Session Information
Session Type: ACR Late-breaking Abstract Session
Session Time: 4:30PM-6:00PM
Background/Purpose: To evaluate the efficacy, safety, and tolerability of guselkumab (GUS), a fully human monoclonal antibody against the p19 subunit of IL-23, in patients (pts) with active psoriatic arthritis (PsA).
Methods: In this double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicenter study, pts with active PsA and ≥3% body surface area (BSA) of plaque psoriasis despite current or previous treatment with standard-of-care therapies, including those previously exposed to anti-TNFα agents, were randomized 2:1 to receive GUS 100 mg subcutaneously (SC) or placebo (PBO) at wks 0, 4, and every 8 wks (q8w) thereafter through wk44. At wk16, pts from either group with <5% improvement from baseline in both swollen and tender joint counts were eligible for early escape to open-label ustekinumab. At wk24, all remaining PBO pts crossed-over to receive GUS 100 mg, and then received GUS at wk28, and q8w thereafter through wk44. The primary endpoint was ACR 20 response at wk24. Major secondary endpoints were PASI 75 and ACR 50 responses, change from baseline in HAQ-DI, and improvement in enthesitis (Leeds enthesitis index) and dactylitis score (by a 0-3 scoring system) at wk24; and ACR 20 response at wk16. Other secondary endpoints included change from baseline in SF-36 and proportion of pts achieving Minimal Disease Activity (MDA). Through wk24, efficacy analyses were performed in a modified Intent-to-Treat (mITT) population. Pts who met treatment failure criteria, early escaped or had missing data at wk24, were considered non-responders for ACR and MDA endpoints at wk24.
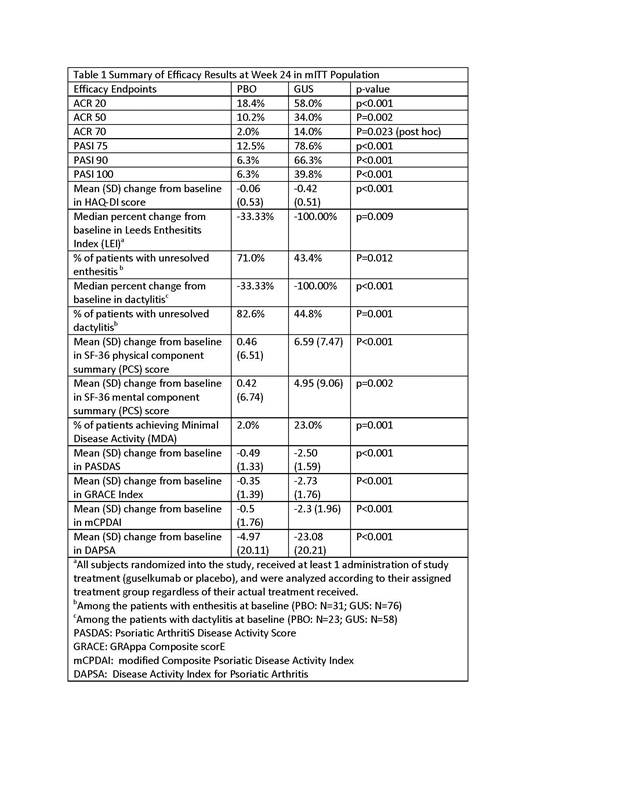
Results: 149 pts were randomized to receive study agent (PBO: 49, GUS: 100). Baseline demographics and ACR component measures were generally similar between the two groups. Four [8.2%] pts in PBO and 9 [9.0%] pts in GUS were previously exposed to TNFα agents. The study met its primary and all secondary endpoints. Significantly more GUS pts achieved ACR 20/50/70 responses and PASI 75/90/100 responses at wk24 (Table 1). Significant treatment effect on ACR20 response was observed as early as wk4 (21% vs 0, p<0.001), and the effect increased over time reaching the maximum by wk16 (60.0% vs. 16.3%, p<0.001) vs. PBO. Results for other secondary efficacy endpoints are summarized in Table 1. Through wk24, proportions of pts with ≥1 AE were comparable between the two groups (PBO: 32.7%; GUS: 36.0%, respectively). Infections were the most common AEs (PBO: 20.4%; GUS: 17.0%, respectively). Two pts had SAEs (knee injury, n=1; myocardial infarction, n=1). There were no serious infections, malignancies, or deaths through wk24.
Conclusion: In pts with active PsA and ≥3% BSA of psoriasis, GUS demonstrated significant improvement on joint symptoms, physical function, psoriasis, enthesitis, dactylitis and quality of life. GUS was well tolerated with no unexpected safety findings in this population.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Deodhar AA, Gottlieb AB, Boehncke WH, Dong B, Wang Y, Barchuk W, Xu X, Hsia EC. Efficacy and Safety Results of Guselkumab, an Anti-IL23 Monoclonal Antibody, in Patients with Active Psoriatic Arthritis over 24 Weeks: A Phase 2a, Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016; 68 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/efficacy-and-safety-results-of-guselkumab-an-anti-il23-monoclonal-antibody-in-patients-with-active-psoriatic-arthritis-over-24-weeks-a-phase-2a-randomized-double-blind-placebo-controlled-study/. Accessed .« Back to 2016 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/efficacy-and-safety-results-of-guselkumab-an-anti-il23-monoclonal-antibody-in-patients-with-active-psoriatic-arthritis-over-24-weeks-a-phase-2a-randomized-double-blind-placebo-controlled-study/