Session Information
Date: Monday, October 22, 2018
Title: Vasculitis Poster II: Behҫet’s Disease and IgG4-Related Disease
Session Type: ACR Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Behçet’s syndrome is a chronic, multi-system inflammatory disorder characterized by recurrent oral ulcers (OU) that can be disabling and negatively affect quality of life. Apremilast (APR), an oral phosphodiesterase 4 inhibitor that modulates inflammatory pathways, has demonstrated efficacy in the treatment of OU of Behçet’s syndrome in a phase III, multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo (PBO)-controlled study (RELIEF).
Methods: In this phase III, multicenter study, adult patients with active Behçet’s syndrome (with ≥3 OU at randomization or ≥2 OU at screening + randomization, without active major organ involvement) were randomized (1:1) to receive APR 30 mg BID or PBO BID for 12 weeks followed by a 52-week active-treatment phase. The primary endpoint was area under the curve for total number of OU over 12 weeks (OU AUCWk0-12). AUC reflects the change in the number of OU over time, accounting for the clinical characteristic that OU repeatedly remit and recur. In a planned analysis, OU AUCWk0-12 was examined among subgroups of patients defined by BL demographics and disease characteristics.
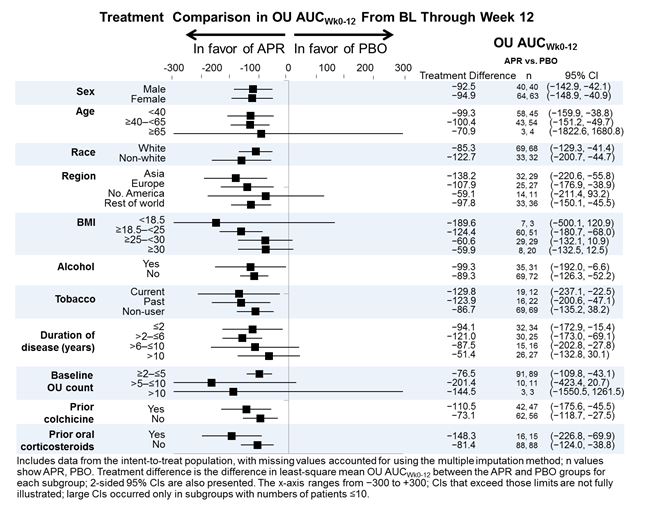
Results: A total of 207 patients were randomized and received ≥1 dose of study medication (APR: n=104; PBO: n=103). At BL, mean numbers of OU were 4.2 for APR and 3.9 for PBO. At Week 12, least-squares mean OU AUCWk0-12 (LS mean ± SE) was significantly lower in patients receiving APR vs. PBO (129.5 ± 15.9 vs. 222.1 ± 15.9; P<0.0001). A treatment effect in favor of the APR treatment group vs. PBO was observed for AUCWk0-12 for OU counts in each of the prespecified subgroups examined. A favorable treatment effect was observed for each demographic subgroup, BL disease characteristic (including duration of disease and BL OU count), geographic region, and prior use of colchicine and corticosteroids (Figure). The incidence of adverse events (AEs) was comparable between APR and PBO (78.8% and 71.8%, respectively). The most common AEs were diarrhea, nausea, headache, and upper respiratory tract infection; most AEs were mild or moderate in severity.
Conclusion: Subgroup analyses of the AUC for the number of OU from BL through Week 12 demonstrated the consistent efficacy of apremilast in all of the subgroups analyzed. The safety profile was consistent with the known safety profile of APR.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Hatemi G, Mahr A, Takeno M, Kim DY, Melikoglu M, Cheng S, McCue S, Paris M, Chen M, Yazici Y. Efficacy of Apremilast for Oral Ulcers Associated with Active Behçet’s Syndrome in a Phase III Study: A Prespecified Analysis By Baseline Patient Demographics and Disease Characteristics [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018; 70 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/efficacy-of-apremilast-for-oral-ulcers-associated-with-active-behcets-syndrome-in-a-phase-iii-study-a-prespecified-analysis-by-baseline-patient-demographics-and-disease-characteristics/. Accessed .« Back to 2018 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/efficacy-of-apremilast-for-oral-ulcers-associated-with-active-behcets-syndrome-in-a-phase-iii-study-a-prespecified-analysis-by-baseline-patient-demographics-and-disease-characteristics/