Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session (Sunday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: ABP 710 is being developed as a biosimilar to infliximab. Both ABP 710 and infliximab reference product (RP) inhibit tumor necrosis factor-alpha. Following demonstration of analytical (structural and functional) similarity and clinical pharmacokinetic equivalence in a phase 1 study, a comparative phase 3 clinical trial in patients with moderate to severe RA was conducted. The objective of this analysis was to show the results of the ACR individual components for ABP 710 in comparison with infliximab RP.
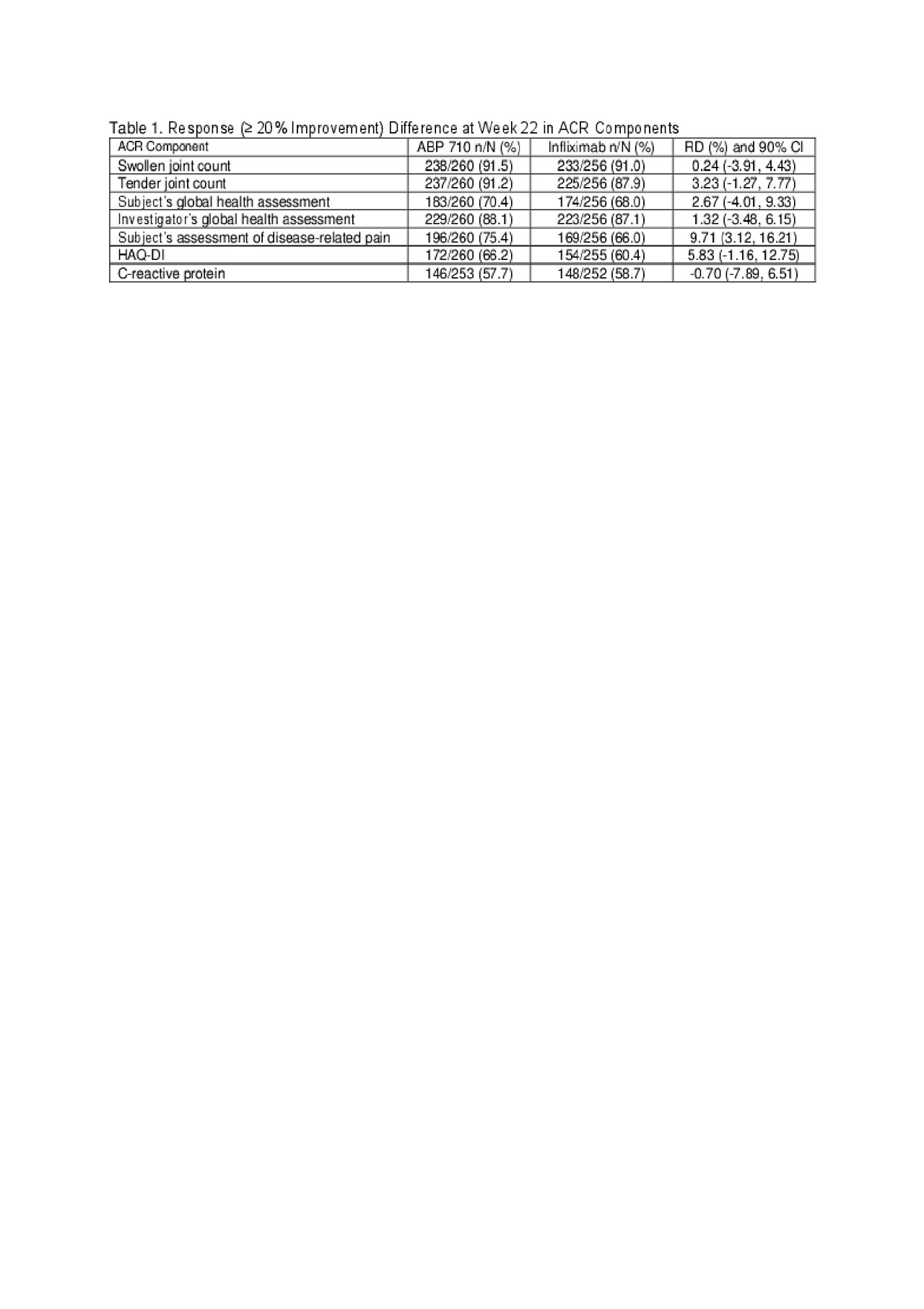
Methods: In this multicenter, randomized, double-blind study, the efficacy and safety of ABP 710 was compared with the RP in subjects with moderate to severe RA. Subjects were maintained on a stable 7.5 to 25 mg/week dose of methotrexate and received 3 mg/kg infusions of the investigational products at predetermined intervals. The primary endpoint of the study was response difference (RD) of at least 20% improvement compared with baseline in ACR core set of measurements (ACR20) at week 22. Individual components of ACR were summarized descriptively at each visit, which included swollen joint count and tender joint count, Subject’s Global Health Assessment, Investigator’s Global Health Assessment, Subject’s Assessment of Disease-related Pain, Health Assessment Questionnaire – Disability Index (HAQ-DI) total score, and C-reactive protein (CRP).
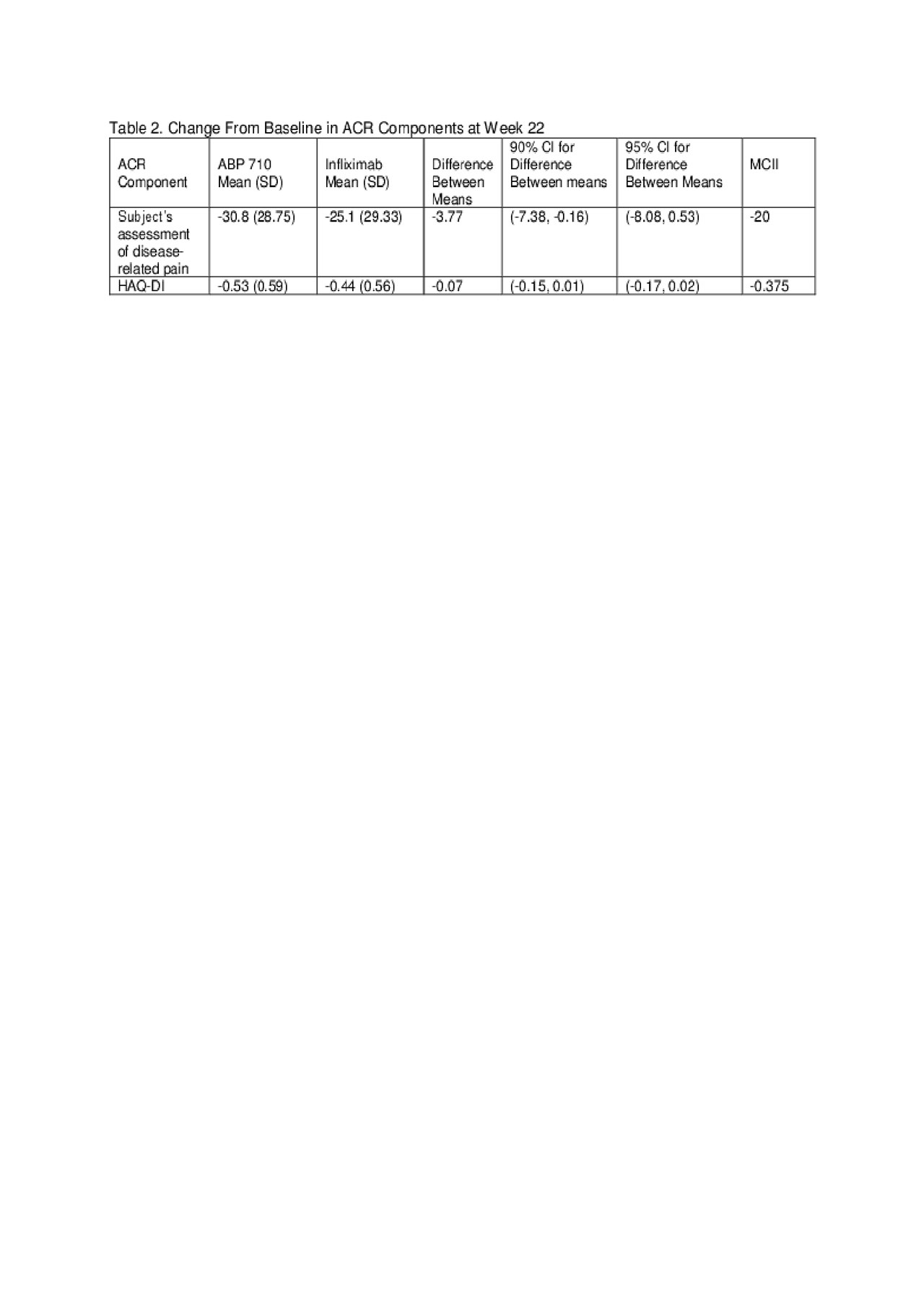
Results: Of the 558 randomized subjects, 556 were treated (ABP 710 n=278; RP n=278); 484 subjects continued in the study through week 22 to be re-randomized (ABP 710/ABP 710: n=244; infliximab RP/infliximab RP: n=121; infliximab RP/ABP 710: n=119), and 435 subjects completed the study. Results of the ACR components (based on a response of ≥20% improvement) at week 22 are shown in Table 1. ACR components with the largest RD between treatment groups were Subject’s Assessment of Disease-related Pain and HAQ-DI; yet the difference in mean change from baseline and associated 90% and 95% confidence intervals (CIs) were well below the thresholds of minimal clinically important improvement and thus, not clinically meaningful (Table 2).
Conclusion: This analysis of ACR individual components further supports the similarity of ABP 710 and infliximab RP.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Genovese M, Sanchez-Burson J, Balázs �, Everding A, Oh M, Fanjiang G, Cohen S. Efficacy of Biosimilar Candidate ABP 710 in a Phase 3 Study in Subjects with Moderate to Severe RA: Additional Analysis Focusing on the ACR Individual Components [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/efficacy-of-biosimilar-candidate-abp-710-in-a-phase-3-study-in-subjects-with-moderate-to-severe-ra-additional-analysis-focusing-on-the-acr-individual-components/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/efficacy-of-biosimilar-candidate-abp-710-in-a-phase-3-study-in-subjects-with-moderate-to-severe-ra-additional-analysis-focusing-on-the-acr-individual-components/