Session Information
Date: Friday, November 6, 2020
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 3:00PM-3:50PM
Background/Purpose: Behçet’s syndrome is a chronic, multi-system inflammatory disorder characterized by painful and recurrent oral ulcers (OU) and other manifestations, such as skin lesions and arthritis, that have a significant impact on quality of life (Hatemi G. Ann Rheum Dis. 2018;77:808-818). Apremilast, an oral phosphodiesterase 4 inhibitor, demonstrated efficacy in the treatment of OU in the phase 3 RELIEF study (Hatemi G, et al. N Engl J Med. 2019;381:1918-1928). We describe outcomes for non-OU manifestations of Behçet’s syndrome in patients (pts) treated with apremilast (APR) 30 mg BID vs placebo (PBO) in RELIEF.
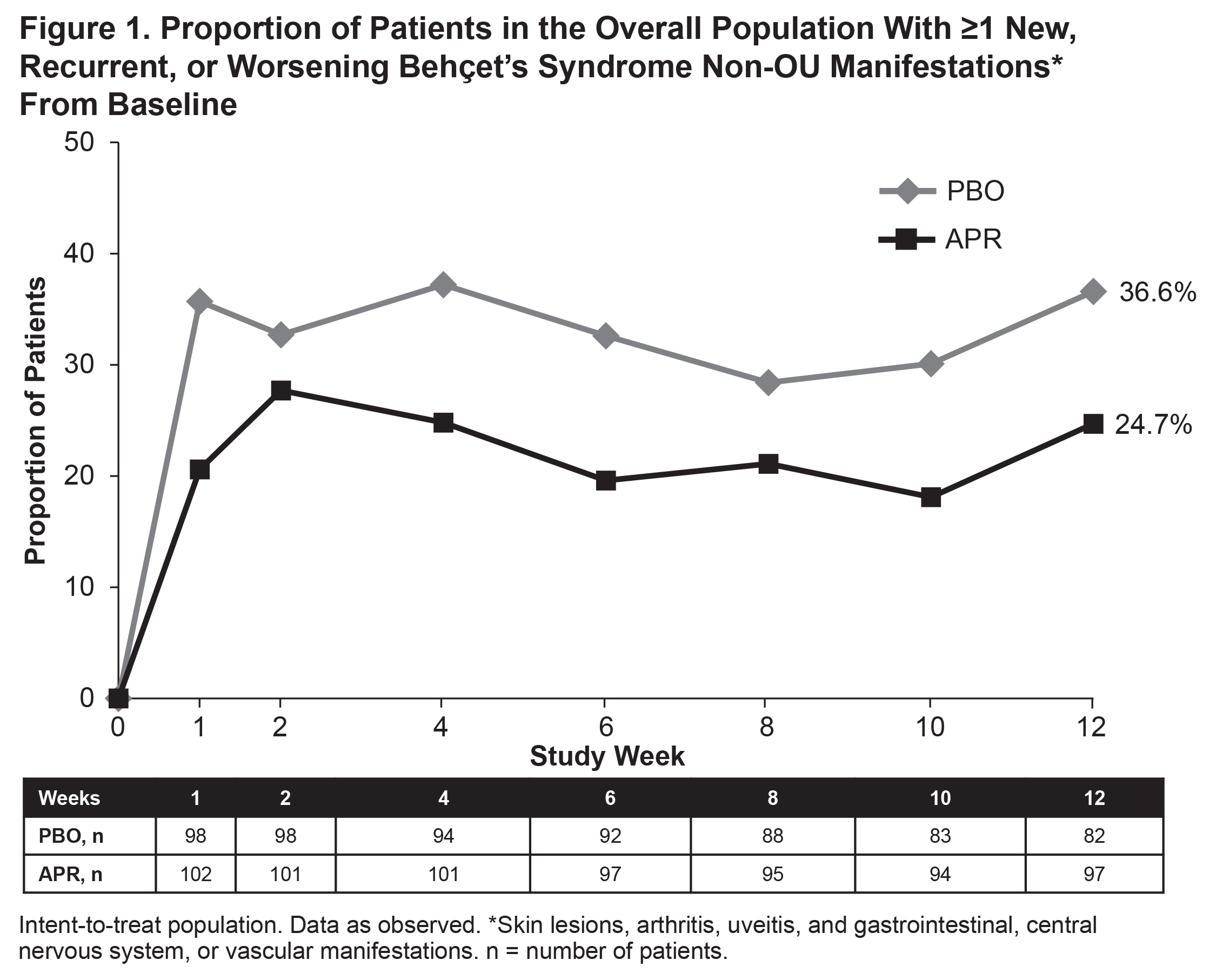
Methods: RELIEF was a multicenter, randomized, double-blind, PBO-controlled study (BCT-002; NCT02307513). Eligible pts were adults with active Behçet’s syndrome and ≥3 OU at randomization or ≥2 OU at screening and randomization, without active major organ involvement. Pts were randomized (1:1) to receive APR or PBO up to Week 12 and stratified by region (Japan/other). The proportions of pts with ≥1 new, recurrent, or worsening non-OU manifestations (ie, skin lesions, arthritis, uveitis, and gastrointestinal, CNS, or vascular manifestations) were assessed up to Week 12 in the overall population and in a Japanese subgroup. Change from baseline (BL) at Week 12 in scores on the Physician’s Global Assessment (PGA) of skin lesions, swollen joint count (SJC), and tender joint count (TJC) in pts with skin lesions, SJC >0, and TJC >0 at BL, respectively, were assessed in the overall and Japanese subgroup populations.
Results: A total of 207 pts were randomized and received ≥1 dose of study medication in the overall population (APR: n=104; PBO: n=103), including 39 pts in the Japanese subgroup (APR: n=19; PBO: n=20). During the 12-week PBO-controlled period, the proportions of pts with ≥1 new, recurrent, or worsening non-OU manifestations (Figure 1), skin lesions (Figure 2), or arthritis (Figure 3) were lower in pts treated with APR vs PBO in the overall population. In the Japanese subgroup, lower proportions of pts in the APR vs PBO group had new, recurrent, or worsening non-OU manifestations (5.9% [1/17] vs 31.3% [5/16]), skin lesions (5.9% [1/17]) vs 18.8% [3/16]), and arthritis (0.0% [0/17] vs 6.3% [1/16]) at Week 12. In the overall population treated with APR vs PBO, mean (SD) BL values were 3.4 (3.1) vs 5.7 (7.1) for SJC and 6.5 (8.5) vs 6.0 (8.0) for TJC; LS mean (95% CI) changes from BL at Week 12 were −0.9 (−1.1, −0.6) vs −0.8 (−1.0, −0.5) for PGA of skin lesions, −3.1 (−5.2, −1.0) vs −2.9 (−5.0, −0.8) for SJC, and −4.4 (−6.3, −2.4) vs −2.7 (−4.5, −0.9) for TJC. In the Japanese subgroup treated with APR vs PBO, mean (SD) BL values were 1.5 (0.7) vs 3.7 (3.8) for SJC and 6.4 (10.5) vs 4.3 (4.8) for TJC; LS mean (95% CI) changes from BL at Week 12 were −0.7 (−1.4, −0.1) vs −0.5 (−1.1, 0.2) for PGA of skin lesions, −3.0 (−9.6, 3.6) vs −2.3 (−8.6, 4.0) for SJC, and −3.7 (−6.1, −1.2) vs −2.4 (−4.4, −0.5) for TJC.
Conclusion: Pts with active Behçet’s syndrome in the overall population and the Japanese subgroup of RELIEF achieved lower rates of new, recurrent, or worsening non-OU manifestations, including skin lesions and arthritis, and numerically greater improvements in PGA of skin lesions, SJC, and TJC with APR vs PBO over 12 weeks.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Hatemi G, Mahr A, Takeno M, Kim D, Melikoğlu M, Cheng S, Richter S, Brunori M, Paris M, Chen M, Yazici Y. Efficacy of Apremilast for the Treatment of Manifestations of Behçet’s Syndrome Other Than Oral Ulcers, Including Skin Lesions and Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/efficacy-of-apremilast-for-the-treatment-of-manifestations-of-behcets-syndrome-other-than-oral-ulcers-including-skin-lesions-and-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/efficacy-of-apremilast-for-the-treatment-of-manifestations-of-behcets-syndrome-other-than-oral-ulcers-including-skin-lesions-and-arthritis/