Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Cenerimod is an orally active, selective sphingosine 1-phosphate (S1P) 1 receptor modulator under investigation for the treatment of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). In the Phase 2 CARE study (NCT03742037), patients treated with cenerimod 4 mg showed reduced disease activity versus placebo after 6 months.1
Type-1 interferon (IFN-1) activation is a robust biomarker of SLE disease activity, and an elevated IFN-1 signature associates with autoantibodies and more active disease. Cenerimod reduces plasma levels of IFN-α and leads to decreased circulating B and T cells in patients with SLE, suggesting effects on innate and acquired immune responses.
Here the efficacy of cenerimod in patients with high IFN-1 gene expression signature and high anti-dsDNA antibody levels is presented, as reported at EULAR 2023.2
Methods: CARE randomized 427 patients with SLE to once-daily cenerimod (0.5, 1, 2, 4 mg) or placebo. At month (M) 6, patients on 4 mg cenerimod were re-randomized to placebo or cenerimod 2 mg for the remaining 6 months; other groups continued their initially assigned treatment to M12. The primary endpoint was change from baseline to M6 in SLEDAI-2K score modified to exclude leukopenia (mSLEDAI-2K) due to the mechanism of action of cenerimod.
Subgroup analyses were performed in patients with high IFN-1 gene expression signature (based on expression of IFI27, RSAD2, HERC5, and IFIT1) or anti-dsDNA levels ≥30 IU/mL.
Results:
At baseline, 207/408 patients (51%) in CARE had high IFN-1 gene expression signature [including 36 (45%) and 40 (50%) on cenerimod 4 mg and placebo, respectively], and 86/426 (20%) had anti-dsDNA antibody levels ≥30 IU/mL [21 (25%) and 15 (17%) for cenerimod 4 mg and placebo, respectively]. There was an association between high IFN-1 gene expression signature and high anti-dsDNA levels, with more than 75% of patients with anti-dsDNA levels ≥30 IU/mL having high IFN-1 gene expression signature.
Cenerimod 4 mg resulted in decreased levels of anti-dsDNA antibodies and IFN-a protein at M6 versus baseline. In patients with high IFN-1 gene expression signature or high anti-dsDNA, 4 mg cenerimod led to greater reductions of disease activity versus placebo, as measured by mSLEDAI and SRI-4 at M6.
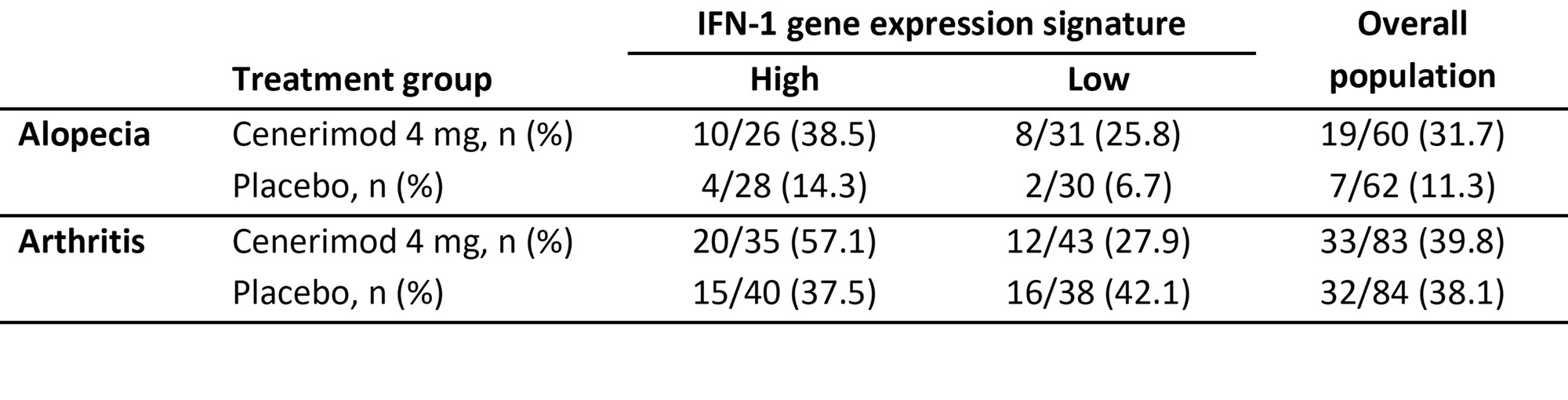
More patients with high IFN-1 gene expression signature at baseline had resolution of arthritis and alopecia at M6 in the treatment arm versus patients with the low IFN-1 gene expression signature (Table 1).
Conclusion: Treatment with cenerimod 4 mg resulted in greater reduction of disease activity versus placebo at M6 in patients with baseline high IFN-1 gene expression signature or high anti-dsDNA antibody levels. Cenerimod treatment also reduced levels of IFN-α protein and anti-dsDNA antibodies in these patients. Two Phase 3 studies designed to evaluate the treatment effect of cenerimod 4 mg in SLE are underway.
References
1. Askanase A et al. Arthritis Rheumatol 2022;74(Suppl 9):3293–7.
2. Adapted by permission from BMJ Publishing Group Limited. Askanase A et al. DOI: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2023-eular.3823.
Acknowledgements Medical writing support was provided by Anne Sayers and funded by Idorsia Pharmaceuticals Ltd.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Askanase A, D'Cruz D, Kalunian K, Merrill J, Navarra S, Cahuzac C, Cornelisse P, Strasser D, Trokan L, Berkani O. Efficacy of Cenerimod in Patients with High IFN-1 Gene Expression Signature and High Anti-dsDNA Antibody Levels: Post-hoc Analysis from a Phase 2 Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/efficacy-of-cenerimod-in-patients-with-high-ifn-1-gene-expression-signature-and-high-anti-dsdna-antibody-levels-post-hoc-analysis-from-a-phase-2-study/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/efficacy-of-cenerimod-in-patients-with-high-ifn-1-gene-expression-signature-and-high-anti-dsdna-antibody-levels-post-hoc-analysis-from-a-phase-2-study/