Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: This Phase 3, randomized, double-blind, placebo (PBO)-controlled study assessed the efficacy and safety of upadacitinib (UPA) in combination with csDMARDs in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) from China, Brazil and South Korea who had an inadequate response to csDMARDs (csDMARD-IR).
Methods: Patients were randomized 1:1 to receive UPA 15 mg once daily (QD) or PBO in combination with csDMARDs. The primary endpoint was ACR20 response at Week 12, using non-responder imputation.
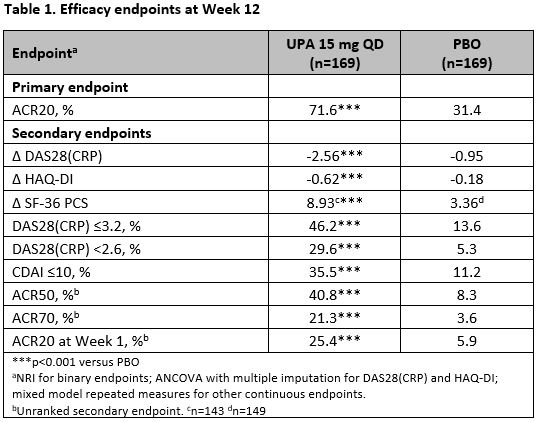
Results: 338 patients were randomized, and 310 (91.7%) completed Week 12. At Week 12, statistically significantly more patients receiving UPA vs PBO achieved the primary endpoint of ACR20 (71.6% vs 31.4%, p< 0.001). UPA also demonstrated statistically significantly improvements in all ranked secondary endpoints vs PBO at Week 12 (Table 1), including mean change in DAS28(CRP), HAQ-DI, and SF-36 PCS, and patients achieving DAS28(CRP) ≤3.2, DAS28(CRP) < 2.6 and CDAI≤10. Greater responses were also seen with UPA vs PBO for other key secondary endpoints including ACR50 and ACR70. Onset of UPA action was rapid with more patients on UPA achieving ACR20 by Week 1 (25.4% vs 5.9%, p< 0.001). The frequency of AEs (61.5% vs 49.1%) and serious AEs (7.1% vs 3.0%) was higher with UPA versus PBO. The frequency of AEs of special interest was generally similar between UPA and PBO, with the exception of herpes zoster (1.8% vs 0.6%), hepatic disorders (9.5% vs 7.1%), neutropenia (3.0% vs 0%), and elevated creatine phosphokinase (1.8% vs 0.6%), which were higher with UPA. One case of breast cancer (on Day 1 of study) and one VTE (pulmonary embolism and deep vein thrombosis in a patient with history of deep vein thrombosis) were reported with UPA treatment.
Conclusion: Efficacy of UPA was demonstrated in this csDMARD-IR population from China, Brazil, and South Korea. The safety of UPA was comparable with the global Phase 3 program.
Reference:
Original abs: Ann Rheum Dis. 2020; 79(S1):1016.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Zeng X, Zhao D, Radominski S, Keiserman M, Lee C, Meerwein S, Enejosa J, Sui Y, Mohamed M, Park W. Efficacy and Safety of Upadacitinib in Patients from China, Brazil, and South Korea with Rheumatoid Arthritis Who Have Had Inadequate Response to Conventional Synthetic Disease-modifying Antirheumatic Drugs [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/efficacy-and-safety-of-upadacitinib-in-patients-from-china-brazil-and-south-korea-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-who-have-had-inadequate-response-to-conventional-synthetic-disease-modifying-antirheumatic/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/efficacy-and-safety-of-upadacitinib-in-patients-from-china-brazil-and-south-korea-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-who-have-had-inadequate-response-to-conventional-synthetic-disease-modifying-antirheumatic/