Session Information
Date: Monday, November 9, 2015
Title: Systemic Lupus Erythematosus - Clinical Aspects and Treatment Poster Session II
Session Type: ACR Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose:
Treatment of lupus nephritis requires aggressive immunosuppressive drugs which includes
high dose glucocorticoids. Immunosuppressive treatment is a risk factor for opportunistic
infections such as mycobacterium tuberculosis (Tbc). However, the efficacy of
isoniazid (INH) chemoprophylaxis has not been evaluated in lupus nephritis
patients.
The aim of this study was to investigate
the preventive effect of INH chemoprophylaxis on incidence of Tbc infection in
patients with lupus nephritis on immunosuppressive treatment.
Methods:
In this retrospective cohort study, 332 patients with lupus nephritis were
enrolled, who received glucocorticoids and immunosuppressive treatment at Seoul
National University Hospital between 2004 and 2015. Information on baseline
clinical characteristics and treatment were obtained from electronic medical
record review. Incidence rates of Tbc were compared
between patients who took INH prophylaxis (prophylaxis group) and those who did
not (non-prophylaxis group), using log-rank test. Then, incidence rates of Tbc
were investigated in subgroups of patients; those who received prednisolone >=
60 mg/day and high dose glucocorticoid pulse therapy.
Results:
A total of 332 patients with lupus nephritis were identified during the study
period. The mean age was 35.3 ±
14.8 years and 266 (80.1%) were female. Among 332 patients, sixty-nine (20.8%) patients
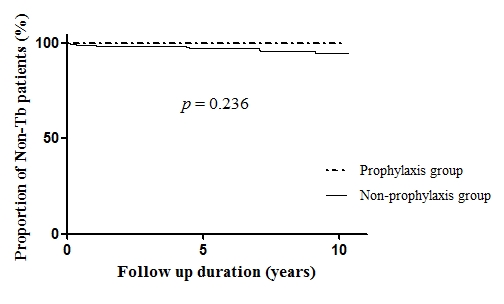
received INH prophylaxis and 263 (79.2%) patients did not. No case of Tbc
developed in 69 patients of INH prophylaxis group while 9 cases of Tbc developed
in 263 patients of non-prophylaxis group (0.0/100 person-years (PY) vs 0.53/100
PYs, p=0.236, by log-rank test). INH prophylaxis was effective neither in high
dose (>= 60 mg/day or its equivalents) prednisolone group (0.00/100 PYs vs 0.58/100
PYs, p=0.288, by log-rank test), nor in patients who received glucocorticoid
pulse therapy (0.00/100 PYs vs 0.69/100 PYs, p=0.161, by log-rank test). No
patient died of Tbc infection.
Conclusion:
In this retrospective review, INH chemoprophylaxis did not lead to
statistically significant prevention of Tbc in lupus nephritis patients.
Table 1. Isoniazid chemoprophylaxis in
patients with lupus nephritis
|
|
Prophylaxis (n = 69) |
Non-prophylaxis (n = 263) |
p-value |
|
Age, mean ± SD years |
37.78±13.47 |
34.60±15.07 |
0.092 |
|
Female sex (%) |
55 (79.7) |
211 (80.2) |
0.924 |
|
Follow up duration, mean ± SD years |
3.74±2.59 |
6.48±3.65 |
<0.001 |
|
Prednisolone >= 60 mg/day (%) |
45 (65.2) |
74 (28.1) |
<0.001 |
|
Steroid cumulative dose, mean ± SD mg |
27556.78±16875.22 |
21967.13±15196.75 |
0.014 |
|
Steroid pulse (%) |
62 (89.9) |
150 (57.0) |
<0.001 |
|
Rituximab (%) |
0 (0) |
6 (2.3) |
0.214 |
|
Mycophenolate mofetil (%) |
16 (23.2) |
144 (54.8) |
<0.001 |
|
Tacrolimus (%) |
23 (33.3) |
57 (21.7) |
0.057 |
|
Cyclophosphamide (%) |
47 (68.1) |
111 (42.2) |
<0.001 |
|
Mycobacterium tuberculosis IR, /100 person-years |
0 |
0.53 |
0.496 |
Figure 1. Mycobacterium Tbc occurrence rate
in all lupus nephritis patients
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Moon JY, Kwon HM, Ahn EY, Park JK, Song YW, Lee EB. Efficacy of Isoniazid Chemoprophylaxis in Lupus Nephritis Patients [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015; 67 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/efficacy-of-isoniazid-chemoprophylaxis-in-lupus-nephritis-patients/. Accessed .« Back to 2015 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/efficacy-of-isoniazid-chemoprophylaxis-in-lupus-nephritis-patients/