Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Interstitial lung disease (ILD) is a severe extra-articular manifestation of rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Usual interstitial pneumonia (UIP) is the most frequent, and severe ILD pattern in RA. Abatacept (ABA) has demonstrated effectiveness in RA-ILD during a 12-month period of treatment [Rheumatology (Oxford) 2020;59(12):3906-16, Rheumatology (Oxford) 2021;61(1):299-308]. However, little is known about the specific effect of ABA in the UIP pattern. Therefore, the aim of this study was to assess the effectiveness and safety of ABA in RA-ILD patients with radiological pattern of UIP during a long-term follow-up.
Methods: From a large observational multicenter study of 509 RA-ILD patients treated with ABA, we selected those with UIP. The following outcomes were assessed from baseline to final follow-up: a) pulmonary function tests (PFTs) -forced vital capacity (FVC) and diffusing capacity of the lungs for carbon monoxide (DLCO)-, c) chest high resolution computed tomography (HRCT), d)dyspnea (evaluated with the modified Medical Research Council scale), and e) arthritis activity (measured with DAS28-ESR).
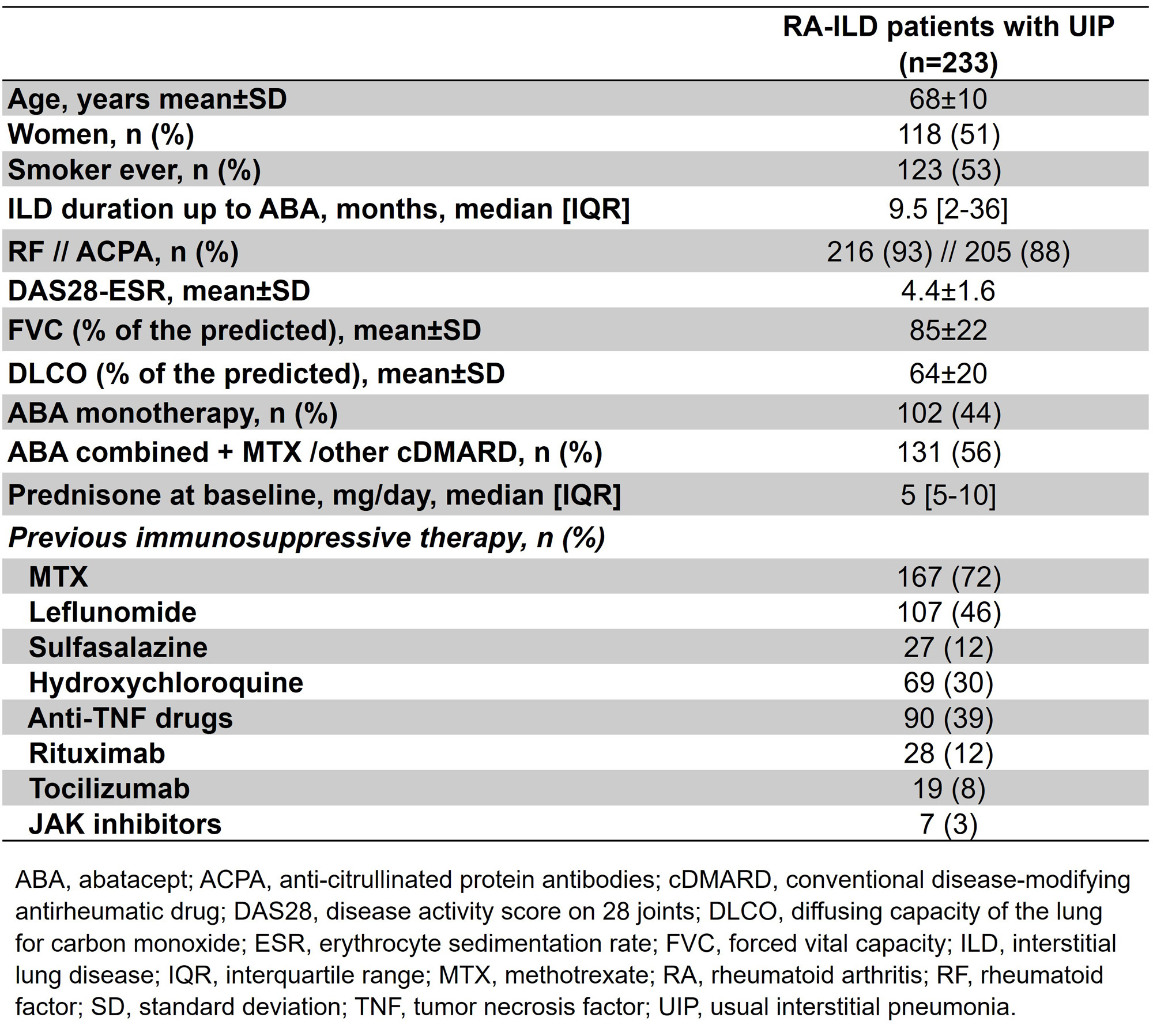
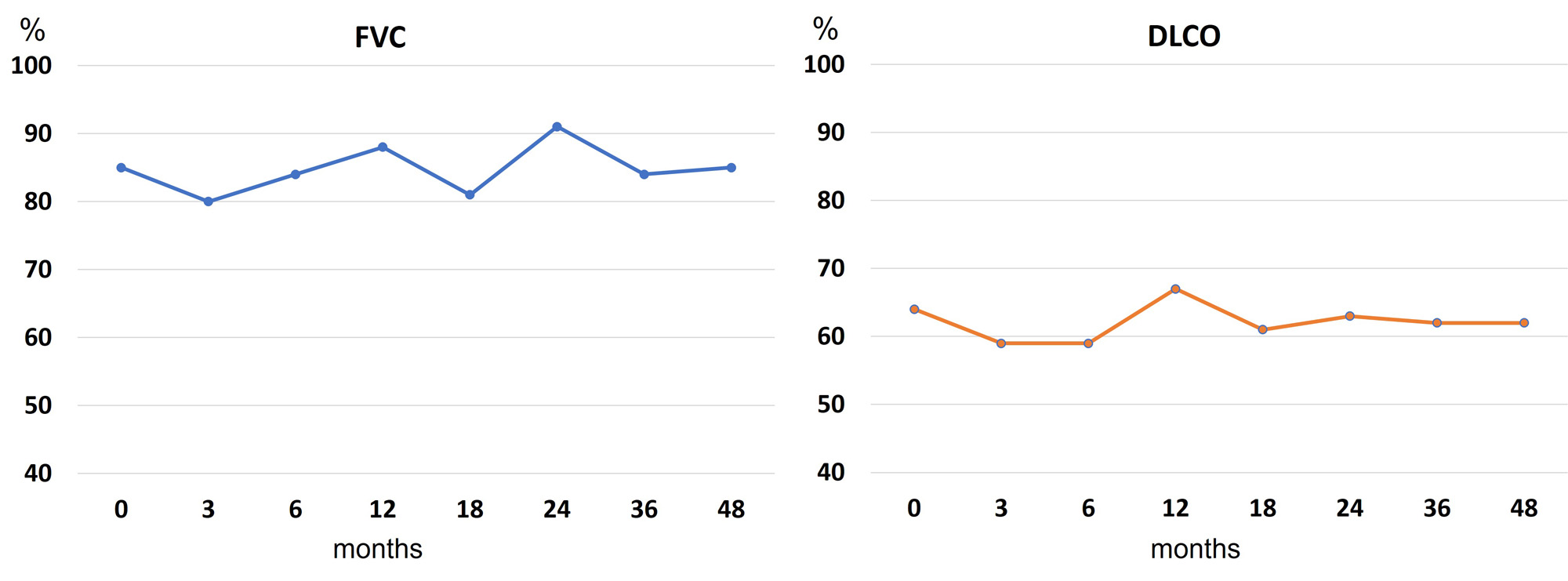
Results: We included a total of 233 patients with UIP (118 women/115 men; mean age of 67.5±9.9 years). Table 1 shows baseline demographic and clinical characteristics. The median ILD duration up to ABA initiation was relatively short, with a median [IQR] of 9.5 [2-36] months. Mean baseline values of FVC and DLCO were >80% and >60%, respectively. During a median of 22 [6-43] months of ABA therapy, 73.8% and 59.4% of patients showed an improvement/ stabilization of FVC and DLCO, respectively. Figure 1 displays the evolution of PFTs along 48 months. Available chest HRCT images improved/ stabilized in 67.1% of patients. Stabilization or improvement of dyspnea was found in 79.5% of patients. The majority of patients showed articular remission or low activity (mean DAS28-ESR of 4.4±1.6 at baseline and 2.6±1.3 at 48 months). ABA was withdrawn in 50 (21.5%) patients due to ILD worsening (n=20), articular inefficacy (n=15), serious infections (n=7), and other causes (n=8, development of malignancy in 3, neutrophilic dermatosis in 1, diagnosis of giant cell arteritis and change to tocilizumab in 1, patient’s decision in 1, and 2 deceases).
Conclusion: ABA demonstrates a long-term efficacy and safety in patients with RA-associated UIP, the most severe pattern of ILD in RA patients.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Atienza-Mateo B, Serrano-Combarro A, del Val del Amo N, Casafont-Sole I, Melero-Gonzalez R, Serrano-García I, Castañeda S, Calvo J, Mena Vazquez N, Vegas Revenga N, Domínguez-Casas L, Osorio Sanjuan M, Díez Morrondo C, Perez-Albadalejo L, Lopez-Sanchez R, Mazano Canabal M, Brandy-Garcia A, Lopez-Viejo P, Bonilla G, Maiz-Alonso O, carrasco-Cubero C, Garijo Bufort M, Moreno M, Urruticoechea A, Ordonez-Palau S, Gonzalez-Montagut Gomez C, Garcia-Valle a, De Dios J, Lozano F, Vazquez-Rodriguez T, Carreira P, Blanco-Madrigal J, ROJAS HERRERA S, Brana Abascal I, Loarce-Martos J, Giner-Serret E, Sarmiento-Monroy J, ventin-Rodriguez C, Rodriguez-lopez M, Andujar-Brazal P, Fernandez-Melon J, Lopez L, Fernandez-Diaz c, Loricera J, Ferraz Amaro I, Ferrer D, Blanco R, Collaborative Group Members O. Efficacy of Abatacept in Rheumatoid Arthritis- associated Usual Interstitial Pneumonia. National Multicenter Study of 233 Patients During a Long-Term Follow Up [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/efficacy-of-abatacept-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-associated-usual-interstitial-pneumonia-national-multicenter-study-of-233-patients-during-a-long-term-follow-up/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/efficacy-of-abatacept-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-associated-usual-interstitial-pneumonia-national-multicenter-study-of-233-patients-during-a-long-term-follow-up/