Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 8, 2020
Title: Spondyloarthritis Including Psoriatic Arthritis – Treatment Poster III
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Upadacitinib (UPA) has demonstrated efficacy for the treatment of AS in patients (pts) who were NSAID inadequate responders (IR).1 Pts with psoriatic arthritis (PsA) and axial involvment often exhibit greater disease activity and quality of life impairments compared with those without axial involvment. The aim of this analysis was to characterize PsA pts with and without axial involvement and compare efficacy of UPA vs placebo (PBO) in PsA pts with axial involvement.
Methods: In SELECT-PsA 1 (NCT03104400; N=1705, non-biologic DMARD IR) and SELECT-PsA 2 (NCT03104374; N=642, biologic DMARD IR), pts with active PsA (≥3 swollen and ≥3 tender joints), active or historical psoriasis, and on ≤2 non-biologic DMARDs were randomized to once daily UPA 15 mg, UPA 30 mg, adalimumab 40 mg every other week (SELECT-PsA 1 only), or PBO. At baseline (BL), the presence of psoriatic spondylitis was assessed by the investigator based on the totality of information available, and characteristics were compared for pts with and without axial involvement. Efficacy was assessed in pts with axial involvement using pooled data from the 2 studies for pts on PBO, UPA 15 mg, or UPA 30 mg. Assessments included change from BL in overall BASDAI, BASDAI question 2 (neck/back/hip pain) and question 3 (joint swelling/pain), and the AS Disease Activity Score (ASDAS) based on CRP, and the percentage of pts with BASDAI 50 response, ASDAS inactive disease (ID), ASDAS low disease activity (LDA), ASDAS major improvement (MI), and ASDAS clinically important improvement (CII) responses. Adverse events were reviewed to identify new onset or worsening uveitis and inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). Data are presented through the end of the 24-week PBO-controlled period.
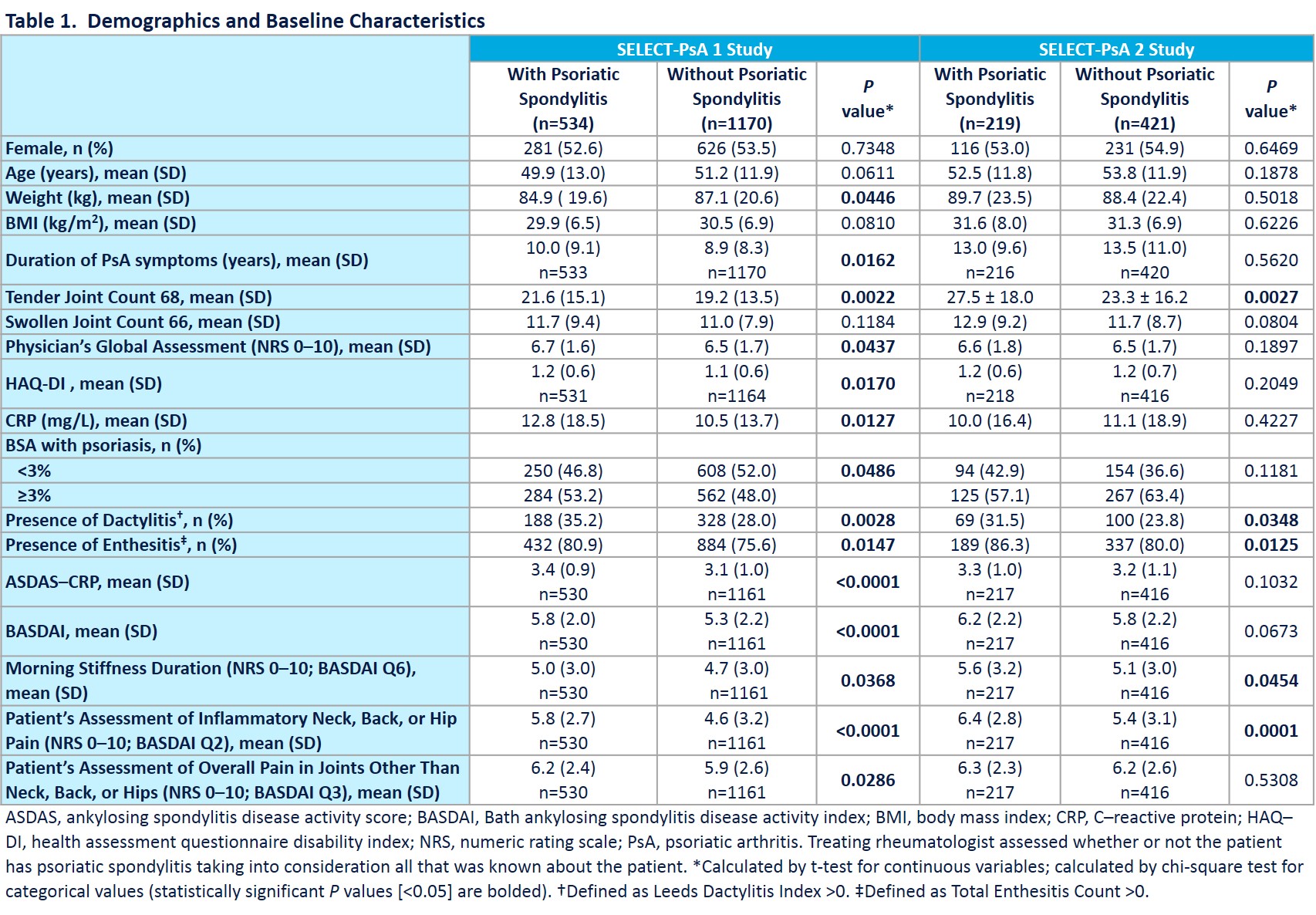
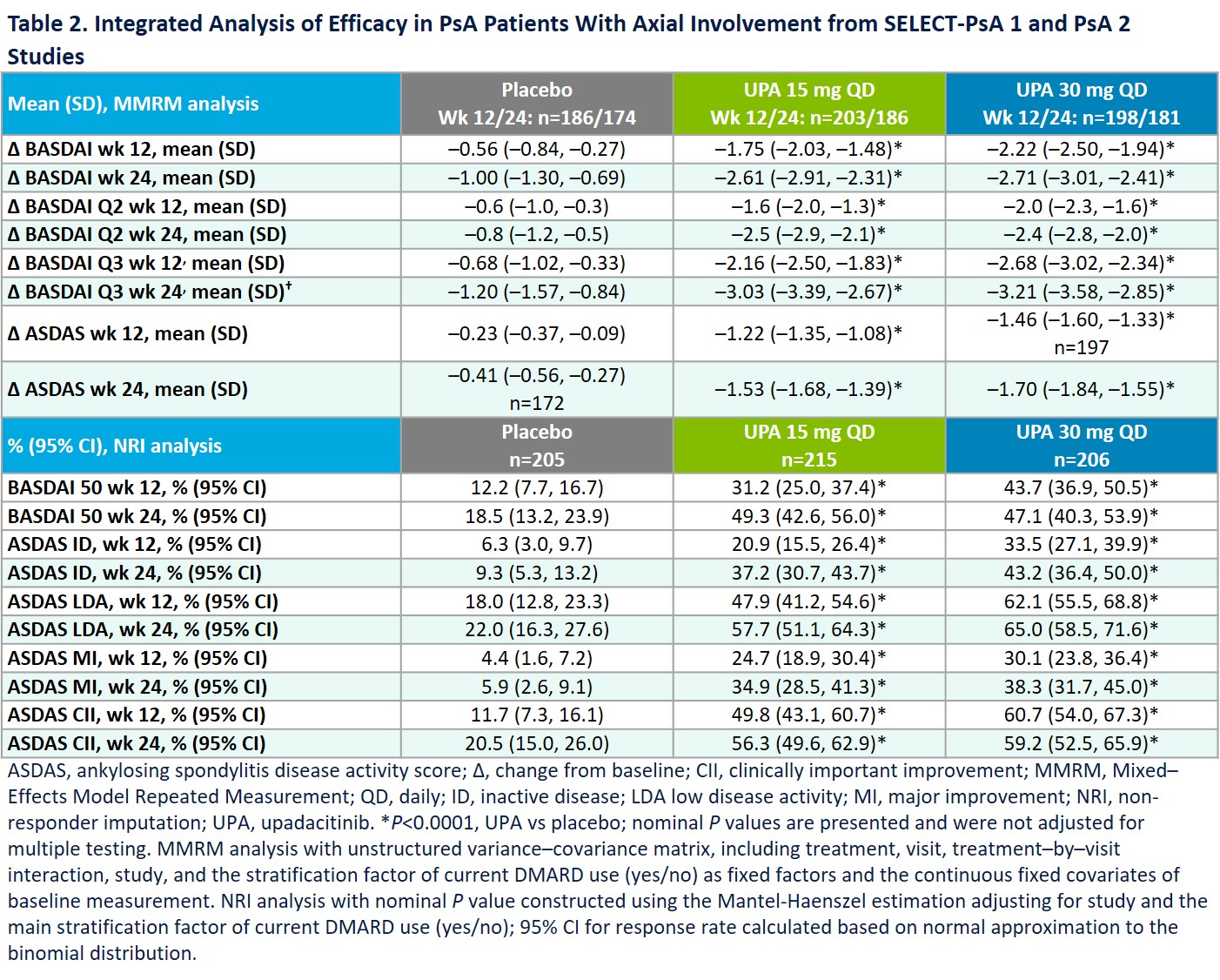
Results: Prevalence of axial involvment was 31.3% in SELECT-PsA 1 and 34.2% in SELECT-PsA 2. Demographics and disease activity for pts with and without axial involvement are presented in Table 1. Treatment with UPA 15 mg and 30 mg resulted in significantly greater improvements from BL in the overall BASDAI, BASDAI Q2 (neck/back/hip pain) and Q3 (joint swelling/pain) and ASDAS-CRP endpoints at weeks 12 and 24 vs PBO (Table 2). Similarly, significantly higher percentages of pts on UPA 15 mg and 30 mg achieved BASDAI 50, ASDAS ID, LDA, MI, and CII at weeks 12 and 24 vs PBO (Table 2). Uveitis was reported in 2 pts on PBO (1 new onset; 1 flare) and 1 pt on UPA 30 mg (new onset). 1 event of Crohn’s disease (flare) was reported on PBO; no IBD events were reported on UPA. Except for the uveitis flare on PBO, all uveitis and IBD events were reported in pts with psoriatic spondylitis.
Conclusion: Pts with PsA and axial involvement were more likely to have higher BL disease burden compared with those without axial involvement. Consistent with results observed in pts with AS, UPA was efficacious in treating axial symptoms in pts with psoriatic spondylits. Uveitis rates did not increase with UPA treatment, and UPA has shown efficacy in phase 2 IBD studies2,3 with no IBD events reported in UPA-treated PsA pts.
- van der Heijde D, et al. Lancet. 2019;394(10214):2108-2117.
- Sandborn W, et al. Gastroenterology 2020;158:2123-2138.
- Sandborn W, et al. Gastroenterology 2020;158:2139-2149.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Deodhar A, Ranza R, Ganz F, Gao T, Anderson J, Östör A. Efficacy and Safety of Upadacitinib in Patients with Psoriatic Arthritis and Axial Involvement [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/efficacy-and-safety-of-upadacitinib-in-patients-with-psoriatic-arthritis-and-axial-involvement/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/efficacy-and-safety-of-upadacitinib-in-patients-with-psoriatic-arthritis-and-axial-involvement/