Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 12, 2023
Title: (0691–0721) Vasculitis – Non-ANCA-Associated & Related Disorders Poster I
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Most patients with IgG4-related disease (IgG4-RD) have a good response to glucocorticoid (GC) therapy, however, disease relapses sometimes occur during GC tapering. Therefore, the immunosuppressants are considered in these cases. On the other hand, the predictors of disease relapse and the efficacy of immunosuppressants have not been fully clarified.
Therefore, we retrospectively analyzed the current treatment status of patients with IgG4-RD to identify the efficacy of immunosuppressants for disease relapse.
Methods: We used the data of patients with IgG4-RD diagnosed by May 2023 based on the 2020 revised comprehensive diagnostic criteria for IgG4-RD, and extracted those who had undergone therapeutic intervention. We retrospectively evaluated the organ involved, immunological findings including serum IgG4 levels, treatment agents, especially in GC dose and concomitant use of immunosuppressants, and the presence of relapse within 2 years after the start of treatment.
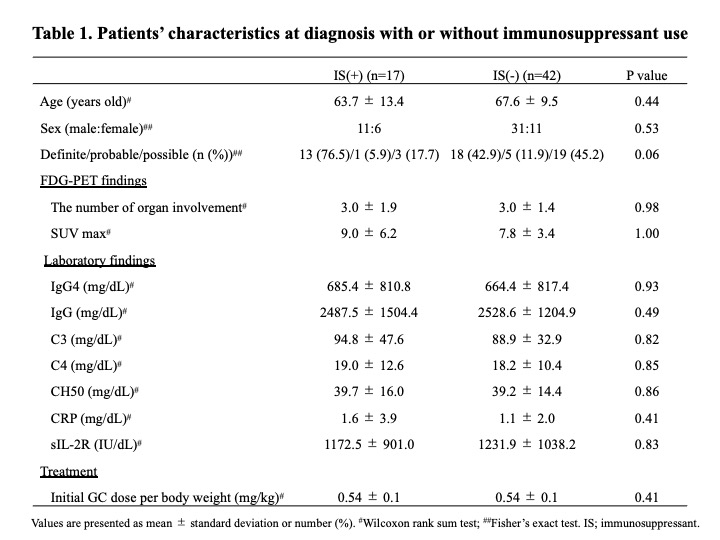
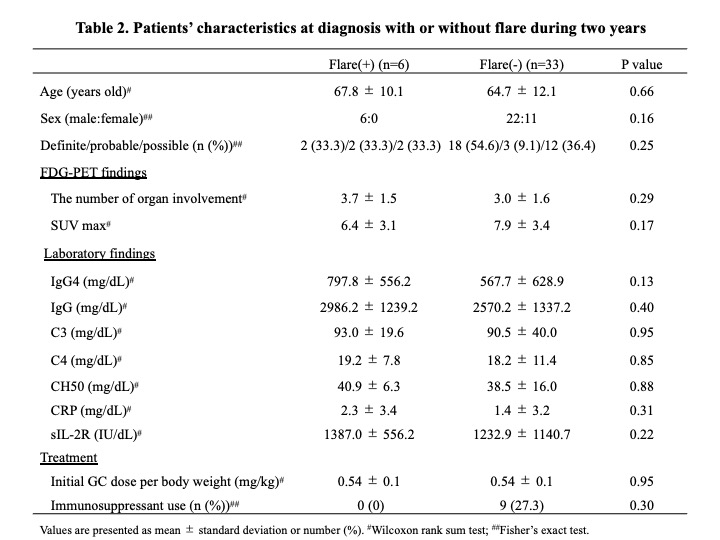
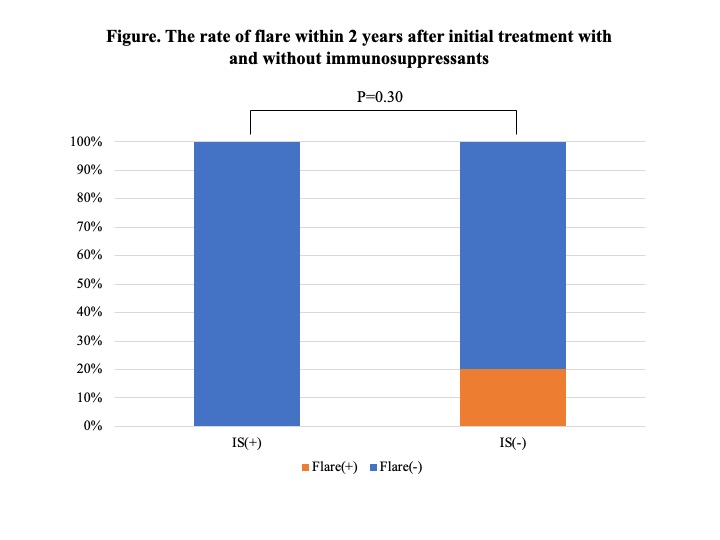
Results: 95 patients were diagnosed according to the 2020 revised comprehensive diagnostic criteria for IgG4-RD. Of these, 59 patients underwent therapeutic intervention, and all cases were initially treated with GC at a mean dose of 0.54 mg/kg body weight. Immunosuppressants were used concomitantly in 30 patients (50.8%), mostly azathioprine. In 17 of these cases, immunosuppressants were started either at the time of initial therapy or GC dose reduction. There was no significant difference between the 17 patients who received these immunosuppressants and the other patients (Table 1), however, the rate of definite cases tended to be higher in the cases who received immunosuppressants (P=0.06). 15 patients (25.4%) relapsed during GC reduction, and the mean time to disease relapse from the start of treatment was 33.2±32.0 months. Most of the disease relapsed cases were treated with GC monotherapy, and after relapse, immunosuppressants were administered in addition to increased doses of GC. Additionally, 39 patients who continued treatment for 2 years were analyzed separately according to whether they relapsed or not (Table 2). There were no significant differences in age at diagnosis, gender, number of lesions, immunological findings including serum IgG4 levels, or GC dose at the start of treatment. However, all patients who had received immunosuppressants either at the time of initial treatment or GC dose reduction did not relapse during the 2-year period (Figure). Their GC dose at 2 years after the start of treatment was 4.1 ± 2.1 mg/day. In contrast, the GC dose at relapse in the 6 patients relapsing within 2 years was 7.8 ± 1.4 mg/day.
Conclusion: No relapses were observed in patients treated with immunosuppressants during the first 2 years of treatment. Early concomitant use of immunosuppressants is a useful therapeutic strategy for IgG4-RD, but further studies are needed to determine which patients should be considered for concomitant use.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Chujo K, Shimada H, Ozaki H, Wakiya R, Nakashima S, miyagi t, Ushio Y, Sugihara K, Mizusaki M, Mino R, Kagawa R, Yamaguchi H, Kameda T, Dobashi H. Efficacy of Immunosuppressants for Disease Relapse in Patients with IgG4-related Disease at Our Institution [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/efficacy-of-immunosuppressants-for-disease-relapse-in-patients-with-igg4-related-disease-at-our-institution/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/efficacy-of-immunosuppressants-for-disease-relapse-in-patients-with-igg4-related-disease-at-our-institution/