Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: SLE is a systemic autoimmune disease requiring long-term treatment. In this placebo-controlled phase 3 TULIP long-term extension (LTE) study,1 the impact of anifrolumab in addition to standard therapy on total and organ-specific disease activity was assessed over 4 years in patients with moderate to severe SLE.
Methods: TULIP-LTE (NCT02794285) was the first randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind, 3-year extension study in SLE. Patients with SLE (1997 ACR criteria) on standard therapy who completed a TULIP trial through the 52-week treatment period could enroll in the LTE. Treatment groups used in this analysis were patients randomized to receive intravenous anifrolumab 300 mg or placebo every 4 weeks in TULIP-1/-2 who continued the same treatment (or would have continued if not discontinued during TULIP-1/-2) in the LTE (anifrolumab 300 mg: n=358; placebo: n=178). Proportions of patients with a ≥4-point reduction in total SLEDAI-2K score from Week 0 (baseline) to Week 208 were compared between treatment groups using summary statistics. Proportions of patients with a SLEDAI-2K improvement (patients with improvement [n1] / patients with baseline involvement and available data at the timepoint [n2]) were further analyzed by organ domain (mucocutaneous, musculoskeletal, immunological, hematological/fever) during the TULIP and LTE periods; SLEDAI-2K improvement was defined as a lower organ domain score than at baseline.
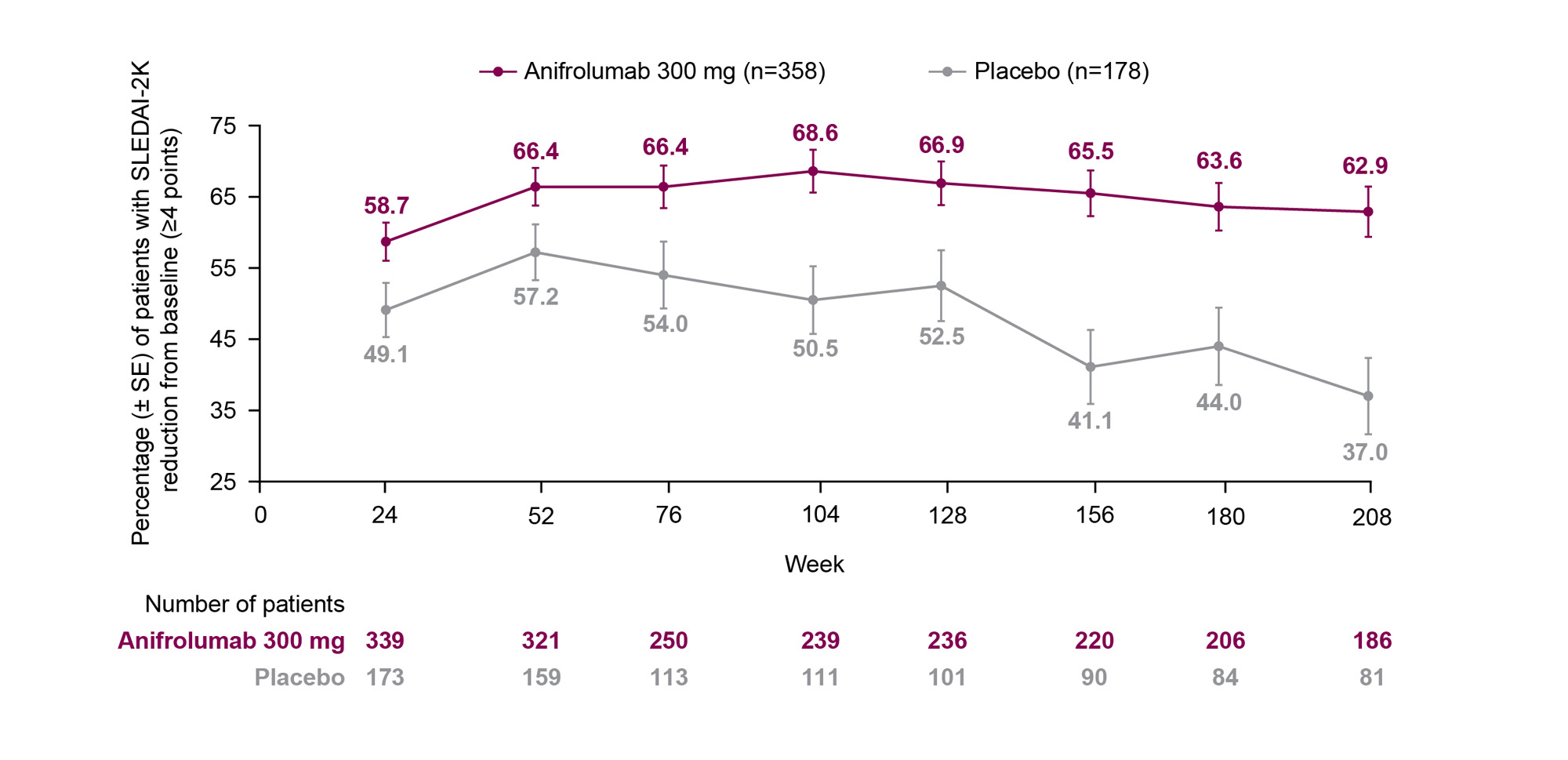
Results: The proportion of patients who achieved a ≥4-point reduction in SLEDAI-2K score from baseline was greater with anifrolumab vs placebo from Week 52 (66.4%, [95% confidence interval: 60.9–71.5] vs 57.2% [49.2–65.0]) to Week 208 (62.9% [55.5–69.9] vs 37.0% [26.6–48.5]), and the difference between the treatment groups increased over time (Figure). Baseline organ involvement was similar between treatment groups in the mucocutaneous and musculoskeletal domains (anifrolumab 300 mg vs placebo: 96.6% vs 95.5% and 93.0% vs 93.8%, respectively). Immunological and hematological/fever baseline involvement were higher in the anifrolumab group compared with placebo (65.6% vs 58.4% and 15.4 vs 9.0%, respectively). Mucocutaneous, musculoskeletal, immunological, and hematological/fever SLEDAI-2K improvements generally occurred more frequently in the anifrolumab group compared with placebo from Week 52 (73.5% [n1/n2: 227/309] vs 60.9% [92/151]; 67.9% [201/296] vs 64.9% [96/148]; 28.8% [61/212] vs 17.2% [16/93]; and 81.6% [40/49] vs 80.0% [12/15]) up to Week 208 (79.8% [142/178] vs 58.7% [44/75]; 71.8% [122/170] vs 56.0% [42/75]; 32.1% [36/112] vs 14.6% [6/41]; and 72.4% [21/29] vs 42.9% [3/7]). By the end of the LTE period, many patients had missing data in the placebo group, due to lack of organ involvement and/or no available data at the timepoint.
Conclusion: Compared with placebo, anifrolumab was associated with long-term, sustained ≥4-point reductions in SLEDAI-2K over the 4-year TULIP and LTE period and, despite the higher drop-out rates in the placebo group, greater improvements were seen in disease activity for individual organ domains. References: 1. Kalunian KC, et al. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023;75:253–65.
LTE, long-term extension; SE, standard error; SLE, systemic lupus erythematosus; SLEDAI_2K, SLE Disease Activity Index 2000.
*Analysis includes patients with a SLEDAI_2K score ≥4 at TULIP baseline (Week 0) and data with discontinuation due to worsening/lack of efficacy non-improvement imputation.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Furie R, Kalunian K, Morand E, Bruce I, Manzi S, Tanaka Y, Withrop K, Hupka I, Hultquist M, Tummala R, Abreu G, Lindholm C, Al-Mossawi H. Efficacy of Anifrolumab in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus by Overall and Organ-Specific SLEDAI-2K Improvements: Results from the Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Phase 3 Long-Term Extension Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/efficacy-of-anifrolumab-in-systemic-lupus-erythematosus-by-overall-and-organ-specific-sledai-2k-improvements-results-from-the-randomized-placebo-controlled-phase-3-long-term-extension-study/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/efficacy-of-anifrolumab-in-systemic-lupus-erythematosus-by-overall-and-organ-specific-sledai-2k-improvements-results-from-the-randomized-placebo-controlled-phase-3-long-term-extension-study/