Session Information
Date: Tuesday, November 10, 2015
Title: Rheumatoid Arthritis - Small Molecules, Biologics and Gene Therapy Poster III
Session Type: ACR Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose:
The investigational drug sarilumab is a human mAb
directed against the IL-6 receptor.1 The phase 3 part of MOBILITY
(NCT01061736) examined sarilumab + MTX vs placebo + MTX in patients with active,
moderate-to-severe RA with inadequate response to MTX.1 Both sarilumab
doses (150 and 200 mg subcutaneously every 2 weeks [q2w]) were generally well
tolerated and demonstrated statistically significant improvements in signs and
symptoms of RA, improvements in physical function, and inhibition of
radiographic progression. The incidence of treatment-emergent adverse events
(TEAEs) was greater with sarilumab than placebo. The most common TEAEs were infections,
neutropenia, injection-site reactions, and increased transaminases. In the
present study, efficacy of sarilumab across prespecified
subpopulations from MOBILITY was assessed.
Methods: The
MOBILITY study design and methods have previously been reported.1 Incidence
of ACR20 at week 24 and least-squares mean difference in change from baseline
in HAQ-DI at week 16, coprimary endpoints in
MOBILITY, were evaluated for placebo (n=398), sarilumab 150 mg q2w (n=400), and
sarilumab 200 mg q2w (n=399) in prespecified subpopulations.
Treatment-by-subgroup interactions were assessed by a logistic regression model
for ACR20 at week 24 and by a mixed-effect model for repeated measures for
HAQ-DI at week 16.
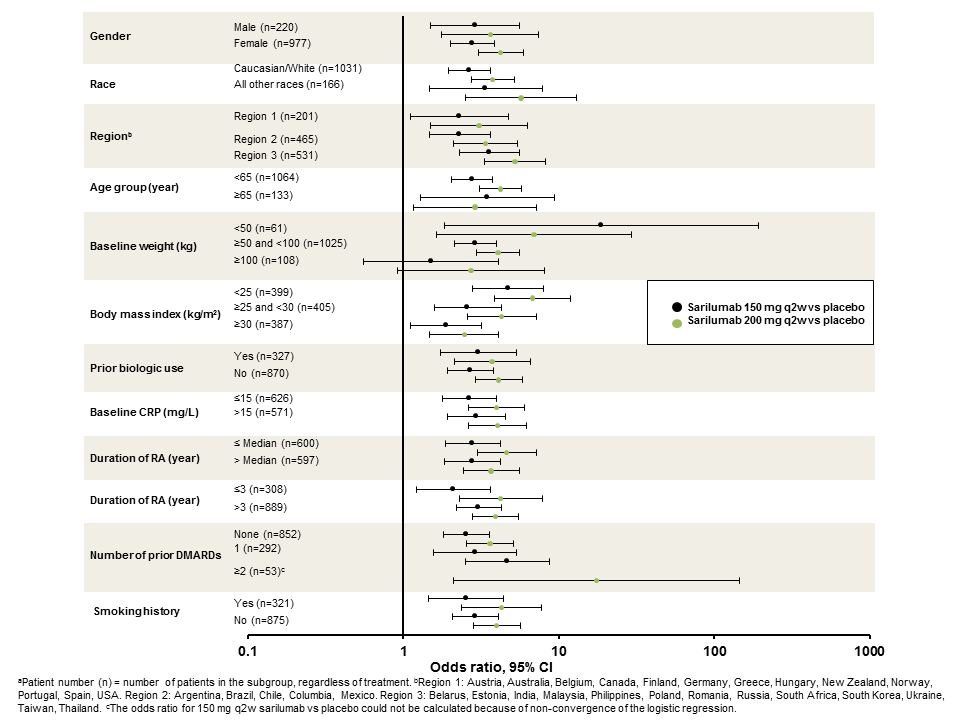
Results: No
treatment-by-subgroup interactions were observed in the proportion of patients
achieving ACR20 response at week 24 (Table), indicating that, across all
subgroups, the efficacy of sarilumab was consistent with the overall study
findings. There appeared to be a trend toward lower efficacy in patients with
increasing weight and BMI, particularly in the sarilumab 150 mg q2w group (Figure).
No treatment-by-subgroup interactions were observed for HAQ-DI improvements at
week 16, and the trends observed with ACR20 response in regards to lower
efficacy with increased weight and BMI were not observed.
Conclusion:
ACR20 and HAQ-DI responses with sarilumab were generally consistent across all subgroups
in MOBILITY, although ACR20 responses may be decreased in patients with
increasing weight and BMI.
- Genovese et al. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015;67:1424-1437.
|
Table. Incidence of ACR20 Response at Week 24: Treatment by Subgroup Interactions |
|
|
Subgroup
|
P value (interaction)a
|
|
Gender
|
0.79 |
|
Race |
0.48 |
|
Regionb
|
0.57 |
|
Age group |
0.47 |
|
Baseline weight |
0.53 |
|
BMI |
0.05 |
|
Prior biologic usec
|
0.86 |
|
Baseline CRP |
0.91 |
|
Duration of RA |
0.84 |
|
Duration of RA |
0.39 |
|
Number of prior DMARDs |
0.42 |
|
Smoking history |
0.89 |
|
BMI, body mass index; CRP, C-reactive protein; DMARD, disease-modifying antirheumatic drug; RA, rheumatoid arthritis. aLogistic regression model with terms of treatment, prior biologic use, region, subgroup, treatment-by-subgroup. bLogistic regression model with terms of treatment, prior biologic use, region, treatment-by-region. cLogistic regression model with terms of treatment, prior biologic use, region, treatment-by-prior biologic use. |
|
Figure. Odds ratio for ACR20 response of
sarilumab versus placebo at week 24 by subgroup.a
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Kavanaugh A, Kivitz AJ, Miranda P, Fiore S, Fay J, Fan C, van Adelsberg J, Huizinga TWJ. Efficacy and Safety of Sarilumab Plus MTX in Subgroups of Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis in a Phase 3 Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015; 67 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/efficacy-and-safety-of-sarilumab-plus-mtx-in-subgroups-of-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-in-a-phase-3-study/. Accessed .« Back to 2015 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/efficacy-and-safety-of-sarilumab-plus-mtx-in-subgroups-of-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-in-a-phase-3-study/