderate-to-severe-rheumatoid-arthritis-stratified-by-baseline-characteristics-a-post-hoc-study-of-a-phase-iii-clinical-trial/
