Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Proteinuria is the most common manifestation of lupus nephritis and is a mediator of progressive kidney damage. Early reductions in urine protein creatinine ratio (UPCR) have shown to be predictive of improved long-term outcomes in LN. However, recent studies with monoclonal antibody therapies have demonstrated a lack of efficacy in patients with moderate to high proteinuria (UPCR ≥2 to ≥3 g/g), potentially due to an increase in renal excretion of drug. In a pooled analysis of the Phase 2 AURA-LV and Phase 3 AURORA 1 studies, the addition of voclosporin to mycophenolate mofetil (MMF) and low-dose glucocorticoids resulted in earlier and greater reductions in proteinuria, regardless of baseline demographics or disease characteristics. To further characterize the efficacy and safety of voclosporin in patients with moderate to high proteinuria, we have analyzed outcomes in patients with UPCR ≥2 g/g using the pooled dataset.
Methods: Both studies enrolled patients with biopsy-proven LN (Class III, IV, or V ± III/IV) within 6 months (or up to 2 years in AURORA 1) and proteinuria ≥1.5 g/g (≥2 g/g for Class V). Patients were randomized to voclosporin (23.7 mg BID) or placebo and treated for up to one year (48 weeks [AURA-LV], 52 weeks [AURORA 1]); all patients received MMF and low-dose glucocorticoids. For this post hoc analysis, complete renal response (CRR) rates were evaluated in patients with baseline UPCR ≥2 g/g. Complete renal response was defined as UPCR ≤0.5 g/g with stable renal function, low-dose steroids, and no rescue medication; partial renal response (PRR) was defined as a ≥50% reduction in UPCR from baseline. Adverse events (AEs) and measures of renal function were also assessed.
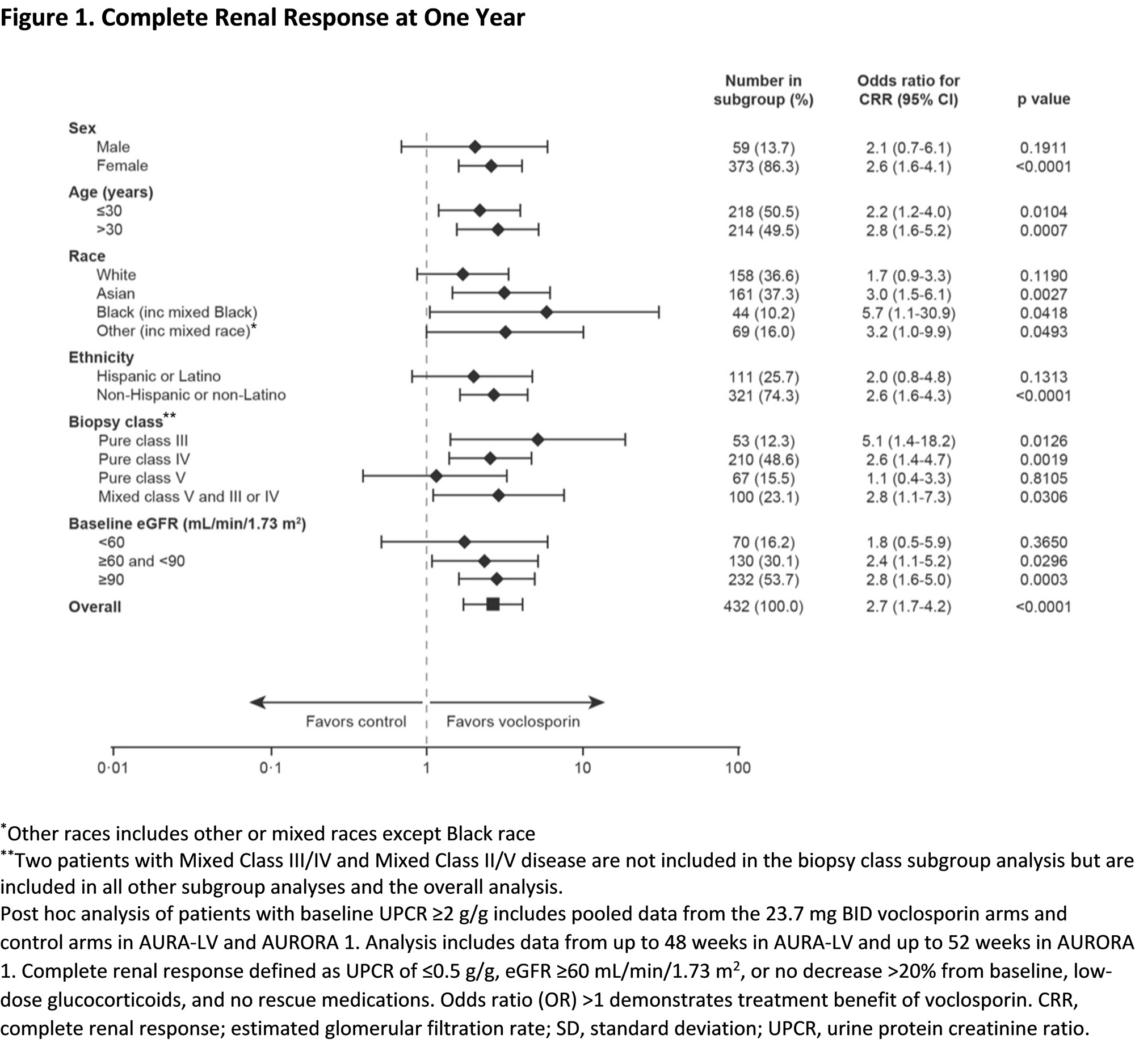
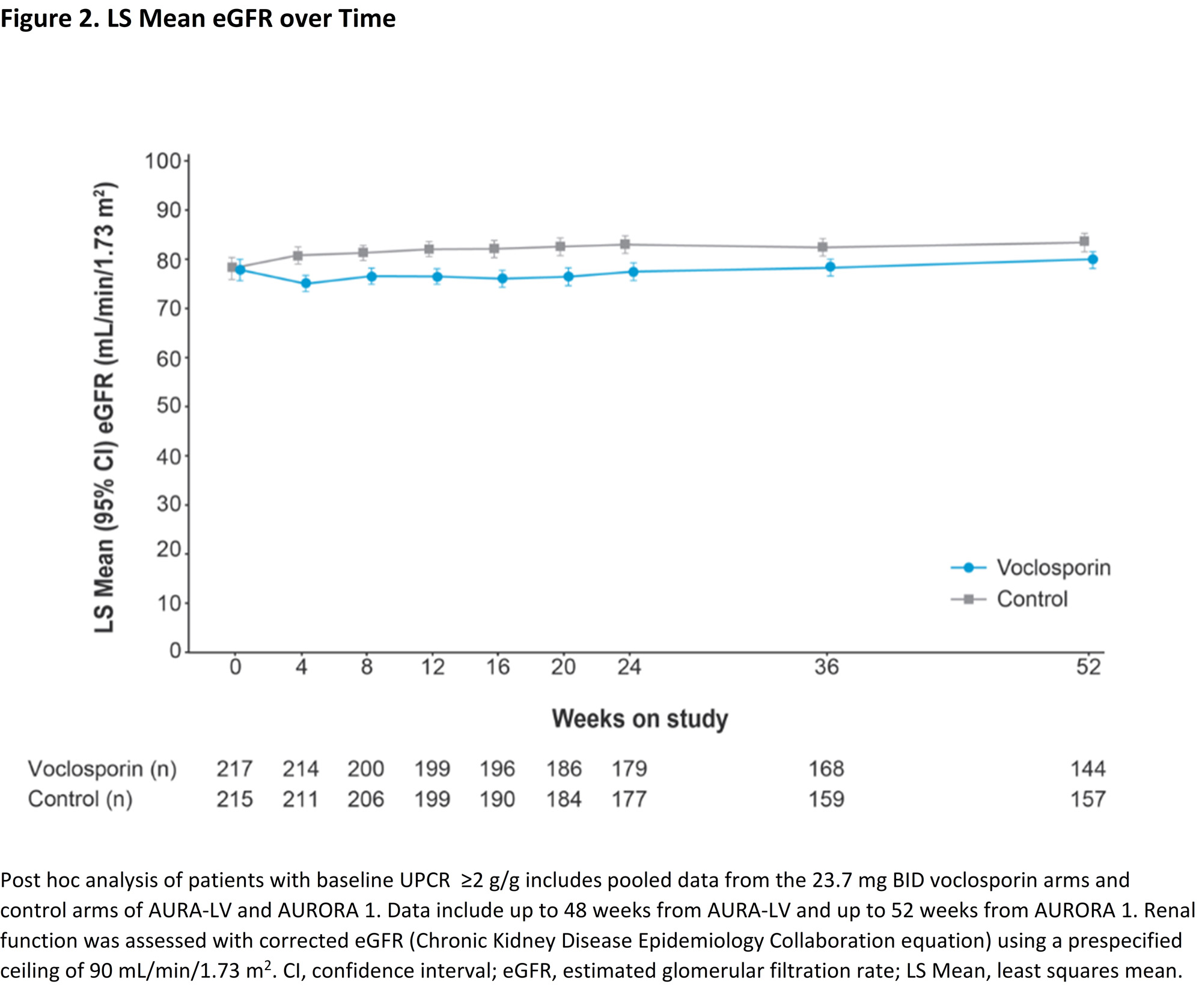
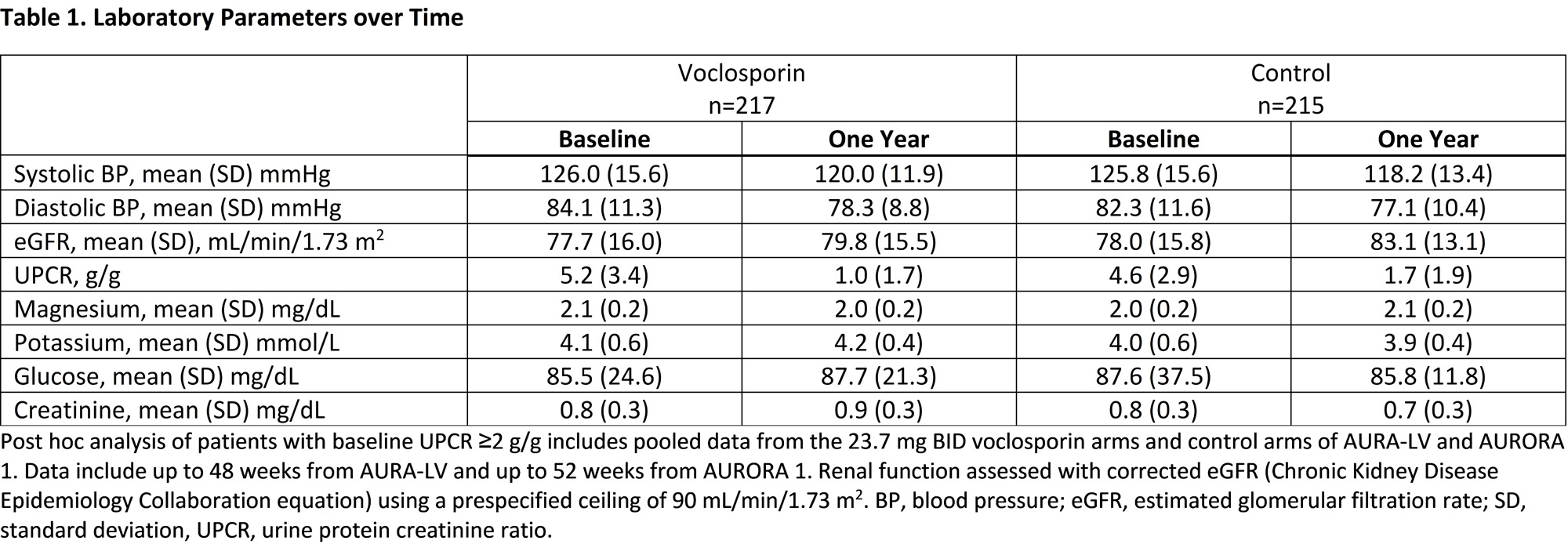
Results: Of the 268 and 266 patients included in the voclosporin and control arms of the pooled analysis, 217 and 215 patients had a baseline UPCR ≥2 g/g (mean [SD], 5.2 [3.4] vs. 4.6 [2.9] g/g). At one year, the change from baseline in least squares (LS) mean UPCR was significantly greater in the voclosporin arm (p=0.0003). A significantly greater percentage of voclosporin-treated patients achieved CRR at one year compared to the control arm (41.0% vs. 21.9%; odds ratio [OR] 2.48, p< 0.0001; Figure 1). Significantly more patients in the voclosporin arm (69.6%) than control arm (50.0%) achieved a PRR at one year (OR 2.3, p< 0.0001). Similar rates of AEs were reported in both arms. Measures of renal function, including mean eGFR, were similar and stable over one year of treatment (Figure 2, Table 1).
Conclusion: Consistent with results from the overall pooled study population, patients with UPCR ≥2 g/g treated with voclosporin achieved significantly higher renal response rates than patients treated with MMF and low-dose glucocorticoids alone while renal function in both arms remained comparable. This is clinically relevant given the lack of safe and effective therapies for patients with high proteinuria.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Littlejohn E, Almaani S, Birardi V, Yap E, Collins C. Efficacy and Safety of Voclosporin in Patients with Proteinuria > 2 G/g [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/efficacy-and-safety-of-voclosporin-in-patients-with-proteinuria-2-g-g/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/efficacy-and-safety-of-voclosporin-in-patients-with-proteinuria-2-g-g/